Contents
Can an abdomen CAT scan diagnose bladder cancer?
· Imaging Techniques To Detect Bladder Cancer. Imaging techniques, which include ultrasound, computed tomography (or CT) scanning, magnetic resonance imaging (or MRI) and x-ray approaches, provide an important means of assessing the urinary tract, including the kidneys, and play an important role in the detection, diagnosis, and monitoring of bladder cancer.
Can a CT scan always catch cancer?
· So, a doctor’s usage of a CT Scan to detect bladder cancer may show certain things. This may include the following: The formation of stones in the urinary tract can be seen. Infections Cysts Obstructions Tumors, and Traumatic Injuries However, a doctor can use a low or high-dose CT Scan to trace urinary stones.
Can bladder cancer be seen on CT scan?
Abdominal CT Scan and the Detection of Bladder Cancer “CT scan is able to detect large bladder irregularities, but not always small lesions,” says Dana Rice, MD, a board certified urologist and creator of the UTI Tracker mobile app, which helps patients catalog daily urinary tract symptoms, medication and behavioral patterns, and offers personalized tips for UTI prevention.
Can a CAT scan detect uterine cancer?
· Do Ct Pelvic Scans Detect Cancer. Diagnosing Bladder Cancer. While pelvic CT scans can detect a variety of issues, they can be especially useful for detecting cancer. In particular, doctors can use this technology to look for tumors in this part of your body, but they can also use these scans to monitor the growth of tumors, to see how treatments are working, …
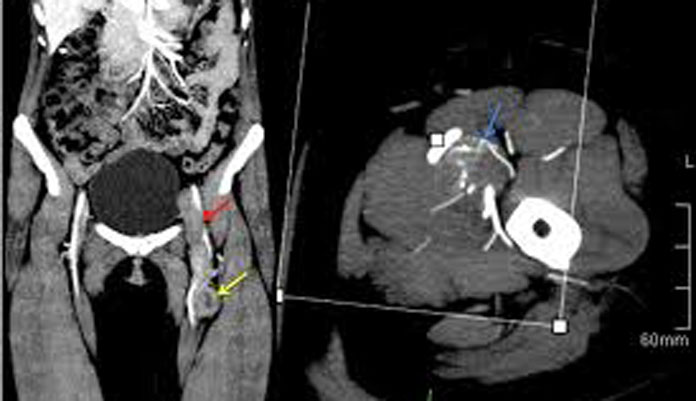
How accurate is CT scan for bladder cancer?
Computed tomography (CT) Multidetector (64-slice) CT scanning has provided the mainstay in radiological assessment. It has a reported sensitivity of 85% and specificity of 94% for the diagnosis of bladder cancers [11]. Detection is dependent on the morphology and size of the tumor.
Can bladder cancer be missed on a CT scan?
Can a CT scan miss bladder cancer? CT scans can provide important information about the urinary tract and bladder tumors. However, while some bladder tumors may be seen on a CT scan, others may not be apparent, such as smaller or flatter tumors.
What can a CT scan of the bladder show?
A CT scan combines x-rays with computer technology to create three-dimensional (3-D) images. These scans can show stones in the urinary tract, as well as obstructions, infections, cysts, tumors, and traumatic injuries. Imaging for urinary stone disease can be done with low or ultra-low dose CT scans.
Do bladder tumors show up in CT scan?
Computed tomography (CT) scan It can provide detailed information about the size, shape, and position of any tumors in the urinary tract, including the bladder. It can also help show enlarged lymph nodes that might contain cancer, as well as other organs in the abdomen (belly) and pelvis.
How do you rule out bladder cancer?
Tests for bladder cancer look for different substances and/or cancer cells in the urine. Urinalysis: One way to test for bladder cancer is to check for blood in the urine ( hematuria). This can be done during a urinalysis, which is a simple test to check for blood and other substances in a sample of urine.
What were your first signs of bladder cancer?
For most people, the first symptom of bladder cancer is blood in the urine, also called hematuria. Sometimes the blood is visible, prompting the patient to visit a doctor….Pain.Burning.Frequent urination.Incomplete emptying of the bladder.Passage of tissue fragments in urine (less frequent than other symptoms)
Can a CT scan miss a tumor?
Imaging tests usually can’t tell if a change has been caused by cancer. CT scans can produce false negatives and false positives. CT scan can miss cancer, or miss tumors in other areas of the body. CT scans are proven to be less effective at diagnosing cancer than PET/CT.
Why would a urologist order a CT scan?
A CT urogram is used to examine the kidneys, ureters and bladder. It lets your doctor see the size and shape of these structures to determine if they’re working properly and to look for any signs of disease that may affect your urinary system.
Is cystoscopy necessary after CT scan?
While some bladder tumors may be found on a CT urogram or other imaging test, others will not. A urologist will often recommend a cystoscopy to evaluate the lower urinary tract (bladder/urethra) for a source of blood in the urine or to workup other urologic symptoms.
How painful is a cystoscopy?
People often worry that a cystoscopy will be painful, but it does not usually hurt. Tell your doctor or nurse if you feel any pain during it. It can be a bit uncomfortable and you may feel like you need to pee during the procedure, but this will only last a few minutes.
How accurate is a CT urogram?
CT urography was found to be as accurate as cystoscopy for patients with hematuria, (94.6% and 94.4% accurate, respectively). Both tests showed lower accuracy in the evaluation of patients with a history of urothelial cancer than in patients with hematuria, CT urography more so than cystoscopy (77.8% vs 84.8%).
What is the difference between a CT scan and a CT urogram?
A CT urogram is a test that uses a CT scan and a special contrast medium or dye that a doctor injects into a vein. The contrast dye provides a high quality image to allow doctors to look at the urinary system and make a diagnosis.
Medical History and Physical Exam
Your doctor will want to get your medical history to learn more about your symptoms. The doctor might also ask about possible risk factors, includi…
Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumor (TURBT)
If an abnormal area (or areas) is seen during a cystoscopy, it will be biopsied to see if it is cancer. A biopsy is the removal of small samples of…
Biopsies to Look For Cancer Spread
If imaging tests suggest the cancer might have spread outside of the bladder, a biopsy might be needed to be sure.In some cases, biopsy samples of…

How many people are diagnosed with bladder cancer every year?
If an abdominal CT scan shows a normal bladder, don’t celebrate yet. But if it comes back indicating cancer, don’t panic yet, either. About 80,000 people in the U.S. are diagnosed with bladder cancer every year. The five year survival rate, on average, is about 76.8 percent.
What is the survival rate for bladder cancer?
The five year survival rate, on average, is about 76.8 percent. This not-so-good survival rate is a function of the disease being caught at a later stage than it is of just a hard-to-treat cancer. About four times more men get bladder cancer than do women.
What is a cystoscope?
It’s a diagnostic procedure (performed either under local anesthetic or general anesthesia) during which a doctor inserts a cystoscope (hollow tube) equipped with a lens into the urethra and further into the bladder.
Can a CT scan detect a UTI?
“CT scan is able to detect large bladder irregularities, but not always small lesions,” says Dana Rice, MD, a board certified urologist and creator of the UTI Tracker mobile app, which helps patients catalog daily urinary tract symptoms, medication and behavioral patterns, and offers personalized tips for UTI prevention.
What is the best way to diagnose bladder cancer?
Cystoscopy. If bladder cancer is suspected, most doctors will recommend a cystoscopy. . A urologist uses a cystoscope, which is a long, thin, flexible tube with a light and a lens or a small video camera on the end. For details on how this procedure is done, see Cystoscopy.
What tests are used to check for bladder cancer?
These include the tests called NMP22 ® (or BladderChek ® ), BTA Stat ®, Immunocyt ® , and UroVysion ®, which are discussed in Can Bladder Cancer Be Found Early?
What is the blue light in a cystoscopy?
Fluorescence cystoscopy (also known as blue light cystoscopy) may be done along with routine cystoscopy. For this exam, a light-activated drug is put into the bladder during cystoscopy. It’s taken up by cancer cells. When the doctor then shines a blue light through the cystoscope, any cells containing the drug will glow (fluoresce). This can help the doctor see abnormal areas that might have been missed by the white light normally used.
What is the biopsy for bladder cancer?
A biopsy is when tiny pieces (called samples) of the abnormal-looking tissue are taken out and tested for cancer cells. If bladder cancer is suspected, a biopsy is needed to be sure of the diagnosis.
What is a physical exam for bladder cancer?
A physical exam can provide information about possible signs of bladder cancer and other health problems. The doctor might do a digital rectal exam (DRE), during which a gloved, lubricated finger is put into your rectum. If you are a woman, the doctor might do a pelvic exam as well.
How long does it take for a urine culture to show up?
It can take time for the bacteria to grow, so it may take a few days to get the results of this test.
How does ultrasound help with bladder cancer?
Ultrasound uses sound waves to create pictures of internal organs. It can be useful in determining the size of a bladder cancer and whether it has spread beyond the bladder to nearby organs or tissues. It can also be used to look at the kidneys. This is usually an easy test to have, and it uses no radiation.
Imaging Techniques To Detect Bladder Cancer
Imaging techniques, which include ultrasound, computed tomography (or CT) scanning, magnetic resonance imaging (or MRI) and x-ray approaches, provide an important means of assessing the urinary tract, including the kidneys, and play an important role in the detection, diagnosis, and monitoring of bladder cancer.
Detecting bladder cancer with ultrasound
An ultrasound (which may also be referred to as a sonogram) uses high frequency sound waves to produce images of internal organs. Echoes, which are created as sound waves bounce off organs and tissues, produce computer images that provide information on the structure and movement of organs and the blood flow through vessels.
How do ultrasounds help detect and monitor bladder cancer?
An ultrasound of the urinary tract can help assess the size of a bladder tumour and whether a bladder cancer has spread. Ultrasound is able to differentiate between fluid-filled cysts and solid tumours, however, it cannot determine if a tumour is cancerous. Ultrasound can also be used to guide a biopsy needle to sample a suspected cancer.
Detecting bladder cancer with CT scans
A CT scan uses x-rays to obtain cross-sectional images of the body. Compared to a general x-ray test, which directs a broad x-ray beam from a single angle, the CT scan uses a number of thin beams to produce a series of images from different angles.
Other imaging approaches to detect or monitor bladder cancer
An MRI scan uses radio waves and magnets to produce more detailed pictures of soft tissues. MRI scans can show whether bladder cancer has spread to other tissues or to the lymph nodes. To improve the quality of the images it’s sometimes necessary to administer an intravenous dye.
How to find bladder cancer?
Most doctors recommend a cystoscopy to find bladder cancer, and it’s often performed without anesthesia. During this procedure, the doctor inserts a long, thin tube with a camera into the urethra to see the inside of the bladder for growths and collect a tissue sample ( biopsy ). The tissue is studied in a lab to search for cancer and obtain more information. During a cystoscopy, doctors may also perform a fluorescence cystoscopy, or blue light cystoscopy, inserting a light-activated drug into the bladder and seeing whether any cancer cells glow when they shine a blue light through the tube.
What tests are done to check for cancer in urine?
Tests may include: Urinalysis (looks for blood in urine) Urine cytology (looks for abnormal cells in urine) Urine culture (looks for an infection, rather than cancer) For patients who have symptoms or have had bladder cancer in the past, newer tests that look for tumor markers in urine may include:
What is the procedure to remove bladder tumor?
Ultrasound uses sound waves to take pictures of the inside of the body. While working to get a full picture of the diagnosis, doctors may order a transurethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT), which is a surgery to remove the tumor and muscle near it for testing.
What is the invasiveness of bladder cancer?
Invasiveness describes how deep the cancer is in the bladder wall, which is crucial to determining treatment. If the cancer is in the inner cell layers, it’s noninvasive or superficial. If it’s grown into deeper bladder layers or spread …
What is the first step in bladder cancer treatment?
A thorough and accurate diagnosis is the first step in developing a bladder cancer treatment plan. At Cancer Treatment Centers of America® (CTCA), our bladder cancer experts use a variety of tests and tools for diagnosing this disease and developing a customized treatment strategy for each patient. Throughout treatment, imaging and laboratory tests are used to track the size of the tumor (s), monitor the response to treatment. and modify the treatment plan when needed.
What is the blue light in a cystoscopy?
During a cystoscopy, doctors may also perform a fluorescence cystoscopy, or blue light cystoscopy, inserting a light-activated drug into the bladder and seeing whether any cancer cells glow when they shine a blue light through the tube. Doctors may also order imaging tests to see whether the cancer has spread.
What tests are used to determine if cancer has spread?
Doctors may also order imaging tests to see whether the cancer has spread. The most common imaging tests include: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses magnets and radio waves to take pictures of the inside of the body.
What is a CT scan?
A CT scan is a fast, painless, and non-invasive medical imaging test used to screen for cancer.
Why do we need CT scans?
One example of a situation that may need regular CT scans is undergoing cancer treatment . If the cancer is in an area such as the lungs, regular CT scans can help practitioners see how the treatment is working. In this case, the patient’s cumulative radiation dose increases.
How long does it take to get a CT scan?
Depending upon the part of the body being scanned, it may take anywhere from 10 to 30 minutes. During the scan, you may be asked to hold your breath for a few seconds.
Which is better, MRI or CT?
In some cases, an MRI is much better at showing certain cancers than a CT scan.
How does a round scanner work?
Inside the round scanner, an X-ray tube rotates and emits a thin beam of X-rays at different angles that quickly pass through the patient’s body and are received at the opposite end. The signals are then passed to a computer where special software creates detailed images of the inside of the body.
Does a CT scan have ionizing radiation?
A CT scan uses ionizing radiation that may increase the risk of developing cancer. An MRI scan does not have harmful ionizing radiation.
Is a single imaging test 100% accurate?
No single imaging test is 100% accurate in detecting abnormalities. There may be a misdiagnosis due to the quality of the scan or due to the expert reading the scan.