Contents

Can a CT scan detect bladder cancer?
· Can a CT scan miss bladder cancer? CT scans can provide important information about the urinary tract and bladder tumors. However, while some bladder tumors may be seen on a CT scan, others may not be apparent, such as smaller or flatter tumors. What to expect when having a CT scan. A CT scan is a painless procedure that is typically performed on an …
Can a CT scan mistake a bladder fold for an abnormal finding?
If an abdominal CT scan shows a normal bladder, don’t celebrate yet. But if it comes back indicating cancer, don’t panic yet, either. About 80,000 people in the U.S. are diagnosed with bladder cancer every year. The five year survival rate, on average, is about 76.8 percent. This not-so-good survival rate is a function of the disease being caught at a later stage than it is of just …
What kind of MRI do you get for bladder cancer?
Conclusion: CT urography is an accurate test for diagnosing bladder cancer; however, in protocols relying predominantly on excretory phase images, overall sensitivity remains insufficient to obviate cystoscopy. Awareness of bladder cancer mimics may reduce false-positive results. Improvements in CTU technique may reduce false-negative results.
Can a black and white cystoscopy detect bladder cancer?
· Can you prevent bladder cancer before its occurrence? People may go for certain tests including CT Scan for detecting bladder cancer. An individual can manage the symptoms of bladder cancer in different ways. So, one may prevent bladder cancer in the following ways: Quit Smoking; Smoking attributes to be the topmost cause of bladder cancer.
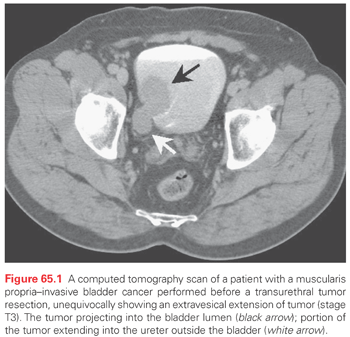
How accurate is CT scan for bladder cancer?
Computed tomography (CT) Multidetector (64-slice) CT scanning has provided the mainstay in radiological assessment. It has a reported sensitivity of 85% and specificity of 94% for the diagnosis of bladder cancers [11]. Detection is dependent on the morphology and size of the tumor.
Do bladder tumors show up in CT scan?
Computed tomography (CT) scan It can provide detailed information about the size, shape, and position of any tumors in the urinary tract, including the bladder. It can also help show enlarged lymph nodes that might contain cancer, as well as other organs in the abdomen (belly) and pelvis.
Can bladder cancer be missed?
In many bladder cancer cases, a delayed diagnosis of a few months or even weeks can be the difference between a treatable condition and a devastating, if not fatal, outcome.
Is cystoscopy necessary after CT scan?
While some bladder tumors may be found on a CT urogram or other imaging test, others will not. A urologist will often recommend a cystoscopy to evaluate the lower urinary tract (bladder/urethra) for a source of blood in the urine or to workup other urologic symptoms.
Can a bladder infection be seen on a CT scan?
CT scans. A CT scan combines x-rays with computer technology to create three-dimensional (3-D) images. These scans can show stones in the urinary tract, as well as obstructions, infections, cysts, tumors, and traumatic injuries. Imaging for urinary stone disease can be done with low or ultra-low dose CT scans.
How accurate is a CT urogram?
CT urography was found to be as accurate as cystoscopy for patients with hematuria, (94.6% and 94.4% accurate, respectively). Both tests showed lower accuracy in the evaluation of patients with a history of urothelial cancer than in patients with hematuria, CT urography more so than cystoscopy (77.8% vs 84.8%).
How do you rule out bladder cancer?
Tests for bladder cancer look for different substances and/or cancer cells in the urine. Urinalysis: One way to test for bladder cancer is to check for blood in the urine ( hematuria). This can be done during a urinalysis, which is a simple test to check for blood and other substances in a sample of urine.
Can bladder cancer symptoms come and go?
Symptoms often come and go, and are often not severe. The most common symptoms include the following: Hematuria (blood in the urine) — The most common sign of bladder cancer is blood in the urine (hematuria).
Can you have bladder cancer with no blood in urine?
Usually, the early stages of bladder cancer (when it’s small and only in the bladder) cause bleeding but little or no pain or other symptoms. Blood in the urine doesn’t always mean you have bladder cancer.
Why would a urologist do a CT scan?
A CT urogram is used to examine the kidneys, ureters and bladder. It lets your doctor see the size and shape of these structures to determine if they’re working properly and to look for any signs of disease that may affect your urinary system.
How accurate is cystoscopy?
Table 9 shows that urine makers and cystoscopy have the same highest sensitivity and the highest specificity of 97.2% and 97%, respectively. The table also shows that of the combined methods, the highest sensitivity of 94% and the highest specificity of 90% are found in urine markers and urine cytology.
Why would a urologist order a cystoscopy?
During a cystoscopy, a urinary tract specialist (urologist) uses a scope to view the inside of the bladder and urethra. Doctors use cystoscopy to diagnose and treat urinary tract problems. These problems include bladder cancer, bladder control issues, enlarged prostates and urinary tract infections.
What are the odds that a tumor in the bladder is cancerous?
Risk of bladder cancer Overall, the chance men will develop this cancer during their life is about 1 in 27. For women, the chance is about 1 in 89.
How common are benign bladder tumors?
“While there are several types of benign masses that can grow in the bladder, these are uncommon and account for fewer than 1% of bladder masses,” says Khurshid Guru, MD, Chair of Roswell Park’s Department of Urology.
Are most bladder tumors benign?
Tumors can be either benign (not malignant or cancerous) or cancerous (malignant, out-of-control cell growth). Bladder cancer or bladder tumors are relatively common in the United States, and most bladder tumors are cancerous.
How serious is a tumor in the bladder?
Bladder cancer can be benign or malignant. Malignant bladder cancer may be life threatening, as it can spread quickly. Without treatment, it can damage tissues and organs. In this article, we cover everything you need to know about bladder cancer, including types, symptoms, causes, and treatments.

How many people are diagnosed with bladder cancer every year?
If an abdominal CT scan shows a normal bladder, don’t celebrate yet. But if it comes back indicating cancer, don’t panic yet, either. About 80,000 people in the U.S. are diagnosed with bladder cancer every year. The five year survival rate, on average, is about 76.8 percent.
What is the survival rate for bladder cancer?
The five year survival rate, on average, is about 76.8 percent. This not-so-good survival rate is a function of the disease being caught at a later stage than it is of just a hard-to-treat cancer. About four times more men get bladder cancer than do women.
What is a cystoscope?
It’s a diagnostic procedure (performed either under local anesthetic or general anesthesia) during which a doctor inserts a cystoscope (hollow tube) equipped with a lens into the urethra and further into the bladder.
Can a CT scan detect a UTI?
“CT scan is able to detect large bladder irregularities, but not always small lesions,” says Dana Rice, MD, a board certified urologist and creator of the UTI Tracker mobile app, which helps patients catalog daily urinary tract symptoms, medication and behavioral patterns, and offers personalized tips for UTI prevention.
About this Community
The Bladder Cancer Advocacy Network Support Community connects patients, families, friends and caregivers for support and inspiration. This community is sponsored by the Bladder Cancer Advocacy Network, an Inspire trusted partner.
sediment or mucus in neph tube and bag???
I am having what looks like mucus always in my nephrostomy tube and bag. I had the tube replaced this last monday. I asked the Interventional radiologist nurse and she said it was sediment and was normal. Tonight I had some blood and talked with the resident on call and he was not sure if it was sediment or if it was mucus from my indiana pouch.
Decompressed bladder
I was recently diagnosed withh a decompressed bladder through a cat scan test. What does this mean or indicate? Thank you for your input. Sign up to continue reading
Unable to sleep with nephrostomy tubes
My husband just had a nephrostomy tube put in the drain his left kidney. He underwent radical cycectomy, prostate removal and still has cancer. He got sepsis after the nephrostomy tubes were placed. And to top it all off now he is having trouble sleeping because the tube is so uncomfortable.
Passed a scab, blood in urine. Should I worry?
Hello, fellow sojourners. This is a follow-up to my message from a month or so ago. Quick refresher: I had my first TURBT in Jan 2015, pathology said low-grade non-muscle invasive. In Jan 2016 (just under two months ago) I had a second TURBT, this time followed immediately with Mitomycin. Pathology came back same as before.

Imaging Techniques To Detect Bladder Cancer
Imaging techniques, which include ultrasound, computed tomography (or CT) scanning, magnetic resonance imaging (or MRI) and x-ray approaches, provide an important means of assessing the urinary tract, including the kidneys, and play an important role in the detection, diagnosis, and monitoring of bladder cancer.
Detecting bladder cancer with ultrasound
An ultrasound (which may also be referred to as a sonogram) uses high frequency sound waves to produce images of internal organs. Echoes, which are created as sound waves bounce off organs and tissues, produce computer images that provide information on the structure and movement of organs and the blood flow through vessels.
How do ultrasounds help detect and monitor bladder cancer?
An ultrasound of the urinary tract can help assess the size of a bladder tumour and whether a bladder cancer has spread. Ultrasound is able to differentiate between fluid-filled cysts and solid tumours, however, it cannot determine if a tumour is cancerous. Ultrasound can also be used to guide a biopsy needle to sample a suspected cancer.

Detecting bladder cancer with CT scans
A CT scan uses x-rays to obtain cross-sectional images of the body. Compared to a general x-ray test, which directs a broad x-ray beam from a single angle, the CT scan uses a number of thin beams to produce a series of images from different angles.
Other imaging approaches to detect or monitor bladder cancer
An MRI scan uses radio waves and magnets to produce more detailed pictures of soft tissues. MRI scans can show whether bladder cancer has spread to other tissues or to the lymph nodes. To improve the quality of the images it’s sometimes necessary to administer an intravenous dye.
What is the best way to diagnose bladder cancer?
Cystoscopy. If bladder cancer is suspected, most doctors will recommend a cystoscopy. . A urologist uses a cystoscope, which is a long, thin, flexible tube with a light and a lens or a small video camera on the end. For details on how this procedure is done, see Cystoscopy.

What tests are used to check for bladder cancer?
These include the tests called NMP22 ® (or BladderChek ® ), BTA Stat ®, Immunocyt ® , and UroVysion ®, which are discussed in Can Bladder Cancer Be Found Early?
What is the blue light in a cystoscopy?
Fluorescence cystoscopy (also known as blue light cystoscopy) may be done along with routine cystoscopy. For this exam, a light-activated drug is put into the bladder during cystoscopy. It’s taken up by cancer cells. When the doctor then shines a blue light through the cystoscope, any cells containing the drug will glow (fluoresce). This can help the doctor see abnormal areas that might have been missed by the white light normally used.
What is the biopsy for bladder cancer?
A biopsy is when tiny pieces (called samples) of the abnormal-looking tissue are taken out and tested for cancer cells. If bladder cancer is suspected, a biopsy is needed to be sure of the diagnosis.

What is a physical exam for bladder cancer?
A physical exam can provide information about possible signs of bladder cancer and other health problems. The doctor might do a digital rectal exam (DRE), during which a gloved, lubricated finger is put into your rectum. If you are a woman, the doctor might do a pelvic exam as well.
How long does it take for a urine culture to show up?
It can take time for the bacteria to grow, so it may take a few days to get the results of this test.
How does ultrasound help with bladder cancer?
Ultrasound uses sound waves to create pictures of internal organs. It can be useful in determining the size of a bladder cancer and whether it has spread beyond the bladder to nearby organs or tissues. It can also be used to look at the kidneys. This is usually an easy test to have, and it uses no radiation.