Contents

Can a CT urogram detect bladder cancer?
· Detecting Bladder Cancer with a Cystoscopy Cystoscopy enables the inside of the urethra and bladder to be examined and sampled. Alongside urine testing and diagnostic imaging procedures, cystoscopy is used in both the initial diagnosis of bladder cancer and in ongoing surveillance for recurrence.
What is the best test for bladder cancer?
If you have had bladder cancer, it might also be used to look for new tumors. You have a suspicious area that might be cancer. Cystoscopy can be used to take biopsy samples from the bladder or urethra (to find out if an abnormal area is cancer, for example). This is done by passing long, thin instruments down the cystoscope, such as small forceps (tweezers) to collect the …
How can urine tests detect bladder cancer?
Most doctors feel that cystoscopy is still the best way to find bladder cancer. Some of these tests are more helpful for finding bladder cancer that has come back in someone who has already had it, rather than first diagnosing it. Cystoscopy If bladder cancer is suspected, most doctors will recommend a cystoscopy. .
What is the test for bladder cancer?
· May 24, 2021 Jason M. Broderick Cystoscopy showed alarming limitations, including failure to detect residual muscle invasive bladder cancer (MIBC) in one-fourth of patients at the time of radical cystectomy, according to findings from a prospective study published in the Journal of Urology. 1,2
What is the name of the doctor who performs a cytoscopy on bladder cancer?
· Cystoscopy is a medical procedure that provides an up-close, detailed look at the inside of the bladder and urethra (the tube that transports urine from the bladder when you urinate). This procedure can help with diagnosing certain bladder or urinary problems, from frequent urinary tract infections to bladder cancer.
Can you have a bladder cystoscopy before a cystoscopy?
The cystoscopy is one of several tests that can be used to diagnose bladder cancer and learn more about the bladder cancer in patients who have already been diagnosed. 1,2 Other tests include: Urine lab tests Examination under anesthesia Transurethral resection of bladder tumor ( …
What is inserted into the bladder that causes the bladder wall to be stretched?
· An ultrasound of the urinary tract can help assess the size of a bladder tumor and whether a bladder cancer has spread. Ultrasound is able to differentiate between fluid-filled cysts and solid tumors, however, it cannot determine if a tumor is cancerous. Ultrasound can also be used to guide a biopsy needle to sample a suspected cancer.
How many stages of bladder cancer are there?
· Patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer often need a more aggressive treatment regime, and chances of recurrence following treatment can still be around 30% to 54%. 3. It can also be very difficult to predict when bladder cancer may recur. Bladder cancer can sometimes come back up to 5, 10, or even 15 years after treatment. 4,5.
What happens in the second stage of bladder cancer?
The CxBladder Detect is performed alongside cystoscopy and utilizes genomes to determine the detection of bladder cancer. CxBladder Triage is similar but incorporates age, gender, and smoking history to exclude bladder cancer for low-risk patients presenting with hematuria.
What is used to analyze the internal structure of urinary tracts and bladder?
See more
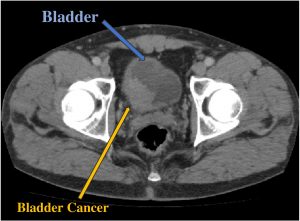
Can bladder cancer be missed on cystoscopy?
Although cystoscopy remains a fundamental investigative tool in the detection and surveillance of bladder cancer, small papillary tumors or carcinoma in situ (CIS) can be easily missed by standard white-light cystoscopy (WLC), which may account for early recurrence.
Can a cystoscopy detect cancer?
During a cystoscopy, the doctor can check for any abnormal areas that may indicate cancer. If they see anything suspicious, like a growth or tumor, they can remove a small piece of the tissue and bring it to a lab where it can be tested for cancer.
How accurate is cystoscopy in bladder cancer?
Table 9 shows that urine makers and cystoscopy have the same highest sensitivity and the highest specificity of 97.2% and 97%, respectively. The table also shows that of the combined methods, the highest sensitivity of 94% and the highest specificity of 90% are found in urine markers and urine cytology.
What can be detected in a cystoscopy?
A cystoscopy can diagnose:Bladder cancer or urethral cancer.Bladder stones.Bladder control problems.Enlarged prostate (benign prostatic hyperplasia).Urethral strictures and urinary fistulas.UTIs.
How do you rule out bladder cancer?
Tests for bladder cancer look for different substances and/or cancer cells in the urine. Urinalysis: One way to test for bladder cancer is to check for blood in the urine ( hematuria). This can be done during a urinalysis, which is a simple test to check for blood and other substances in a sample of urine.
Does bladder cancer show in urine test?
Urine tumor marker tests. These look for substances that are released by bladder cancer cells. Your doctor may use one or more of these along with a urine cytology to see if you have the disease.
Can a biopsy be done during a cystoscopy?
Cystoscopy can be used to take biopsy samples from the bladder or urethra (to find out if an abnormal area is cancer, for example). This is done by passing long, thin instruments down the cystoscope, such as small forceps (tweezers) to collect the samples. The biopsy samples are then looked at in the lab.
What are the signs of bladder cancer in adults?
Bladder Cancer: Symptoms and SignsBlood or blood clots in the urine.Pain or burning sensation during urination.Frequent urination.Feeling the need to urinate many times throughout the night.Feeling the need to urinate, but not being able to pass urine.Lower back pain on 1 side of the body.
Is a cystoscopy helpful?
This is the most important test for diagnosing cancer of the bladder. As well as examining the bladder your doctor can take samples of the bladder lining (biopsies) to check for cancer cells. Other reasons you might have a cystoscopy is to check: whether your cancer has come back.
Why would a doctor order a cystoscopy?
Cystoscopy is used to diagnose, monitor and treat conditions affecting the bladder and urethra. Your doctor might recommend cystoscopy to: Investigate causes of signs and symptoms. Those signs and symptoms can include blood in the urine, incontinence, overactive bladder and painful urination.
Why do I need a cystoscopy after a CT scan?
While some bladder tumors may be found on a CT urogram or other imaging test, others will not. A urologist will often recommend a cystoscopy to evaluate the lower urinary tract (bladder/urethra) for a source of blood in the urine or to workup other urologic symptoms.
Is there an alternative to a cystoscopy?
There are no real alternatives to cystoscopy. Imaging studies such as ultrasound or CT can miss small lesions such as tumours. For this reason, a cystoscopy is recommended for anyone who has bladder symptoms such as bleeding.
Why would a doctor order a cystoscopy?
Cystoscopy is used to diagnose, monitor and treat conditions affecting the bladder and urethra. Your doctor might recommend cystoscopy to: Investigate causes of signs and symptoms. Those signs and symptoms can include blood in the urine, incontinence, overactive bladder and painful urination.
Can a biopsy be done during a cystoscopy?
Cystoscopy can be used to take biopsy samples from the bladder or urethra (to find out if an abnormal area is cancer, for example). This is done by passing long, thin instruments down the cystoscope, such as small forceps (tweezers) to collect the samples. The biopsy samples are then looked at in the lab.
Would bladder cancer show up on a CT scan?
A CT scan uses X-rays and a computer to create three-dimensional, cross-sectional pictures of the bladder, as well as the ureters and kidneys. A CT scan may be used to see whether bladder cancer has invaded the bladder wall or has spread to other organs or nearby lymph nodes.
Do you get cystoscopy results right away?
You should get your results within 1 or 2 weeks at a follow up appointment.
Medical History and Physical Exam
Your doctor will want to get your medical history to learn more about your symptoms. The doctor might also ask about possible risk factors, includi…
Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumor (TURBT)
If an abnormal area (or areas) is seen during a cystoscopy, it will be biopsied to see if it is cancer. A biopsy is the removal of small samples of…
Biopsies to Look For Cancer Spread
If imaging tests suggest the cancer might have spread outside of the bladder, a biopsy might be needed to be sure.In some cases, biopsy samples of…
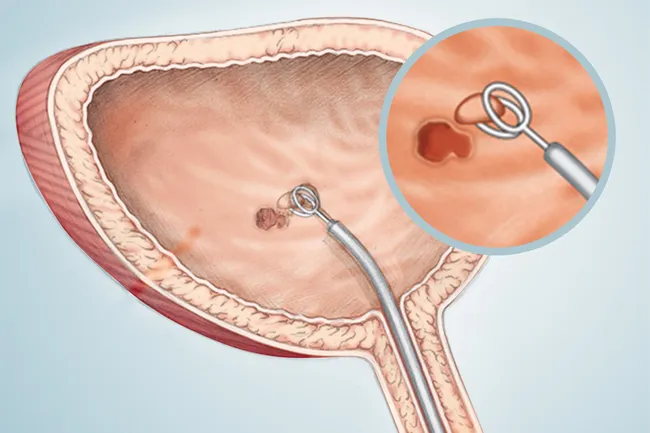
What is the test for bladder cancer?
Cystoscopy: As mentioned above, a thin fiber-optic tube is inserted into the bladder for internal investigations. This is considered as key test in Bladder Cancer cases. Transurethral resection of Bladder Tumor (TURBT): In some cases it is also simply termed Biopsy. Here, a cell sample and bladder muscle is collected to test the tumor.
What is the name of the doctor who performs a cytoscopy on bladder cancer?
Cystoscope have lens (like telescope or microscope) placed at its inserting end that reproduces the inside image focused upon by enlarging it. Urologist is the specialist Doctor that conducts Cystoscopy test for Bladder Cancer. Usually stones, blockages, enlarged glands, bleeding, and related bladder abnormalities causes Cystoscopy.
Can you have a bladder cystoscopy before a cystoscopy?
You may be asked to vacant your bladder before the Cystoscopy test procedure begins. Anesthetic gel is applied at the urethra tube of your external bladder to numb it as anesthesia. The genitals are treated with antiseptic to cleanse them and a sterile sheet is placed at the area.
What is inserted into the bladder that causes the bladder wall to be stretched?
Water or saline is inserted with cystoscope into the bladder that causes the bladder wall to be stretched. This helps the Urologist to examine and investigate the bladder clearly. The Urologist may collect tissue samples for laboratory testing.
How many stages of bladder cancer are there?
Bladder cancer goes through four stages. The first stage sees the development of cancer in the inner lining of bladder. In second stage the cancer spreads to bladder wall. In third stage, the cancer cells spread from wall to other tissues.
What happens in the second stage of bladder cancer?
In second stage the cancer spreads to bladder wall. In third stage, the cancer cells spread from wall to other tissues. During fourth stage the cancer cells advance to other parts of the body like liver, lungs, etc. Cystoscopy test for Bladder Cancer provides clear information about condition of problem. There are different procedures …
What is used to analyze the internal structure of urinary tracts and bladder?
X-rays, sound waves, magnetic fields, radioactive substance, etc are used to analyze the internal structure of urinary tracts and bladder for further examination. MRI [Magnetic Resonance Imagining] or CT [Computerized Tomography] scans are usually conducted in this procedure. Ultrasound is used to generate sound waves and know …
What is a cystoscopy?
What is cystoscopy? Cystoscopy is a procedure a doctor uses to look at the inside of the bladder and urethra ( the tube that connects the bladder to the outside of the body). This is done with a cystoscope, a thin tube with a light and a lens or small video camera on the end. The tube is put in through your urethra.
Is a cystoscopy safe?
Cystoscopy is usually safe, but there is a small risk of: Reactions to anesthesia. Bladder infection. Rupture of the bladder wall. Your doctor or nurse should give you specific instructions on when you might need to call the doctor’s office. Be sure you understand when you should call.
Can you lie on your back for a urethra test?
You will most likely need to lie on your back for this test, and you might have your feet up in stirrups. The doctor will apply numbing medicine (often as a gel) around the opening of the urethra, and possibly inside the urethra as well.
Can you sleep during a cystoscopy?
You might also be given a sedative through an IV line to help you relax during the test. For a rigid cystoscopy, you might be asleep (under general anesthesia) for the test. The doctor will then insert the cystoscope into your urethra and up into your bladder.
How long does it take for a biopsy to show results?
If biopsies were done as part of the procedure, the results will typically be available within a few days, although some tests on the biopsy samples might take longer.
What is the biopsy for bladder cancer?
A biopsy is when tiny pieces (called samples) of the abnormal-looking tissue are taken out and tested for cancer cells. If bladder cancer is suspected, a biopsy is needed to be sure of the diagnosis.
Why do we need tests for bladder cancer?
Tests for Bladder Cancer. Bladder cancer is often found because of signs or symptoms a person is having. Or it might be found because of lab tests a person gets for another reason. If bladder cancer is suspected, exams and tests will be needed to confirm the diagnosis. If cancer is found, more tests will be done to help find out the extent ( stage) …
Why is bladder cancer found?
Bladder cancer is often found because of signs or symptoms a person is having. Or it might be found because of lab tests a person gets for another reason. If bladder cancer is suspected, exams and tests will be needed to confirm the diagnosis. If cancer is found, more tests will be done to help find out the extent ( stage) of the cancer.
What is a physical exam for bladder cancer?
A physical exam can provide information about possible signs of bladder cancer and other health problems. The doctor might do a digital rectal exam (DRE), during which a gloved, lubricated finger is put into your rectum. If you are a woman, the doctor might do a pelvic exam as well.
Can a urine cytology test detect cancer?
Cytology is also done on any bladder washings taken during a cystoscopy (see below). Cytology can help find some cancers, but it isn’t perfect.
Can a urine culture show cancer?
If you’re having urinary symptoms, this test may be done to see if an infection (rather than cancer) is the cause. Urinary tract infections and bladder cancers can cause the same symptoms. For a urine culture, a sample of urine is put into a dish in the lab to allow any bacteria that are present to grow. It can take time for the bacteria to grow, so it may take a few days to get the results of this test.
What is the procedure to biopsy a bladder tumor?
The procedure used to biopsy an abnormal area is a transurethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT), also known as just a transurethral resection (TUR).
Does cystoscopy detect MIBC?
Cystoscopy showed alarming limitations, including failure to detect residual muscle invasive bladder cancer (MIBC) in one-fourth of patients at the time of radical cystectomy, according to findings from a prospective study published in the Journal of Urology. 1,2
Who was the primary investigator for the urologic oncology trial?
Yet, the issue was never approached systematically and tackled in a standardized way,” Alexander Kutikov, MD, FACS, chief of the Division of Urology and Urologic Oncology, who was the primary investigator for the trial, stated in a press release.
What is a cystoscopy for cancer?
If they see anything suspicious, like a growth or tumor, they can remove a small piece of the tissue and bring it to a lab where it can be tested for cancer. This is also known as a biopsy.
Can a cystoscopy remove bladder stones?
Kidney or bladder stones: If there are kidney or bladder stones in the bladder, your doctor can remove them during a cystoscopy.
What is the procedure to check bladder?
Cystoscopy. Cystoscopy is a medical procedure that provides an up-close, detailed look at the inside of the bladder and urethra (the tube that transports urine from the bladder when you urinate). This procedure can help with diagnosing certain bladder or urinary problems, from frequent urinary tract infections to bladder cancer.
What is a cystoscopy?
Cystoscopy is a medical procedure that provides an up-close, detailed look at the inside of the bladder and urethra (the tube that transports urine from the bladder when you urinate). This procedure can help with diagnosing certain bladder or urinary problems, from frequent urinary tract infections to bladder cancer.
Why do doctors recommend cystoscopy?
Why might your doctor recommend a cystoscopy? A cystoscopy can help your doctor find the cause of urinary symptoms. The procedure can be used to treat certain problems too, like a blockage in the urethra that is disrupting the flow of urine. Reasons a cystoscopy may be recommended include:
What are the symptoms of a cystoscopy?
A cystoscopy may also be able to identify the cause of the following urinary symptoms: Blood in the urine. Frequent urination (urinating eight or more times a day) Unintentional urination or urine loss (urinary incontinence) Pain/burning while urinating. Difficulty starting or completing urination.
How long does it take to get a cystoscopy?
The procedure itself will take roughly five to 20 minutes. It can take longer if the doctor needs to take a tissue sample or remove something from inside the bladder.
How is a cystoscopy used to diagnose bladder cancer?
A cystoscopy allows a healthcare provider to check for signs of cancer by examining the inside of the bladder and the urethra, which is the hollow, tube-like organ that connects to the bladder and allows urine to flow out of the body.
What happens during a cystoscopy procedure?
A cystoscopy is often performed by a urologist, which is a doctor who specializes in urinary tract health, including bladder cancer. 1,3 Depending upon your circumstances, the cystoscopy procedure can be performed in a healthcare providers office or in an operating room at a hospital, for example.
What is an enhanced cystoscopy?
An enhanced cystoscopy is an additional procedure that may be carried out during a cystoscopy. 1 Enhanced cystoscopy is also called fluorescence or blue light cystoscopy. During this procedure, a type of drug that is only absorbed by cancer cells is put into the bladder.
What are the next steps when diagnosing bladder cancer?
The cystoscopy is one of several tests that can be used to diagnose bladder cancer and learn more about the bladder cancer in patients who have already been diagnosed. 1,2 Other tests include:
Imaging Techniques To Detect Bladder Cancer
Imaging techniques, which include ultrasound, computed tomography (or CT) scanning, magnetic resonance imaging (or MRI) and x-ray approaches, provide an important means of assessing the urinary tract, including the kidneys, and play an important role in the detection, diagnosis, and monitoring of bladder cancer.
Detecting bladder cancer with ultrasound
An ultrasound (which may also be referred to as a sonogram) uses high frequency sound waves to produce images of internal organs. Echoes, which are created as sound waves bounce off organs and tissues, produce computer images that provide information on the structure and movement of organs and the blood flow through vessels.
How do ultrasounds help detect and monitor bladder cancer?
An ultrasound of the urinary tract can help assess the size of a bladder tumor and whether a bladder cancer has spread. Ultrasound is able to differentiate between fluid-filled cysts and solid tumors, however, it cannot determine if a tumor is cancerous. Ultrasound can also be used to guide a biopsy needle to sample a suspected cancer.
Detecting bladder cancer with CT scans
A CT scan uses x-rays to obtain cross-sectional images of the body. Compared to a general x-ray test, which directs a broad x-ray beam from a single angle, the CT scan uses a number of thin beams to produce a series of images from different angles.
Other imaging approaches to detect or monitor bladder cancer
An MRI scan uses radio waves and magnets to produce more detailed pictures of soft tissues. MRI scans can show whether bladder cancer has spread to other tissues or to the lymph nodes. To improve the quality of the images it’s sometimes necessary to administer an intravenous dye.
What is the test for bladder cancer?
Cystoscopy: As mentioned above, a thin fiber-optic tube is inserted into the bladder for internal investigations. This is considered as key test in Bladder Cancer cases. Transurethral resection of Bladder Tumor (TURBT): In some cases it is also simply termed Biopsy. Here, a cell sample and bladder muscle is collected to test the tumor.
What is the name of the doctor who performs a cytoscopy on bladder cancer?
Cystoscope have lens (like telescope or microscope) placed at its inserting end that reproduces the inside image focused upon by enlarging it. Urologist is the specialist Doctor that conducts Cystoscopy test for Bladder Cancer. Usually stones, blockages, enlarged glands, bleeding, and related bladder abnormalities causes Cystoscopy.
Can you have a bladder cystoscopy before a cystoscopy?
You may be asked to vacant your bladder before the Cystoscopy test procedure begins. Anesthetic gel is applied at the urethra tube of your external bladder to numb it as anesthesia. The genitals are treated with antiseptic to cleanse them and a sterile sheet is placed at the area.
What is inserted into the bladder that causes the bladder wall to be stretched?
Water or saline is inserted with cystoscope into the bladder that causes the bladder wall to be stretched. This helps the Urologist to examine and investigate the bladder clearly. The Urologist may collect tissue samples for laboratory testing.
How many stages of bladder cancer are there?
Bladder cancer goes through four stages. The first stage sees the development of cancer in the inner lining of bladder. In second stage the cancer spreads to bladder wall. In third stage, the cancer cells spread from wall to other tissues.
What happens in the second stage of bladder cancer?
In second stage the cancer spreads to bladder wall. In third stage, the cancer cells spread from wall to other tissues. During fourth stage the cancer cells advance to other parts of the body like liver, lungs, etc. Cystoscopy test for Bladder Cancer provides clear information about condition of problem. There are different procedures …
What is used to analyze the internal structure of urinary tracts and bladder?
X-rays, sound waves, magnetic fields, radioactive substance, etc are used to analyze the internal structure of urinary tracts and bladder for further examination. MRI [Magnetic Resonance Imagining] or CT [Computerized Tomography] scans are usually conducted in this procedure. Ultrasound is used to generate sound waves and know …
Overview
Diagnosis
-
Usually stones, blockages, enlarged glands, bleeding, and related bladder abnormalities causes Cystoscopy. The Urologist will insert the Cystoscope tube through your urethra. If the case is of investigative nature of the case, then flexible Cystoscopy test is conducted with a flexible cystoscope. In flexible Cystoscopy test the examinee is instructed to lie flat on the operation be…
Purpose
-
The Cystoscopy test is conducted to find the cause of urinary system problems, bladder cancer, urinary infections, inject a dye for x-rays and kidney problems, collect tissue samples and eliminate foreign objects from the body. The scanning of bone is executed when any abnormalities are observed in the bones in prior tests. It is to detect if the c…
Treatment
-
In some cases, the Urologist Doctor will prescribe antibiotics before and after the Cystoscopy test. You may be asked to vacant your bladder before the Cystoscopy test procedure begins. Anesthetic gel is applied at the urethra tube of your external bladder to numb it as anesthesia. The genitals are treated with antiseptic to cleanse them and a sterile sheet is placed at the area.
Results
-
Usually the Cystoscopy test procedure takes 15 to 30 minutes. With anesthesia the pain is reduced to negligible or very minute that the patient might face during the Cystoscopy test procedure.
Pathophysiology
-
Bladder cancer goes through four stages. The first stage sees the development of cancer in the inner lining of bladder. In second stage the cancer spreads to bladder wall. In third stage, the cancer cells spread from wall to other tissues. During fourth stage the cancer cells advance to other parts of the body like liver, lungs, etc.
Clinical significance
-
As mentioned above, a thin fiber-optic tube is inserted into the bladder for internal investigations. This is considered as key test in Bladder Cancer cases. Transurethral resection of Bladder Tumor (TURBT): In some cases it is also simply termed Biopsy. Here, a cell sample and bladder muscle is collected to test the tumor. It is only conducted when abnormal tissues are found in cystoscopy …
Risks
-
Usually, subjects dont experience any side-effects or complications after Cystoscopy test. But some cases may face bleeding problems or difficulties in passing urine. A very rare chance of developing a urinary tract infection might also affect the subject after the Cystoscopy test.