Contents

What can you do to treat interstitial cystitis?
Depends: Interstitial cystitis is a diagnosis of exclusion. It causes suprapubic pain and a persistent, urgent need to urinate. Bladder cancer can cause no … Read More
Can natural remedies ease interstitial cystitis?
Aims: Interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome (IC/BPS) is a prevalent disorder that may contribute to bladder cancer (BC). This cohort study set out to investigate the association between IC/BPS and BC by using a population-based dataset.
What should you know about interstitial cystitis?
· In 1% of cases, bladder cancer may be diagnosed wrongly as interstitial cystitis. Often symptoms of bladder cancer are similar to interstitial cystitis leading to the misdiagnosis. These include irritating symptoms of urination resembling IC may be due to bladder cancer. This is also true for people who have no usual risk factors for bladder cancer.
Can interstitial cystitis ever go away?
· As Nancy said above I was one of the ones to have both interstitial cystitis and bladder cancer. It was absolutely horrible! My bladder cancer began as non invasive so I was treated for a few years before it became invasive. I always wonder if I was misdiagnosed.
Can chronic cystitis cause bladder cancer?
Chronic bladder inflammation. Chronic or repeated urinary infections or inflammations (cystitis), such as might happen with long-term use of a urinary catheter, may increase the risk of a squamous cell bladder cancer.
Can bladder cancer be mistaken for interstitial cystitis?
Women are more likely to mistake bladder cancer symptoms for urinary tract infections or menstruation. Rarely, bladder cancer may also be misdiagnosed as interstitial cystitis in women. IC is a painful, inflammatory bladder condition that affects more women than men.
What is the leading cause of bladder cancer?
Smoking is the most important risk factor for bladder cancer. People who smoke are at least 3 times as likely to get bladder cancer as people who don’t. Smoking causes about half of all bladder cancers.
What happens if interstitial cystitis goes untreated?
Lower quality of life. Frequent urination and chronic pain may interfere with everyday life. Sexual intimacy problems. Frequent urination and pain may strain sexual intimacy.
Does IC increase your risk of bladder cancer?
Interstitial cystitis is not contagious. It does not spread in the body and does not seem to worsen with time. It is not a cause of bladder cancer. Though more research is needed, IC does not seem to affect fertility or the health of a fetus.
Would I know if I had bladder cancer?
Having to urinate more often than usual. Pain or burning during urination. Feeling as if you need to go right away, even when your bladder isn’t full. Having trouble urinating or having a weak urine stream.
Which of the following is usually the first symptom of bladder cancer?
For most people, the first symptom of bladder cancer is blood in the urine, also called hematuria. Sometimes the blood is visible, prompting the patient to visit a doctor.
Can CT scan detect bladder cancer?
A CT scan uses X-rays and a computer to create three-dimensional, cross-sectional pictures of the bladder, as well as the ureters and kidneys. A CT scan may be used to see whether bladder cancer has invaded the bladder wall or has spread to other organs or nearby lymph nodes.
What are the odds that a tumor in the bladder is cancerous?
Risk of bladder cancer Overall, the chance men will develop this cancer during their life is about 1 in 27. For women, the chance is about 1 in 89.
How serious is interstitial cystitis?
IC is a chronic disease. Patients may find some comfort in the fact that it is not life-threatening and it does not lead to cancer. However, because the symptoms are always present, patients need to develop coping skills to deal with them.
Are there stages of interstitial cystitis?
Excessive frequency of urination, urinary urgency, and urethra, bladder or pelvic pain are common symptoms. Treatment is divided into five phases, ranging from lifestyle changes to injections to surgery.
What is end stage interstitial cystitis?
End-stage interstitial cystitis is defined as a hard bladder that triggers intense pain and possesses very low bladder capacity. Many cases of end-stage interstitial cystitis involve Hunner’s ulcers. Also known as “end-stage IC”, only about 5% of IC patients develop this severe condition.

Is interstitial cystitis a cancer?
InterstitialCystitis: I think you meant to say you have Interstitial Cystitis, a bladder condition which is not really well-understood. It is not thought to be a cancer pr … Read More
Is painless hematuria a cancer?
If you have: painless hematuria, it is cardinal sign of neoplasm of urinary tract. At your age, cancer is not likely, but benign tumors can also cause this. Cons … Read More
Why does my urine resemble IC?
These include irritating symptoms of urination resembling IC may be due to bladder cancer. This is also true for people who have no usual risk factors for bladder cancer. (3, 4) Since the exact causes and pathological mechanisms of interstitial cystitis remain unknown, no specific treatment could be developed.
What is the name of the drug that is used to repair the bladder wall?
Pain medication (analgesics, anti-inflammatory drugs, antispasmodics, antihistamines in allergic patients); sodium pentosan polysulfate (a derivative of heparin) which acts to repair the bladder wall; a hydrodistension of the bladder that works for most patients; instillation into the bladder with heparin; hyaluronic acid, Di-methyl-sulfoxide.
What is IC in a sex?
Interstitial cystitis (IC) is a chronic inflammatory disease of the bladder. (1) Inflammation of the bladder causes pain, urinary disorders, and sexual disorders, outside any infectious context. Probably underdiagnosed, it is difficult to know the exact number of people affected by this disease. (2)
Can cystitis cause ulcers in the bladder?
In the case of interstitial cystitis, micro-hemorrhages revealing cracks in the bladder wall can be observed. In severe forms, the bladder wall can even ulcerate.
Does urinating help with vaginal pain?
The pain may also involve the urethra and the vagina (in the case of women). Urinating parti ally or completely relieves the pains in most cases.
Is interstitial cystitis a psychological disorder?
The causes of interstitial cystitis remain unknown to this day and this disease has long been associated with psychological or even psychiatric disorders. Currently, specialists assume that this pathology would group several diseases with multiple origins.
Can a neo bladder be successful for women?
it is my understanding that neo bladders are not as successful for women as they are for men. That does not mean that all women have issues, but it does seem to present more problems for women than men
Can interstitial cystitis cause DNA damage?
I think that interstitial cystitis has a lot to do with your BC. Infections can cause DNA damage in the bladder lining. Do you think you can cath your neo? It’s easier done for men than for women.
How long does it take to diagnose interstitial cystitis?
The symptoms of interstitial cystitis are similar to those of other bladder problems, making it difficult to diagnose. In fact, it can take more than four years before a patient is accurately diagnosed.
What is IC in urology?
Interstitial cystitis (IC) is a chronic inflammation of the bladder wall, occasionally accompanied by small spots of bleeding ( glomerulations) or areas of broken skin (Hunner’s ulcer s). This condition affects the urinary system and can cause pain or discomfort in the bladder and pelvic area, as well as the need to urinate urgently or frequently.
What are the complications of interstitial cystitis?
Interstitial cystitis can result in a number of complications, including: 1 Reduced bladder capacity. Interstitial cystitis can cause stiffening of the bladder wall, which allows your bladder to hold less urine. 2 Lower quality of life. Frequent urination and pain may interfere with social activities, work and other activities of daily life. 3 Sexual intimacy problems. Frequent urination and pain may strain your personal relationships, and sexual intimacy may suffer. 4 Emotional troubles. The chronic pain and interrupted sleep associated with interstitial cystitis may cause emotional stress and can lead to depression.
How do you know if you have interstitial cystitis?
If you have interstitial cystitis, your symptoms may also vary over time, periodically flaring in response to common triggers, such as menstruation, sitting for a long time, stress, exercise and sexual activity.
Why does my bladder hold less urine?
Reduced bladder capacity. Interstitial cystitis can cause stiffening of the bladder wall, which allows your bladder to hold less urine.
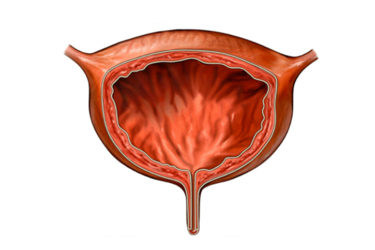
What makes up the urinary system?
Your bladder, kidneys, ureters and urethra make up your urinary system. When you have interstitial cystitis, the walls of your bladder become irritated and inflamed (shown right), compared with those of a normal bladder (shown top).
What is the pain of a bladder?
The pain ranges from mild discomfort to severe pain. The condition is a part of a spectrum of diseases known as painful bladder syndrome. Your bladder is a hollow, muscular organ that stores urine. The bladder expands until it’s full and then signals your brain that it’s time to urinate, communicating through the pelvic nerves.
Can interstitial cystitis cause a woman to urinate?
With interstitial cystitis, these signals get mixed up — you feel the need to urinate more often and with smaller volumes of urine than most people. Interstitial cystitis most often affects women and can have a long-lasting impact on quality of life.
Can interstitial cystitis be worse?
However, symptoms may worsen if a person with interstitial cystitis gets a urinary tract infection.
How many people get bladder cancer a year?
With Bladder Cancer (BC) affecting about 79,000 adults every year in the United States, it’s one of the more common cancers. The symptoms for BC are pretty similar to IC and UTI’s, with symptoms that include: 2
Why do they recommend a bladder biopsy?
Even with the various tests, Dr. Steinberg recommends a bladder biopsy to correctly establish a diagnosis because urinary cytology “is not especially helpful in early diagnosis of [cancers]. Most of these tumors are not diagnosed until they are at an advanced stage.” 3.
What is the UTI in the urinary tract?
Urinary tract infection (UTI) As you probably know, the urethra carries waste from the bladder outside the body. In some circumstances, the urethra can become infected by any number of bacteria. With this, the urethra can become red, swollen and inflamed. Common symptoms can include: 1.
What tests can you request for bladder cancer?
Requesting different tests. You could request a set of tests, including a urine cytology test or other tests that are available that look for bladder cancer markers. These tests are highly sensitive in detecting cancer.
What is IC in a woman?
Interstitial Cystitis (IC) is a painful bladder syndrome, where the lining of the bladder is inflamed. This inflammation appears with the presence of bacteria or an infection. Approximately 8 million women in the United States suffer from this condition. Just like a UTI, the symptoms for IC include: 1
What is the purpose of a cystoscopy?
Doctors may perform a cystoscopy to visually inspect the urethra. Dr. Steinberg says a cystoscopy may “reveal a characteristic red, velvety appearance that resembles an area of inflammation. In some cases, however, [cancer] is not visible on gross inspection.” 3 So, after getting an additional evaluation that still may misdiagnose the cancer as a UTI, what can you do?
Does bladdercancer.net endorse products?
The BladderCancer.net team does not recommend or endorse any products or treatments discussed herein. Learn more about how we maintain editorial integrity here.
Can you have a fish test and a cytology test?
You could have a FISH test (Fluorescent In-Situ Hybridization test) and a cytology test. If you test negative with both tests, your chance of having Carcinoma In-Situ of the bladder is extremely small. The cytology test is not very expensive (maybe a couple of hundred dollars). I think my insurance company is charged about $2000 for each FISH test that I have. (I understand that false negatives for CIS can be pretty high with in-office cystoscopies) I was an example of a false negative for CIS from an in-office Cystoscopy.#N#Eric Kiralyfalvi (Former CIS patient — originally incorrectly diagnosed with IC — Diagnosed with CIS May 2014 after surgical biopsy) I’ll try to provide some papers with test statistics later today.
Is IC a risk for bladder cancer?
IC is one of the risks for bladder cancer.