Contents

Can bladder cancer be picked up on ultrasound?
· An ultrasound of the urinary tract can help assess the size of a bladder tumor and whether a bladder cancer has spread. Ultrasound is able to differentiate between fluid-filled cysts and solid tumors, however, it cannot determine if a tumor is cancerous. Ultrasound can also be used to guide a biopsy needle to sample a suspected cancer. Ultrasound scan showing a …
How is bladder cancer identified on an ultrasound?
· As the incidence of bladder cancer rises, urologists are using transabdominal ultrasound for initial screening and to visualize the location and size of bladder carcinomas. A 2017 study of patients with indications for cystoscopy found that ultrasound has high sensitivity and specificity in the diagnosis of bladder cancer in patients suspected in the first stage.
Would cancer show up on an ultrasound?
· An ultrasound of the urinary tract can help assess the size of a bladder tumor and whether a bladder cancer has spread. Ultrasound is able to differentiate between fluid-filled cysts and solid tumors, however, it cannot determine if a tumor is cancerous. Ultrasound can also be used to guide a biopsy needle to sample a suspected cancer.
Can an ultra sound show stomach cancer?
· The doctor will make an official diagnosis after an ultrasound based on the report from the radiologist. Apart from overactive bladder, …
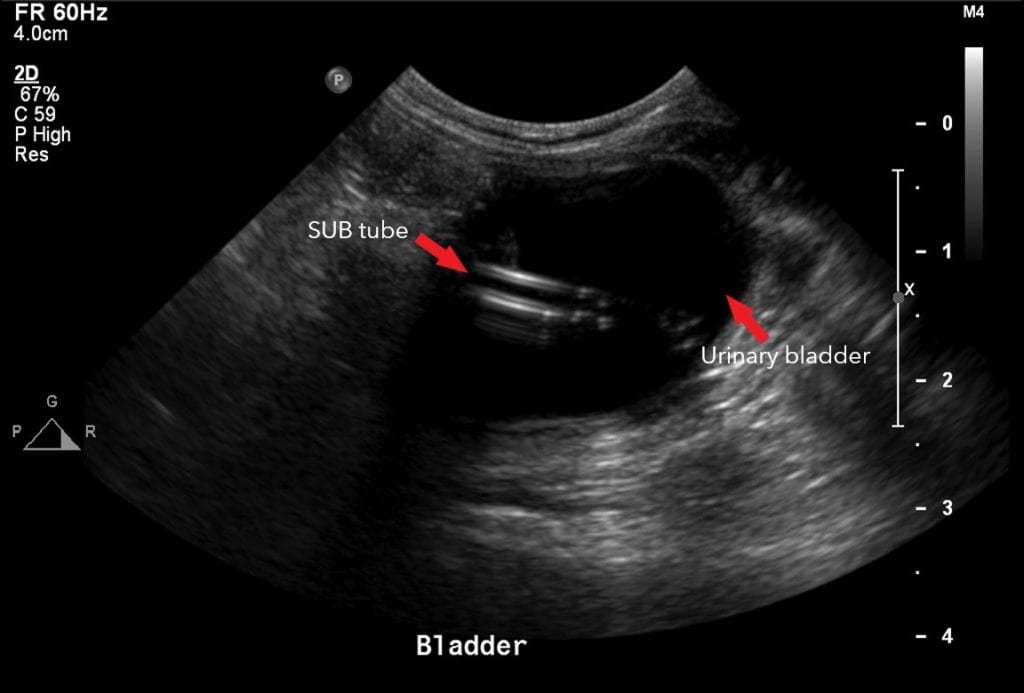
How accurate is ultrasound in detecting bladder cancer?
The accuracy of baseline ultrasound in bladder cancer detection per patient was 72.09% (31/43 patients), with a sensitivity of 81.81% (27/33), specificity of 40% (4/10), positive predictive value of 81.81% (27/33) and negative predictive value of 40% (4/10) (Figure 1).
How is bladder cancer detected?
A sample of your urine is analyzed under a microscope to check for cancer cells in a procedure called urine cytology. Imaging tests. Imaging tests, such as computerized tomography (CT) urogram or retrograde pyelogram, allow your doctor to examine the structures of your urinary tract.
What does an ultrasound of the bladder show?
Bladder ultrasound can give information about the bladder wall, diverticula (pouches) of the bladder, bladder stones, and large tumors in the bladder. Kidney ultrasound can show if the kidneys are in the right place or if they have blockages, kidney stones, or tumors.
What is the best test to diagnose bladder cancer?
Cystoscopy. Cystoscopy is the key diagnostic procedure for bladder cancer. It allows the doctor to see inside the body with a thin, lighted, flexible tube called a cystoscope. Flexible cystoscopy is performed in a doctor’s office and does not require anesthesia, which is medication that blocks the awareness of pain.
What is usually the first symptom of bladder cancer?
In most cases, blood in the urine (called hematuria) is the first sign of bladder cancer. There may be enough blood to change the color of the urine to orange, pink, or, less often, dark red.
What are the symptoms of stage 1 bladder cancer?
SymptomsBlood in urine (hematuria), which may cause urine to appear bright red or cola colored, though sometimes the urine appears normal and blood is detected on a lab test.Frequent urination.Painful urination.Back pain.
Can you see a tumor in an ultrasound?
An ultrasound (also known as ultrasonography, sonography, or sonogram) helps doctors look for tumors in certain areas of the body that don’t show up well on x-rays. Doctors often use this procedure to guide a needle during a biopsy.
Why would a doctor order a bladder ultrasound?
Doctors order bladder ultrasounds when there’s a concern about bladder problems, such as trouble with peeing or daytime wetting. A bladder ultrasound can show how much urine the bladder holds when it’s full and whether someone completely empties the bladder when peeing.
Can a pelvic ultrasound detect bladder problems?
Bladder ultrasound can detect bladder stones, bladder tumors (cancers) and bladder diverticula. It may also detect ureteroceles among other urological problems. A pelvic ultrasound can help identify bladder tumors, kidney stones, and other disorders of the urinary tract in both men and women.
What are the signs of bladder cancer in a woman?
Bladder Cancer: Symptoms and SignsBlood or blood clots in the urine.Pain or burning sensation during urination.Frequent urination.Feeling the need to urinate many times throughout the night.Feeling the need to urinate, but not being able to pass urine.Lower back pain on 1 side of the body.
Does bladder cancer show in blood work?
Tests to diagnose bladder cancer If bladder cancer is suspected, these tests may be performed to diagnose the disease: Physical exam. Blood test: Blood samples are used to measure certain substances released into the blood by organs and tissues in the body.
Do you feel bloated with bladder cancer?
Abdominal Pain The types of pains can vary and include: Generalized pain — felt in more than half of the stomach area. Cramp-like pain — less serious and most likely due to bloating and gas.
How long does it take to video chat with a doctor?
Video chat with a U.S. board-certified doctor 24/7 in less than one minute for common issues such as: colds and coughs, stomach symptoms, bladder infections, rashes, and more.
Can a urologist perform a cystoscopy?
Bladder cancer: Ultrasound is a poor test for detecting bladder cancer. The definitive test remains cystoscopy. This must be performed by a qualified urologist. It can, however, usually be performed in the office.
Can you see bladder cancer with ultrasound?
Yes, but……: Ultrasound is not the most sensitive way to look for bladder cancer meaning it can miss early cases and there are other tests that are more sensitive and specific. However, bladder cancers are sometimes seen with ultrasound, especially if they are large.
Is U/S a good test for bladder cancer?
Yes: U/s is a poor test to look for bladder cancer. Gold standard is a cystoscopy (look in bladder with a camera).
Can a sonogram show early stage bladder cancer?
Too late,late stage: Early stage of bladder cancer can be detected by simple urine cytology and cystoscopy , sonography will not show early in stages.
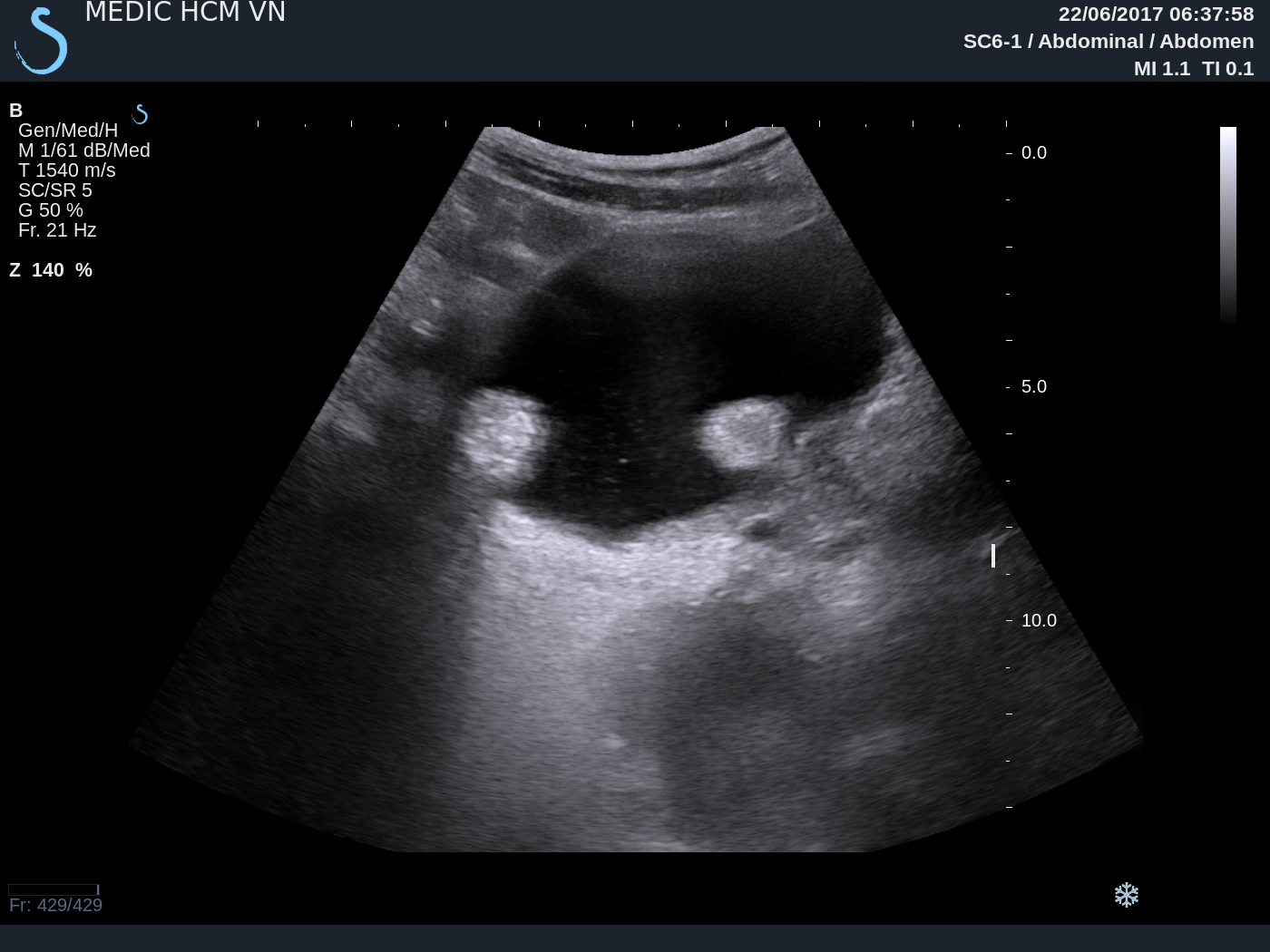
Can ultrasound scans detect bladder tumors?
Yes sometimes: Ultrasound technology can identify tumors in the bladder, but this is not a common method of detection. The fact that is is visible on ultrasound does not mean it is too late by any means. Removal of the tumor for analysis along with more precise imaging like ct scan will help determine the extent and severity if the tumor and guide subsequent treatment.
Can a cystoscope reveal bladder cancer?
Yes, but….: This would be an incidental finding on an ultrasound that unfortunately picks up a large likely advanced bladder cancer. Typically some symptoms most commonly blood in urine or pain cause someone to go to the doctor and then a ct scan, urinalysis and cystoscope exam will find or reveal a suspicious area that gets biopsied. The cystoscopic exam directly visualizing bladder lining is best study.
Actos And Bladder Cancer What Does Bladder Cancer Look Like
Ultrasound Video showing a large vesical growth in the urinary bladder.
Endoscopic Teflon Or Deflux Gel Treatment For Vesico
This patient shows an echogenic mound in the left vesico-ureteric junction. The Color Doppler image shows a ureteric jet emerging from this region suggesting that the left distal ureteric orificeis patent. This patient had a history of vesico-ureteric reflux.
Bilharziasis Of The Urinary Bladder
This patient presented with lower urinary symptoms, dysuria and hematuria. Sonography of the pelvis showed thickening of the wall of the urinary bladder with extensive calcification. Theseultrasound images suggest a diagnosis of schistosomiasis or bilharziasis of the wall of the urinary bladder.
If You Have Liver Disease
Certain diseases can make you more likely to get liver cancer, including:
Detecting Bladder Cancer With Ct Scans
A CT scan uses x-rays to obtain cross-sectional images of the body. Compared to a general x-ray test, which directs a broad x-ray beam from a single angle, the CT scan uses a number of thin beams to produce a series of images from different angles.
Screening For Bladder Cancer
Early-stage bladder cancer often shows no symptoms, or symptoms that are similar to those of benign conditions such as bladder stones, an enlarged prostate, or urinary tract infection. For this reason it is important to be examined regularly by a physician.
Can An Ultrasound Tell If An Ovarian Cyst Is Cancerous
Vaginal ultrasound can help to show whether any cysts on your ovaries contain cancer or not. If a cyst has any solid areas it is more likely to be cancer. Sometimes, in women who are past their menopause, the ovaries do not show up on an ultrasound. This means that the ovaries are small and not likely to be cancerous.
How does ultrasound help with bladder cancer?
Ultrasound uses sound waves to create pictures of internal organs. It can be useful in determining the size of a bladder cancer and whether it has spread beyond the bladder to nearby organs or tissues. It can also be used to look at the kidneys. This is usually an easy test to have, and it uses no radiation.
What is the best way to diagnose bladder cancer?
Cystoscopy. If bladder cancer is suspected, most doctors will recommend a cystoscopy. . A urologist uses a cystoscope, which is a long, thin, flexible tube with a light and a lens or a small video camera on the end. For details on how this procedure is done, see Cystoscopy.
What tests are used to check for bladder cancer?
These include the tests called NMP22 ® (or BladderChek ® ), BTA Stat ®, Immunocyt ® , and UroVysion ®, which are discussed in Can Bladder Cancer Be Found Early?
What is the blue light in a cystoscopy?
Fluorescence cystoscopy (also known as blue light cystoscopy) may be done along with routine cystoscopy. For this exam, a light-activated drug is put into the bladder during cystoscopy. It’s taken up by cancer cells. When the doctor then shines a blue light through the cystoscope, any cells containing the drug will glow (fluoresce). This can help the doctor see abnormal areas that might have been missed by the white light normally used.
What is the biopsy for bladder cancer?
A biopsy is when tiny pieces (called samples) of the abnormal-looking tissue are taken out and tested for cancer cells. If bladder cancer is suspected, a biopsy is needed to be sure of the diagnosis.
What is a physical exam for bladder cancer?
A physical exam can provide information about possible signs of bladder cancer and other health problems. The doctor might do a digital rectal exam (DRE), during which a gloved, lubricated finger is put into your rectum. If you are a woman, the doctor might do a pelvic exam as well.
How long does it take for a urine culture to show up?
It can take time for the bacteria to grow, so it may take a few days to get the results of this test.
What is the mean discomfort level of cystoscopy?
The mean discomfort level of cystoscopy estimated by each patient on optical pain-meter was 5.74. This value was slightly higher when calculated only for men and slightly lower when calculated only for women. Differences in cystoscopy tolerability (ranged from 0-8 in males, 4-10 in females) between males and females were not of statistical significance.
Is hematuria a symptom of bladder cancer?
Painless hematuria usually is the sole presenting symptom in the majority of patients with bladder cancer.1Ther efore, painless hematuria of any degree in adults should be regarded as a symptom that is suspicious for malignancy until proved otherwise. Cystoscopy is considered the gold standard in the evaluation of hematuria.2This technique directly visualizes lower urinary tract anatomy and macroscopic pathology, which may be responsible for the clinical picture under evaluation. However, cystoscopy is invasive, time-consuming and expensive.3
Is ultrasonography better than cystoscopy?
According to our findings, despite remarkable improvements in diagnostic accuracy, ultrasonography is still inferior to cystoscopy in the evaluation of the bladder as a possible source of hematuria and neither ultrasound nor the combination of urinary cytology and ultrasonography can replace the standard cystoscopic examination.12
Is cystoscopy a good test for bladder cancer?
Cystoscopy is currently the best test for evaluation of the bladder as a possible source of hematuria; however, as seen in our study, in rare cases cystoscopy may not reveal a tumor in the bladder.2Additionally, diagnostic cystoscopy is usually performed on an outpatient basis under local anaesthesia and is usually considered a painful diagnostic procedure. However, the tolerability and acceptance of diagnostic cystoscopy by patients has not been thoroughly documented. As seen from our study, the pain is moderately tolerated. Our findings are comparable to those of a few previous studies examining the tolerability and morbidity of other endoscopic procedures (eg. ureteroscopic lithotripsy under local anaesthesia, urodynamic studies etc).4–7In previous studies, differences in cystoscopy tolerability among male and female patients were attributed in these studies to the normal anatomical difference between the male and female urethra as well as by the additional difficulties in performing cystoscopy in male patients with enlarged prostates. Moreover, since routine pelvic gynecologic exams are usually performed annually among women of childbearing years it is plausible that women feel less discomfort than men when undergoing cystoscopy.
Is ultrasonography necessary for bladder cancer?
Since the diagnosis of bladder cancer requires histopathological confirmation (on the core biopsy obtained during cystoscopy or of the bladder specimens obtained after Transurethral resection of the tumor) ultrasonography is certainly not the most adequate examination.
Did Maassen do a pelvic with a full bladder?
Thank you all for the support, and yes Maassen, i did a pelvic with a full bladder, and then a trans with an empty bladder. Regardless i am going to book to see a urologist just to be sure!
Can a urologist perform a cytoscopy?
The Urologist will probably perform a Cystoscopy. The procedure is not pleasant, but it is tollerable. This will leave no doubt if there is or is not a problem. Wishing you the best result. Vince
Can ultrasound detect a mass?
Ultrasounds can detect larger masses , but not early superficial lesions which is what you want to know about. The earlier the better, so if you have persistent symptoms, microscopic blood in your urine, a urologist is a good next step
Can blood in urine be a UTI?
Blood in urine can be either a UTI, easily checked out with a culture test or a tumor in the bladder which is the most common form of detection. I have read in an excellent study on bladder cancer management that sonagrams are not advised as they are not accurate detectors and much too highly dependent upon operators. That said, a large bladder tumor can be detected via ultra sound, but you should ask, nay, insist on a CT Scan where tumor development in the bladder and anywhere else in the urinary tract including the kidneys will be easily detected. Even better, your primary physician can refer you to a urologist who will insert a scope via the urethra and will take a good look and a picture within 5 minutes and be able to easily see if you have anything growing there. Blood in the urine should be thoroughly checked out. JC