Contents

What are the warning signs of bladder cancer?
· Not typically, according to Tessa Flores, MD, Medical Director of Cancer Survivorship and Screening at Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center. While a urinary tract infection (UTI) and bladder cancer can produce similar symptoms, Dr. Flores says, having frequent UTIs doesn’t mean you have bladder cancer. “There is preliminary data that there …
Can frequent UTI cause bladder cancer?
The researchers found that bladder cancer diagnoses take longer and health outcomes are worse in men and women who have UTIs than in men with blood in …
How does bladder cancer affect the urinary system?
· Other UTI symptoms include irritation or pain when urinating or a frequent and urgent need to urinate and can also be symptoms of bladder cancer. Because UTIs and bladder cancer share symptoms, bladder cancer can be challenging to diagnose.
Is there a cure for bladder cancer?
Many experts and individuals with bladder cancer have wondered if true UTIs are related to bladder cancer risk. Inflammation related to infection, most commonly due to the rare parasitic infection schistosomiasis or long-term use of a urinary catheter, has been thought to increase the risk of developing squamous cell carcinoma of the bladder.

Do frequent UTIs cause bladder cancer?
Flores says, having frequent UTIs doesn’t mean you have bladder cancer. “There is preliminary data that there might be an association between recurrent UTIs and a specific and rare type of bladder cancer called squamous cell carcinoma,” she says. “But typically, no, having UTIs doesn’t mean you have bladder cancer.”
Does bladder cancer Start with a UTI?
Unfortunately, the most common symptom of bladder cancer—blood in the urine—is also a common symptom of a UTI. Other UTI symptoms include irritation or pain when urinating or a frequent and urgent need to urinate and can also be symptoms of bladder cancer.
Can bladder cancer be mistaken for UTI?
Bladder cancer can be mistaken for a Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) because many of the symptoms overlap. Patients may experience increased frequency and urgency of urination, pain with urination, or urinary incontinence.
What can chronic UTIs lead to?
People who suffer from chronic UTIs may experience complications. Recurring urinary tract infections may eventually cause: kidney infections, kidney disease, and other permanent kidney damage, especially in young children. sepsis, which is a life-threatening complication due to infection.
What is usually the first symptom of bladder cancer?
In most cases, blood in the urine (called hematuria) is the first sign of bladder cancer. There may be enough blood to change the color of the urine to orange, pink, or, less often, dark red.
What were your first signs of bladder cancer?
For most people, the first symptom of bladder cancer is blood in the urine, also called hematuria. Sometimes the blood is visible, prompting the patient to visit a doctor….Pain.Burning.Frequent urination.Incomplete emptying of the bladder.Passage of tissue fragments in urine (less frequent than other symptoms)
How do you rule out bladder cancer?
Tests for bladder cancer look for different substances and/or cancer cells in the urine. Urinalysis: One way to test for bladder cancer is to check for blood in the urine ( hematuria). This can be done during a urinalysis, which is a simple test to check for blood and other substances in a sample of urine.
Does bladder cancer show up in blood tests?
Tests to diagnose bladder cancer If bladder cancer is suspected, these tests may be performed to diagnose the disease: Physical exam. Blood test: Blood samples are used to measure certain substances released into the blood by organs and tissues in the body.
Can you have bladder cancer for years and not know it?
It may be seen as a symptom of post-menopausal bleeding, simple cystitis or a urinary tract infection. As a result, a bladder cancer diagnosis can be overlooked for a year or more.
How many UTIs is too many?
(3) When a UTI occurs more than twice in six months, or three or more times in one year, it is considered to be a recurrent urinary infection, according to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG).
What happens if a UTI goes untreated for a month?
The main danger associated with untreated UTIs is that the infection may spread from the bladder to one or both kidneys. When bacteria attack the kidneys, they can cause damage that will permanently reduce kidney function. In people who already have kidney problems, this can raise the risk of kidney failure.
Can you have a UTI for years?
We’ve talked elsewhere about what causes UTIs. And above, we explained that recurrent UTIs can be attributed to a persistent bladder infection that is not properly eradicated by treatment. A persistent bladder infection can last for years in the form of a chronic urinary tract infection.
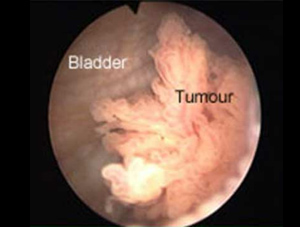
Can a woman get bladder cancer?
While bladder cancer is more prevalent among men, women can get it, too. When they do, their diagnosis tends to be delayed, and therefore, women diagnosed with bladder cancer tend to present with later stages of the disease. That is at least in part to the main symptom of bladder cancer—gross hematuria, or blood in the urine—being more easily …
Can bladder cancer cause blood in urine?
Unfortunately, the most common symptom of bladder cancer —blood in the urine—is also a common symptom of a UTI. Other UTI symptoms include irritation or pain when urinating or a frequent and urgent need to urinate …
How many people die from bladder cancer each year?
With approximately 73,000 cases being diagnosed annually, bladder cancer is the sixth most common type of cancer in the U.S. Each year, about 15,000 deaths occur from this disease. Dr.
Can bladder cancer be delayed?
When they do, their diagnosis tends to be delayed, and therefore, women diagnosed with bladder cancer tend to present with later stages of the disease. That is at least in part to the main symptom of bladder cancer—gross hematuria, or blood in the urine—being more easily shrugged off as something else when compared to men.
Is smoking a risk factor for bladder cancer?
Additionally, be aware that smoking is the biggest risk factor for bladder cancer. Fifty percent of all bladder cancer cases are in people with a history of smoking, so this is another reason to quit smoking.
Is blood in urine normal?
Blood in the urine is never normal, and if it does not go away after a course of antibiotics for a UTI, go back to your doctor. Speak up if medicine for a UTI does not improve urinary symptoms. Additionally, be aware that smoking is the biggest risk factor for bladder cancer.
Does UTI cause bladder cancer?
Another theory is that developing a UTI promotes an immune system response in the body aimed at the urinary system that could also protect against bladder cancer. In addition to destroying bacterial invaders, the immune system may recognize cancerous cells that are developing and destroy these as well. 8 This is similar to the mechanism of action behind the BCG vaccine treatment which initiates an immune system response against cancerous cells.
Can UTIs cause cancer?
Currently, research into the relationship between UTIs and urothelial carcinoma has provided mixed results. Some experts have theorized that having a few, treated UTIs earlier in life may decrease an individual’s risk of developing the condition, as the antibiotics used to treat the UTI may also impede the development of cancerous cells …
Can bladder cancer be misdiagnosed?
If a woman’s bladder cancer-related urinary symptoms are continuously treated as a UTI, it’s possible that she may experience repeated UTI-like episodes that are misdiagnosed and mistreated. If these episodes become severe, she may be referred to a urologist who might then suspect and diagnose bladder cancer.
What are the symptoms of UTI?
The most common symptoms of UTIs are also common symptoms of bladder cancer, such as blood in the urine, a burning sensation when urinating, and painful urination. 1,2 Up to 80% of all UTIs occur in women, and roughly 50% of all women will experience at least one UTI with accompanying symptoms in their lifetime.
What is the most common form of bladder cancer?
The most commonly diagnosed form of bladder cancer in the United States is urothelial carcinoma, with 90% of individuals with the condition being diagnosed with this type. 7 As such, determining the relationship between UTIs and urothelial carcinoma is of interest to many in the urological field.
Can antibiotics help with UTI?
Some experts have theorized that having a few, treated UTIs earlier in life may decrease an individual’s risk of developing the condition, as the antibiotics used to treat the UTI may also impede the development of cancerous cells and have a protect effect against cancer. 3,8.
What does it mean when you see blood in your urine?
When a woman notices blood in her urine, she may think it’s related to her menstrual cycle, menopause, or to a UTI before she suspects bladder cancer. If the blood in the urine has no accompanying pain or goes away in a relatively short period of time, she may not seek treatment. Even when a woman does seek treatment for blood in her urine or painful urination, it’s possible that her primary care provider or OB-GYN physician may diagnose and treat her for a UTI rather than suspecting bladder cancer.
Can bladder cancer cause blood in urine?
Blood in the urine, the most common symptom of bladder cancer, may be discounted by women as being related to menstruation or post- menopaus al bleeding. When blood in the urine and urinary irritation are reported to a doctor they may be initially misdiagnosed as a UTI.
Is bladder cancer more common in women than men?
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are much more common in women than in men, and the symptoms can be similar to bladder cancer, reinforcing the importance of an accurate diagnosis. Here we give an overview of UTIs and discuss why it is important to rule out bladder cancer if you are experiencing recurring UTI symptoms. What Causes UTIs.
What is the most common sign of bladder cancer?
Blood in the urine (hematuria) Blood in the urine is the most common sign of bladder cancer and is also often the first sign noticed. This is because early bladder cancer frequently causes bleeding without pain or other symptoms.
Can bladder cancer cause pain in the pelvic region?
Bladder cancer that has grown in size or spread to other areas of the body may cause a variety of symptoms including an inability to pass urine, lower back pain on one side of the body, pain in the pelvic region, appetite/weight loss, general weakness, swollen feet, or bone pain.
What is the average age for bladder cancer?
Age: Bladder cancer mostly affects people >55 years of age. In the United States, the average age of individuals diagnosed with bladder cancer is 73 years.
Can bladder cancer be delayed?
Because of this diagnostic confusion, a definitive diagnosis of bladder cancer may be delayed in some women. Of particular concern in this case is the risk that bladder cancer has reached a more advanced stage that may be more difficult to treat.
Why are UTIs more common in women than men?
UTIs are considerably more common in women than men because of their differing anatomy: Women have a shorter distance between the urethral opening and the perianal area, which increases their vulnerability to the spread of gastrointestinal bacteria such as E. coli.
Can UTI cause bladder cancer?
In a mouse model of UTI, colibactin-producing bacteria-induced extensive DNA damage in bladder cells. According to the authors, the findings support the idea that UTIs may play a role in bladder cancer. “Currently the main risk factors for bladder cancers are tobacco and occupational exposure to solvents, which are more frequently investigated …
How many people get UTIs in a year?
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are one of the most common bacterial infections, affecting approximately 150 million individuals each year. The severity of these infections ranges from asymptomatic to developing sepsis if left untreated over a period of time, which can be fatal.
What is the most common outpatient infection?
Researchers have known that the presence of E.coli bacteria is responsible for the most common outpatient infections —urinary tract infections (UTIs) —that have a lifetime incidence of around 60 percent in women. A recent study published in PLOS Pathogens has found that a DNA-damaging bacterial toxin called colibactin is produced in people …
What is the most common infection in women?
Researchers have known that the presence of E.coli bacteria is responsible for the most common outpatient infections —urinary tract infections ( UTIs) —that have a lifetime incidence of around 60 percent in women.
Does UTI cause cancer?
On the other hand, the body produces certain chemicals in response to a UTI, such as nitric oxide, that cause further inflammation. This could literally promote the growth of a tumor, which then increases the risk of cancer or the risk of cancer becoming more severe and spreading.
What are the risks of bladder cancer?
Risk factors for bladder cancer include: 1 Gender. Unlike UTIs, however, bladder cancer is more common in men. 2 Age. On average, bladder cancer develops and is diagnosed in individuals over the age of fifty-five. 3 Tobacco use. Individuals who currently or have previously used tobacco are at a higher risk for multiple types of cancer, including bladder cancer. 4 Chemotherapy. If a person has already undergone treatment of another type of cancer with chemotherapy, they are at a higher risk of developing bladder cancer. 5 Exposure. Those who work or worked with certain types of industrial chemicals or dyes are more likely to develop bladder cancer. 6 Infection. While studies are still underway to confirm, a history of chronic bladder infections, or UTIs, could be a risk factor for bladder cancer.
What is the most common type of UTI?
The most common type of UTI is a bladder infection, though a more complex or untreated infection can back up into the kidneys and cause additional complications. Risk factors for developing a UTI start …
Can bladder cancer spread to other parts of the body?
These overgrowths form tumors, or cell clusters, and over time, the cells can spread to other parts of the body ( metastasize ). Bladder cancer involves these growths within the bladder or the surrounding urinary tract, including the urethra and ureters.
How old do you have to be to get bladder cancer?
On average, bladder cancer develops and is diagnosed in individuals over the age of fifty-five. Tobacco use. Individuals who currently or have previously used tobacco are at a higher risk for multiple types of cancer, including bladder cancer. Chemotherapy.
Can dyes cause bladder cancer?
Those who work or worked with certain types of industrial chemicals or dyes are more likely to develop bladder cancer. Infection. While studies are still underway to confirm, a history of chronic bladder infections, or UTIs, could be a risk factor for bladder cancer.
What percentage of bladder cancer is urothelial?
Also, while urothelial cancer is the most common type, the link between UTIs causing cancer seems to lean more toward other types of bladder cancer, which are far less common (urothelial cancer comprises about ninety percent of bladder cancer in the United States).
Toxin-induced DNA damage to bladder cells
Doctors say that approximately 80 percent (an overwhelming majority) of UTIs are caused by a bacteria known as Uropathogenic E. coli or UPEC. And now, a new study has shown that this bacteria is capable of producing a toxin known as colibactin, which has long been suspected of being involved in cancer.
A reservoir of E. coli bacteria
That last was a lot of scientific talk, but it came down to two very important points:
By Dr. Adria Schmedthorst
Dr. Adria Schmedthorst is a board-certified Doctor of Chiropractic, with more than 20 years of experience. She has dedicated herself to helping others enjoy life at every age through the use of alternative medicine and natural wellness options. Dr.