Contents

Can bladder cancer be picked up on ultrasound?
· Apart from overactive bladder, a bladder ultrasound may also be able to help diagnose bladder cancer. After a diagnosis, the doctor can begin treatments or therapies to help your symptoms, such as…
How is bladder cancer identified on an ultrasound?
· An ultrasound of the urinary tract can help assess the size of a bladder tumor and whether a bladder cancer has spread. Ultrasound is able to differentiate between fluid-filled cysts and solid tumors, however, it cannot determine if a tumor is cancerous. Ultrasound can also be used to guide a biopsy needle to sample a suspected cancer.
Would cancer show up on an ultrasound?
· A 2017 study of patients with indications for cystoscopy found that ultrasound has high sensitivity and specificity in the diagnosis of bladder cancer in patients suspected in the first stage. The most common finding was presence of papillary tumors in the bladder and the lowest frequency was related to cystic tumours.
Can an ultra sound show stomach cancer?
You have an ultrasound scan to check: for any signs of cancer in your bladder how big it is and whether it has spread for blockages in the tubes that move urine between your kidneys and bladder (the ureters) Colour ultrasound (called Doppler ultrasound) can also show the blood flow into your kidneys and the urine flow into your bladder.

How accurate is ultrasound in detecting bladder cancer?
The accuracy of baseline ultrasound in bladder cancer detection per patient was 72.09% (31/43 patients), with a sensitivity of 81.81% (27/33), specificity of 40% (4/10), positive predictive value of 81.81% (27/33) and negative predictive value of 40% (4/10) (Figure 1).
Can you tell if you have bladder cancer from an ultrasound?
Ultrasound. Ultrasound uses sound waves to create pictures of internal organs. It can be useful in determining the size of a bladder cancer and whether it has spread beyond the bladder to nearby organs or tissues. It can also be used to look at the kidneys.
What will a bladder ultrasound show?
Bladder ultrasound can give information about the bladder wall, diverticula (pouches) of the bladder, bladder stones, and large tumors in the bladder. Kidney ultrasound can show if the kidneys are in the right place or if they have blockages, kidney stones, or tumors.
How is bladder cancer detected?
A sample of your urine is analyzed under a microscope to check for cancer cells in a procedure called urine cytology. Imaging tests. Imaging tests, such as computerized tomography (CT) urogram or retrograde pyelogram, allow your doctor to examine the structures of your urinary tract.
Can bladder cancer be missed on ultrasound?
While bladder tumors may be visualized using ultrasound, a negative test does not exclude the presence of bladder cancer. An ultrasound may also not have sufficient sensitivity to detect small tumors and is unable to detect tumors in some parts of the urinary tract (for example, the ureters).
Is cystoscopy better than ultrasound?
While the tolerability of cystoscopy is relatively low, it is still superior to ultrasonography in the evaluation of the bladder as a possible source of hematuria. Painless hematuria usually is the sole presenting symptom in the majority of patients with bladder cancer.
Why would you have an ultrasound on your bladder?
A bladder ultrasound can show how much urine the bladder holds when it’s full and whether someone completely empties the bladder when peeing. It can show if there’s anything unusual about the bladder, such as its size, the thickness of the bladder walls, and if there are blockages or kidney stones.
Can a pelvic ultrasound detect bladder problems?
Bladder ultrasound can detect bladder stones, bladder tumors (cancers) and bladder diverticula. It may also detect ureteroceles among other urological problems. A pelvic ultrasound can help identify bladder tumors, kidney stones, and other disorders of the urinary tract in both men and women.
Does ultrasound show bladder infection?
Ultrasound. If you have frequent urinary tract infections, your doctor may order an ultrasound to check the kidneys and bladder for irregularities that may require treatment. This test uses sound waves to create images of structures inside the body.
What is usually the first symptom of bladder cancer?
In most cases, blood in the urine (called hematuria) is the first sign of bladder cancer. There may be enough blood to change the color of the urine to orange, pink, or, less often, dark red.
What are the symptoms of stage 1 bladder cancer?
SymptomsBlood in urine (hematuria), which may cause urine to appear bright red or cola colored, though sometimes the urine appears normal and blood is detected on a lab test.Frequent urination.Painful urination.Back pain.
Does bladder cancer feel like a UTI?
Bladder cancer can be mistaken for a Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) because many of the symptoms overlap. Patients may experience increased frequency and urgency of urination, pain with urination, or urinary incontinence.
What is the best test to diagnose bladder cancer?
Cystoscopy. Cystoscopy is the key diagnostic procedure for bladder cancer. It allows the doctor to see inside the body with a thin, lighted, flexible tube called a cystoscope. Flexible cystoscopy is performed in a doctor’s office and does not require anesthesia, which is medication that blocks the awareness of pain.
Does a pelvic ultrasound show the bladder?
A pelvic ultrasound is a test that uses sound waves to make a picture of the inside of the lower belly (pelvis). It allows your doctor to see your bladder, cervix, uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries. The sound waves create a picture on a video monitor.
Does an abdominal ultrasound show the bladder?
An ultrasound machine sends sound waves into the abdominal area and images are recorded on a computer. The black-and-white images show internal structures such as the appendix, intestines, liver, gall bladder, pancreas, spleen, kidneys, and bladder.
Is a bladder scan an ultrasound?
A bladder scan uses a noninvasive, portable ultrasound device that provides a virtual 3D image of the bladder and the volume of urine retained within the bladder.

Imaging Techniques To Detect Bladder Cancer
Imaging techniques, which include ultrasound, computed tomography (or CT) scanning, magnetic resonance imaging (or MRI) and x-ray approaches, provide an important means of assessing the urinary tract, including the kidneys, and play an important role in the detection, diagnosis, and monitoring of bladder cancer.
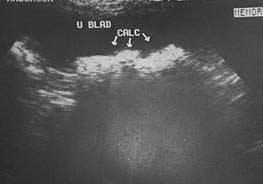
Detecting bladder cancer with ultrasound
An ultrasound (which may also be referred to as a sonogram) uses high frequency sound waves to produce images of internal organs. Echoes, which are created as sound waves bounce off organs and tissues, produce computer images that provide information on the structure and movement of organs and the blood flow through vessels.
How do ultrasounds help detect and monitor bladder cancer?
An ultrasound of the urinary tract can help assess the size of a bladder tumor and whether a bladder cancer has spread. Ultrasound is able to differentiate between fluid-filled cysts and solid tumors, however, it cannot determine if a tumor is cancerous. Ultrasound can also be used to guide a biopsy needle to sample a suspected cancer.
Detecting bladder cancer with CT scans
A CT scan uses x-rays to obtain cross-sectional images of the body. Compared to a general x-ray test, which directs a broad x-ray beam from a single angle, the CT scan uses a number of thin beams to produce a series of images from different angles.
Other imaging approaches to detect or monitor bladder cancer
An MRI scan uses radio waves and magnets to produce more detailed pictures of soft tissues. MRI scans can show whether bladder cancer has spread to other tissues or to the lymph nodes. To improve the quality of the images it’s sometimes necessary to administer an intravenous dye.
How to check for bladder cancer?
You have an ultrasound scan to check: 1 for any signs of cancer in your bladder 2 how big it is and whether it has spread 3 for blockages in the tubes that move urine between your kidneys and bladder (the ureters)

What is the ultrasound of the bladder?
You have an ultrasound scan to check: for any signs of cancer in your bladder. how big it is and whether it has spread. for blockages in the tubes that move urine between your kidneys and bladder (the ureters) Colour ultrasound (called Doppler ultrasound) can also show the blood flow into your kidneys and the urine flow into your bladder.
How to contact Cancer Research UK?
For support and information, you can call the Cancer Research UK nurses on freephone 0808 800 4040. The lines are open from 9am to 5pm, Monday to Friday.
How does an ultrasound scanner work?
The ultrasound scanner has a microphone that gives off sound waves. The sound waves bounce off the organs inside your body, and the microphone picks them up. The microphone links to a computer that turns the sound waves into a picture on the screen. Ultrasound scans are completely painless. You usually have the scan in the hospital x-ray department …

How long does an ultrasound scan take?
A sonographer is a trained professional who is specialised in ultrasound scanning. The scan usually takes about 10 to 15 minutes, but it can take longer.
Why do sonographers use gel?
The gel helps the sonographer get clear pictures on the screen. You might feel a little pressure when the sonographer moves the probe over your abdomen. Tell them if it is uncomfortable. The sonographer might ask you to change position a few times or hold your breath so they can get clear pictures.
Can you get results from a CT scan?
You won’t get any results at the time of the scan. Waiting for test results can make you anxious. Ask your doctor or nurse how long it will take to get them. Contact them if you haven’t heard anything after a couple of weeks. You might have the contact details for a specialist nurse.
Imaging Techniques To Detect Bladder Cancer
Imaging techniques, which include ultrasound, computed tomography (or CT) scanning, magnetic resonance imaging (or MRI) and x-ray approaches, provide an important means of assessing the urinary tract, including the kidneys, and play an important role in the detection, diagnosis, and monitoring of bladder cancer.
Detecting bladder cancer with ultrasound
An ultrasound (which may also be referred to as a sonogram) uses high frequency sound waves to produce images of internal organs. Echoes, which are created as sound waves bounce off organs and tissues, produce computer images that provide information on the structure and movement of organs and the blood flow through vessels.
How do ultrasounds help detect and monitor bladder cancer?
An ultrasound of the urinary tract can help assess the size of a bladder tumour and whether a bladder cancer has spread. Ultrasound is able to differentiate between fluid-filled cysts and solid tumours, however, it cannot determine if a tumour is cancerous. Ultrasound can also be used to guide a biopsy needle to sample a suspected cancer.

Detecting bladder cancer with CT scans
A CT scan uses x-rays to obtain cross-sectional images of the body. Compared to a general x-ray test, which directs a broad x-ray beam from a single angle, the CT scan uses a number of thin beams to produce a series of images from different angles.
Other imaging approaches to detect or monitor bladder cancer
An MRI scan uses radio waves and magnets to produce more detailed pictures of soft tissues. MRI scans can show whether bladder cancer has spread to other tissues or to the lymph nodes. To improve the quality of the images it’s sometimes necessary to administer an intravenous dye.
Can pelvic ultrasound detect bladder cancer?
Bladder Cancer. A pelvic ultrasound can often detect bladder cancer, even when they are being done for other reasons because the bladder needs to be full to create clear pictures of all the organs and structures in the pelvis, which in turn creates a clear picture of the bladder.

Can ultrasound detect cancer?
It can detect abnormal tissues, growths, and cysts and give a suspicion of cancer based on how those images look. While it can‘t diagnose cancer, it can detect the abnormal tissues that may possibly be cancerous. Some different types of cancers …
Why is ultrasound important for breast cancer?
Ultrasound is very useful in both the detection of breast cancer and diagnosis because the doctor can do a “fine needle guided biopsy” to aspirate some of the tissue. This is then sent to the lab to look for the actual cancer cells.
What type of cancer is detected by ultrasound?
Ultrasound can be used to detect abnormal cysts and whether they are hard or fluid filled. 3. Pancreatic Cancer. Pancreatic cancer is one of the fastest growing cancers with only an 8% survival rate after five years. Early detection is critical with this type of cancer.

What is the fastest growing cancer?
Pancreatic Cancer. Pancreatic cancer is one of the fastest growing cancers with only an 8% survival rate after five years. Early detection is critical with this type of cancer. In cases of pancreatitis and severe upper abdominal pain, an ultrasound can detect the presence of cysts or pseudocysts on the pancreas.
What is the best way to check for liver cancer?
Liver cancer is usually a cancer from other places in the body that has spread to the liver, although there is a small chance of primary liver cancer. An ultrasound can check for cysts on the liver and help differentiate cysts from fatty liver disease or cirrhosis. An ultrasound on the liver can also help guide a needle in liver …
Can thyroid nodules turn into cancer?
There are autoimmune conditions that can cause thyroid nodules that never turn into cancer. When these occur, doctors often choose to watch them closely for changes that could turn into thyroid cancer in some cases. Ultrasound is used to check the nodules to see if they are hard nodules or fluid filled nodules.

How does ultrasound help with bladder cancer?
Ultrasound uses sound waves to create pictures of internal organs. It can be useful in determining the size of a bladder cancer and whether it has spread beyond the bladder to nearby organs or tissues. It can also be used to look at the kidneys. This is usually an easy test to have, and it uses no radiation.
What is the biopsy for bladder cancer?
A biopsy is when tiny pieces (called samples) of the abnormal-looking tissue are taken out and tested for cancer cells. If bladder cancer is suspected, a biopsy is needed to be sure of the diagnosis.
Why is bladder cancer found?
Bladder cancer is often found because of signs or symptoms a person is having. Or it might be found because of lab tests a person gets for another reason. If bladder cancer is suspected, exams and tests will be needed to confirm the diagnosis. If cancer is found, more tests will be done to help find out the extent ( stage) of the cancer.

Can a urine culture show cancer?
If you’re having urinary symptoms, this test may be done to see if an infection (rather than cancer) is the cause. Urinary tract infections and bladder cancers can cause the same symptoms. For a urine culture, a sample of urine is put into a dish in the lab to allow any bacteria that are present to grow. It can take time for the bacteria to grow, so it may take a few days to get the results of this test.
What type of tube is used for bladder cancer?
If bladder cancer is suspected, most doctors will recommend a cystoscopy. . A urologist uses a cystoscope, which is a long, thin, flexible tube with a light and a lens or a small video camera on the end. For details on how this procedure is done, see Cystoscopy.
Is bladder cancer invasive or noninvasive?
This is very important in deciding treatment. If the cancer stays in the inner layer of cells without growing into the deeper layers, it’s called non-invasive. If the cancer grows into the deeper layers of the bladder, it’s called invasive. Invasive cancers are more likely to spread and are harder to treat.

What is high grade cancer?
These cancers may also be called poorly differentiated or undifferentiated. High-grade cancers are more likely to grow into the bladder wall and spread outside the bladder.
How do you know if you have bladder cancer?
Bladder cancers that have grown large or have spread to other parts of the body can sometimes cause other symptoms, such as: Being unable to urinate. Lower back pain on one side. Loss of appetite and weight loss. Feeling tired or weak.
What are the symptoms of bladder cancer?
Being unable to urinate. Lower back pain on one side. Loss of appetite and weight loss. Feeling tired or weak. Swelling in the feet. Bone pain. Again, many of these symptoms are more likely to be caused by something other than bladder cancer, but it’s important to have them checked.

Can bladder cancer cause bleeding?
Usually, the early stages of bladder cancer (when it’s small and only in the bladder) cause bleeding but little or no pain or other symptoms. Blood in the urine doesn’t always mean you have bladder cancer.
Can bladder cancer spread to other parts of the body?
Bladder cancers that have grown large or have spread to other parts of the body can sometimes cause other symptoms, such as: Again, many of these symptoms are more likely to be caused by something other than bladder cancer, but it’s important to have them checked.
Can bladder cancer cause lower back pain?
Bladder cancers that have grown large or have spread to other parts of the body can sometimes cause other symptoms, such as: Being unable to urinate. Lower back pain on one side. Loss of appetite and weight loss. Feeling tired or weak.

What does it mean when you have blood in your urine?
Blood in the urine. In most cases, blood in the urine (called hematuria) is the first sign of bladder cancer. There may be enough blood to change the color of the urine to orange, pink, or, less often, dark red.
Is urine a normal color?
Sometimes, the color of the urine is normal but small amounts of blood are found when a urine test (urinalysis) is done because of other symptoms or as part of a general medical check-up. Blood may be present one day and absent the next, with the urine remaining clear for weeks or even months.