Contents

Symptoms
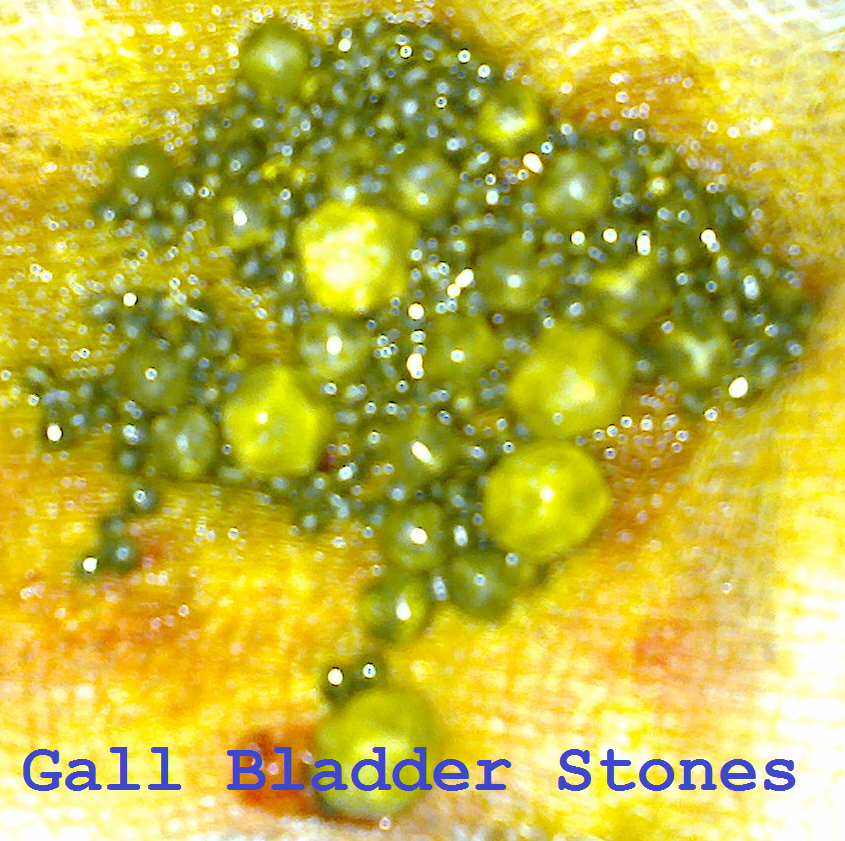
· In fact, gallstones happen to be the most common risk factor for developing gallbladder cancer. Small, hard pebbles formed from bile elements such as cholesterol or bilirubin can range in size from tiny particles to large marbles and may completely fill and block the gallbladder from functioning properly.
Causes
Gallstones were significantly associated with increased risk of hepatobiliary cancer mortality, especially liver/intrahepatic biliary cancer, and gallbladder cancer mortality.
Prevention
Doctors believe that large gallstones grow over a long time, irritating the gallbladder wall and increasing the risk for cancer. Although gallstones are common, most people with gallstones rarely develop gallbladder cancer. Female gender Gallbladder cancer occurs more than twice as often in women as in men in the United States. Older age Gallbladder cancer occurs more often …
Complications
· Older people with large gallstones (equal to or greater than 3 cm) are at a greater risk of gallbladder cancer. Thus, gallstones are a major indicator of gallbladder cancer. The only way to prevent and treat gallbladder cancer is to undergo surgery …
Can untreated gallstones cause cancer?
If gallstones lodge in a bile duct and cause a blockage, it eventually results in severe life-threatening complications such as bile duct inflammation and infection, pancreatitis or cholecystitis (an inflammation of gallbladder). In addition, if left untreated, it might increase risk of “gallbladder cancer”.
Can gallbladder give you cancer?
The risk of gallbladder cancer is around 5 times higher in people with a history of gallbladder conditions (mainly gallstones), compared to those who don’t. Gallstones are very common but gallbladder cancer is very rare. Most people with an inflamed gallbladder or gallstones do not get gallbladder cancer.
Can gallstones cause liver cancer?
A population-based study in US showed that gallstones and cholecystectomy were associated with elevated risk of liver cancer (OR = 2.35 (95% CI: 2.18, 2.54) and OR = 1.26 (95% CI: 1.12, 1.41)).
What size of gallstone causes cancer?
Persons with large gallstones were found to be at increased risk for cancer. For those with stone diameters of 2.0 to 2.9 cm, the odds ratio ( v stone size <1 cm) was 2.4; for stones 3 cm or larger, the ratio was 10.1.
Can you get cancer after gallbladder removal?
Cancer found after surgery for another gallbladder problem Some gallbladder cancers are found when the gallbladder is removed to treat gallstones or chronic inflammation. The removed gallbladder is looked at and tested in a lab, at which time the cancer is found. These are often early-stage cancers.
How is gallbladder cancer detected?
Computed tomography (CT) scan Help diagnose gallbladder cancer by showing tumors in the area. Help stage the cancer (find out how far it has spread). CT scans can show the organs near the gallbladder (especially the liver), as well as lymph nodes and distant organs the cancer might have spread to.
Is gallbladder cancer fast growing?
They are slow-growing and less likely to spread. Higher grade cells look and act abnormally. They grow faster and are more likely to spread. The grade of cancer can help predict how quickly the cancer might spread.
How long can you live after gallbladder cancer?
5-year relative survival rates for gallbladder cancerSEER stage5-year relative survival rateLocalized66%Regional28%Distant2%All SEER stages combined19%Feb 28, 2022
Can gallbladder cancer be seen on ultrasound?
An abdominal ultrasound is often the first imaging test done when doctors suspect gallbladder cancer. It can confirm if the wall of the gallbladder is thicker than normal and provide information about the size of a tumour. An ultrasound is also used to see if the cancer has spread to the liver.
Is a 5 cm gallstone big?
The answer is that there is no normal size when it comes to gallstones. Some patients have anywhere from a few to hundreds of tiny gallstones. Other patients will have a single gallstone as large as 5 cm, although a gallstone of this size is rare.
Is a 12mm gallstone big?
Gallstones vary greatly in size. Some people may form one large stone, whereas others may have hundreds of tiny stones. Most commonly, gallstones are 5–10 mm in diameter. Most people with gallstones do not experience any symptoms.
What size of gallstone requires surgery?
Any stone more than 1.5CMS in size needs removal of gall bladder.
Why do people get gallbladder cancer?
Many of these are related to swelling and chronic inflammation of tissue that can result from having gallstones.
What is the condition called when the gallbladder is covered in calcium?
Chronic gallbladder inflammation, (cholecystitis) can lead to development of a condition called porcelain gallbladder. The inner walls of the gallbladder become covered in hardened calcium deposits.
Can cancer thrive in stagnant bile?
Excessive toxicity in the form of stagnant bile over prolonged periods of time may in some individuals yield the ideal acidic environment where cancer can thrive.
Who has the highest rate of gallstones?
Women, especially those who have had multiple children or are taking hormone replacement therapy are also more likely to develop gallstones due to the influence of hormones. Mexican Americans and Native Americans demonstrate higher rates of both gallstone development and gallbladder cancer diagnosis in the United States. Individuals with these risk factors should take extra care to maintain a healthy diet and weight that will contribute to healthy digestion.
Can gallstones cause cancer?
In fact, gallstones happen to be the most common risk factor for developing gallbladder cancer. Small, hard pebbles formed from bile elements such as cholesterol or bilirubin can range in size from tiny particles to large marbles and may completely fill and block the gallbladder from functioning properly. Often people do not notice gallbladder symptoms right away and will only be diagnosed with a disease once they start to experience painful symptoms. At that point, gallbladder inflammation due to irritation of the gallbladder walls and bile duct blockages may already be taking place.
How does gallbladder cancer form?
Doctors know that gallbladder cancer forms when healthy gallbladder cells develop changes (mutations) in their DNA. A cell’s DNA contains the instructions that tell a cell what to do. The changes tell the cells to grow out of control and to continue living when other cells would normally die. The accumulating cells form a tumor that can grow beyond the gallbladder and spread to other areas of the body.
Why is gallbladder cancer not detected?
Gallbladder cancer may not be discovered until it’s advanced because it often causes no specific signs or symptoms. Also, the relatively hidden nature of the gallbladder makes it easier for gallbladder cancer to grow without being detected.
What causes bile duct inflammation?
Inflammation of the bile ducts. Primary sclerosing cholangitis, which causes inflammation of the ducts that drain bile from the gallbladder and liver, increases the risk of gallbladder cancer. Niederhuber JE, et al., eds. Liver and bile duct cancer.
How do you know if you have gallbladder cancer?
Gallbladder cancer signs and symptoms may include: 1 Abdominal pain, particularly in the upper right portion of the abdomen 2 Abdominal bloating 3 Losing weight without trying 4 Yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice)
What is the name of the fluid that flows from the liver to the gallbladder?
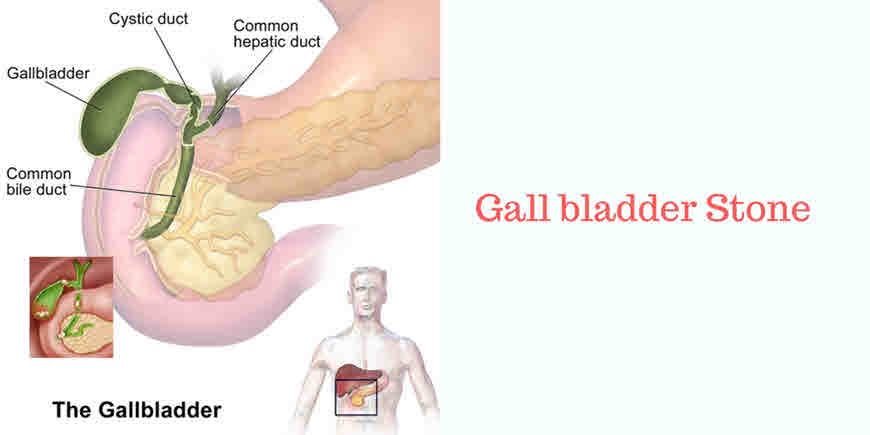
Close. Gallbladder and bile duct. Gallbladder and bile duct. The gallbladder serves as a reservoir for bile, a yellow-green fluid produced in your liver. Bile flows from your liver into your gallbladder, where it’s held until needed during the digestion of food.
What is the name of the cancer that starts in the glandular cells that line the inner surface of the gallblad
The accumulating cells form a tumor that can grow beyond the gallbladder and spread to other areas of the body. Most gallbladder cancer begins in the glandular cells that line the inner surface of the gallbladder. Gallbladder cancer that begins in this type of cell is called adenocarcinoma.
Where is the gallbladder located?
Your gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ on the right side of your abdomen, just beneath your liver. The gallbladder stores bile, a digestive fluid produced by your liver. Gallbladder cancer is uncommon. When gallbladder cancer is discovered at its earliest stages, the chance for a cure is very good.
Why is gallbladder cancer dangerous?
There are several carcinogens that have been linked to gallbladder cancer. The reason the gallbladder is at risk is because toxic substances are filtered by the liver and excreted into the bile. Since bile flows through the gallbladder, it’s exposed to these substances.
What are the risk factors for gallbladder cancer?
List of risk factors. These are some of the risk factors associated with gallbladder cancer. Gallstones. This is the most common risk factor. At least three out of four people with gallbladder cancer also have gallstones and an inflamed gallbladder.
What are the risks of gallbladder polyps?
Polyps bigger than 1 centimeter (about one-half inch) are more likely to become cancerous. Chronic typhoid and paratyphoid infection.
How often does gallbladder cancer occur?
Gallbladder cancer occurs more than twice as often in women as in men in the United States. Older age. Gallbladder cancer occurs more often in people older than 65 years of age, although it may occur in younger people. Ethnicity.
Which ethnicity has the highest gallbladder cancer rate?
Ethnicity. In the United States, Hispanics of Mexican descent and Native Americans have the highest rates of gallbladder cancer, compared to other racial and ethnic groups, while African-Americans have the lowest rate. Carcinogens. These are cancer-causing agents.
Can you get gallbladder cancer?
Risk Factors for Gallbladder Cancer. Certain factors can make you more likely to get gallbladder cancer than another person. These are called risk factors. However, just because you have one or more risk factors doesn’t necessarily mean you will get gallbladder cancer. In fact, you can have all the known risk factors and still not get gallbladder …
Can gallstones cause cancer?
Doctors believe that large gallstones grow over a long time, irritating the gallbladder wall and increasing the risk for cancer. Although gallstones are common, most people with gallstones rarely develop gallbladder cancer. Gallbladder cancer occurs more than twice as often in women as in men in the United States.
Why does my gallbladder get stones?
Gallbladder problems are usually caused due to the presence of small stones. Stones in the gallbladder can form due to cholesterol and bile salts in the gallbladder or in the bile duct.
How to treat gallbladder cancer?
The only way to prevent and treat gallbladder cancer is to undergo surgery as soon as gallstone disease is diagnosed.
How many incisions are needed for gallbladder removal?
A laparoscopic cholecystectomy is an advanced approach for gallbladder removal. In this minimally invasive surgery, the doctor makes 4 incisions on the abdomen. Through the incisions, they insert a tube with a light and a camera called a laparoscope and surgical tools to take out the gallbladder. There are only a few minor incisions involved and thus the patient experiences very little pain and difficulty while recovering. Also, the recovery period is short and smooth.
What happens if your gallbladder doesn’t empty?
When your gallbladder doesn’t empty properly, the bile might concentrate in the organ and clump together to form gallstones.
What happens if you have too much cholesterol in your body?
Your bile has chemicals that dissolve the cholesterol. But, if the cholesterol is in excess, it can form into crystals called cholesterol gallstones.
What are the chances of developing gallstones?
The chances of developing stones in the gallbladder increase with age. People who are above 40 are more susceptible to developing gallstones. Some factors that increase the risk of gallstone disease are-. Family history of developing gallstones. Being overweight or obese.
What are the symptoms of gallbladder cancer?
Being overweight or obese. Suffering from diabetes. Suffering from high blood pressure. Consuming alcohol regularly. Have the habit of smoking. Young women. Women with multiple pregnancies. Long term use of contraceptive pills. Also Read: Gallbladder Cancer Causes and Early Symptoms.
What are the risk factors for gallbladder cancer?
Risk Factors for Gallbladder Cancer. A risk factor is anything that affects your chance of getting a disease such as cancer. Different cancers have different risk factors. Some risk factors, like smoking, can be changed. Others, like a person’s age or family history, can’t be changed. But having a risk factor, or even many risk factors, …
Where is gallbladder cancer most common?
The risk is lowest among African Americans. Worldwide, gallbladder cancer is much more common in India, Pakistan, and Central European and South American countries than it is in the US.
What is the cause of sclerosing cholangitis?
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is a condition in which inflammation of the bile ducts (cholangitis) leads to the formation of scar tissue (sclerosis). People with PSC have an increased risk of gallbladder and bile duct cancer. The cause of the inflammation is not usually known. Many people with PSC also have ulcerative colitis, a type of inflammatory bowel disease.
How often does gallbladder cancer occur in women?
In the US, gallbladder cancer occurs 3 to 4 times more often in women than in men. Gallstones and gallbladder inflammation are important risk factors for gallbladder cancer and are also much more common in women than men.
What is a gallbladder polyp?
Gallbladder polyps. A gallbladder polyp is a growth that bulges from the surface of the inner gallbladder wall. Some polyps are formed by cholesterol deposits in the gallbladder wall. Others may be small tumors (either cancer or not cancer) or may be caused by inflammation.
How much bile does a gallbladder cyst contain?
The cysts can grow large over time and may contain as much as 1 to 2 quarts of bile. The cells lining the sac often have areas of pre-cancerous changes, which can progress to gallbladder cancer over time.
What is porcelain gallbladder?
Porcelain gallbladder. Porcelain gallbladder is a condition in which the wall of the gallbladder becomes covered with calcium deposits. It sometimes occurs after long-term inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis), which can be caused by gallstones. People with this condition have a higher risk of developing gallbladder cancer, …
How to prevent gallstones?
Include more fiber-rich foods in your diet, such as fruits, vegetables and whole grains. Maintain a healthy weight. Obesity and being overweight increase the risk of gallstones.
What are the symptoms of gallstones?
Seek immediate care if you develop signs and symptoms of a serious gallstone complication, such as: Abdominal pain so intense that you can’t sit still or find a comfortable position. Yellowing of your skin and the whites of your eyes (jaundice) High fever with chills.
What causes pain in the pancreas?
Pancreatic juices, which aid in digestion, flow through the pancreatic duct. A gallstone can cause a blockage in the pancreatic duct, which can lead to inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis). Pancreatitis causes intense, constant abdominal pain and usually requires hospitalization. Gallbladder cancer.
What is the fluid in the gallbladder called?
The gallbladder holds a digestive fluid called bile that’s released into your small intestine. Gallstones range in size from as small as a grain of sand to as large as a golf ball. Some people develop just one gallstone, while others develop many gallstones at the same time.
What is the name of the fluid that is produced in the liver and stored in the gallbladder?
Gallstones. Gallstones are hardened deposits of bile that can form in your gallbladder. Bile is a digestive fluid produced in your liver and stored in your gallbladder. When you eat, your gallbladder contracts and empties bile into your small intestine (duodenum).
Why is bile so high in bilirubin?
Bilirubin is a chemical that’s produced when your body breaks down red blood cells. Certain conditions cause your liver to make too much bilirubin, including liver cirrhosis, biliary tract infections and certain blood disorders. The excess bilirubin contributes to gallstone formation.
What are the different types of gallstones?
Types of gallstones. Types of gallstones that can form in the gallbladder include: Cholesterol gallstones. The most common type of gallstone, called a cholesterol gallstone, often appears yellow in color. These gallstones are composed mainly of undissolved cholesterol, but may contain other components.
How many apples should I eat a day to get rid of stones?
I was told by a health specialist to go on a fat-free diet and eat at least 4 to 5 apples per day (pure apple juice is even better) as the potassium may help breaking down the stones.
Can biliary pain be fatal?
Majority of patients rarely develop severe, potentially life-threatening complications, such as acute suppurative cholangitis or severe acute pancreatitis, without first having at least one episode of biliary pain.
Is gallbladder cancer a malignancy?
Gallstones represent an important risk factor for this malignancy, being present in most (~ 85%) patients with gallbladder cancer. Further, gallbladder cancer rates correlate well with the prevalence of gallstone disease, 12 which more commonly affects certain indigenous populations, particularly in North and South America. From a different perspective, however, the overall risk of gallbladder cancer occurring in those with stones is low; fewer than 3% of individuals with cholelithiasis have gallbladder cancer.
Can you remove gallbladder polyps?
if living in North India or being an American Native female, it seems best to monitor the gallbladder for polyp formation by echography, and remove the gallbladder if a polyp on serial monitoring is seen growing to surgically cure potential gallbladder cancer and prevent it from spreading, prophylactically removing the gallstone containing gallbladder especially if the gallstones aren’t calcified (≈cholesterol stones) or if the gallbladder is calcified could be another way to deal with a potential problem, but is very, very controversial at this moment. Not advised if one is not in one of these high risk population groups. Remember, no surgical procedure is without risk, according to this 2015 Swedish paper Mortality after a cholecystectomy: a population-based study mortality at present is 2.58%, close to the usual background mortality, higher in those > 70 yo and havingcomplicaqtions after the operation, and those having a worse preoperative general health condition.
Can gallstones cause cancer?
Gallstones do not cause cancer but may be found in association with conditions that cause cancer. One such condition with almost 100% chance of cancer is “porcelain gallbladder” wherein the gallbladder wall becomes calcified.
Can gall bladder surgery cause cancer?
Surgery on the gall bladder as such should not lead to cancer. In any case, if there is any cancer in the gall bladder… it would be tested in the laboratory (post surgery).
Does gallstone size affect gallbladder cancer?
Gallstone characteristics further influence the frequency at which gallbladder cancer develops. Increasing stone size augments the risk of gallbladder cancer; stones >3 cm carry a tenfold increased risk when compared with smaller stones. 20, 21 The stone type may also matter. American Indians and other groups who have a high incidence of carcinoma of the gallbladder also have an inordinately high prevalence of cholesterol gallstone disease. 22 The basis for this relationship likely resides in gallstones creating local mucosal irritation and chronic inflammation, perhaps aided by the local production of carcinogens, such as secondary bile acids. 23