Contents

See more
Depending on the stage of the cancer and other factors, treatment options for people with bladder cancer can include: Bladder Cancer Surgery Intravesical Therapy for Bladder Cancer Chemotherapy for Bladder Cancer Radiation Therapy for Bladder Cancer Immunotherapy for Bladder Cancer Targeted Therapy Drugs for Bladder Cancer
Is bladder cancer curable?
Follow-up and outlook after treatment The outlook for people with stage 0a (non-invasive papillary) bladder cancer is very good. These cancers can be cured with treatment. During long-term follow-up care, more superficial cancers are often found in the bladder or in other parts of the urinary system.
How is bladder cancer usually treated?
Bladder cancer treatment may include: Surgery, to remove the cancer cells. Chemotherapy in the bladder (intravesical chemotherapy), to treat cancers that are confined to the lining of the bladder but have a high risk of recurrence or progression to a higher stage.
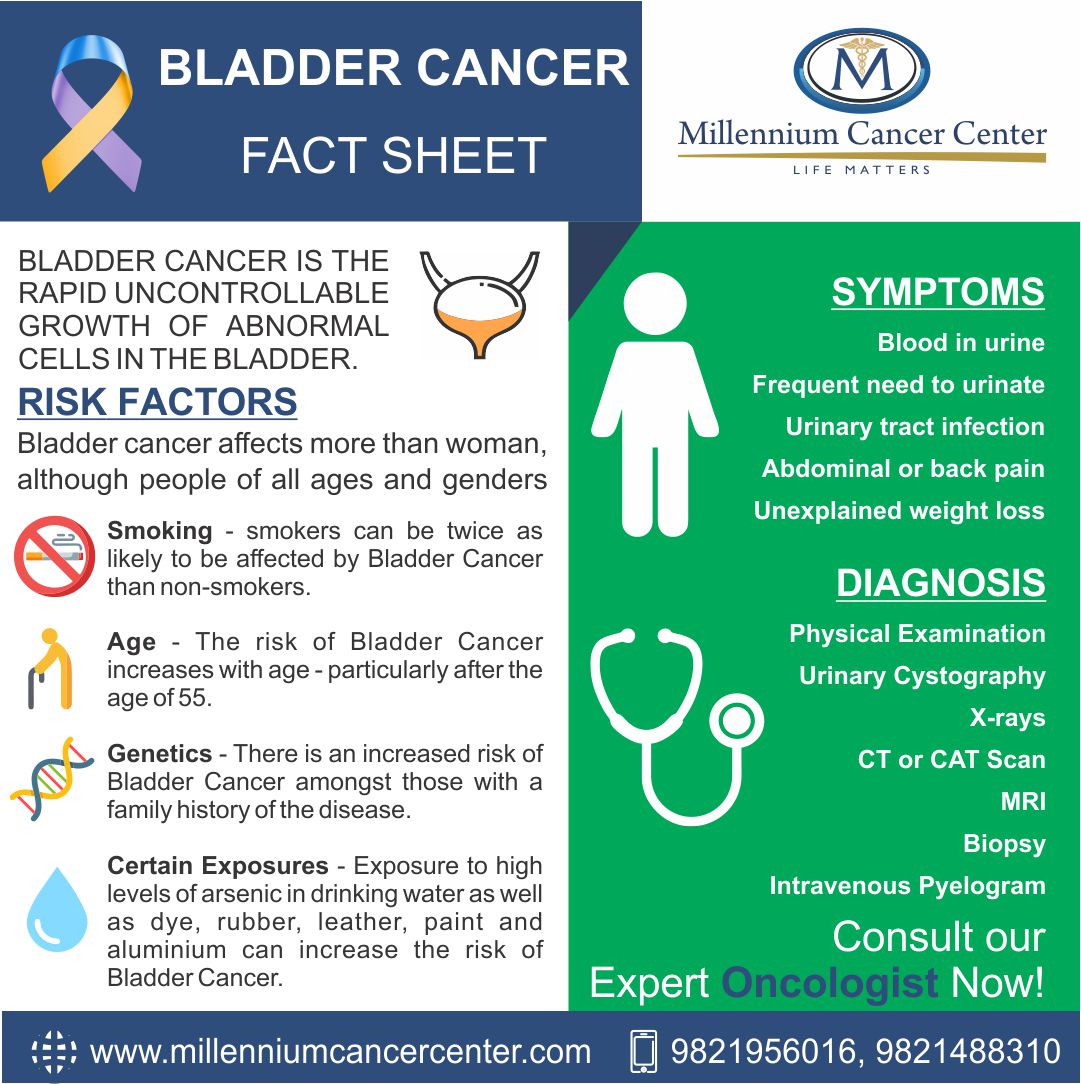
Does bladder cancer spread quickly?
They tend to grow and spread slowly. High-grade bladder cancers look less like normal bladder cells. These cancers are more likely to grow and spread.
What percentage of bladder cancer is curable?
5-year relative survival rates for bladder cancerSEER Stage5-year Relative Survival RateIn situ alone Localized96% 70%Regional38%Distant6%All SEER stages combined77%Mar 1, 2022
What are the symptoms of stage 1 bladder cancer?
Bladder cancer sometimes causes changes in bladder habits like having to urinate more often or feeling an urgent need to urinate without producing urine. Another symptom of bladder cancer is pain or burning during urination without evidence of a urinary tract infection.
Can bladder cancer be cured without surgery?
Many people with bladder cancer need surgery. But in some cases, it can’t remove all of the disease. So you’ll need other treatments along with, or instead of, an operation. These could include chemotherapy, radiation, and immunotherapy.
What are the warning signs of bladder cancer?
Bladder Cancer: Symptoms and SignsBlood or blood clots in the urine.Pain or burning sensation during urination.Frequent urination.Feeling the need to urinate many times throughout the night.Feeling the need to urinate, but not being able to pass urine.Lower back pain on 1 side of the body.
Where is the first place bladder cancer spreads?
When bladder cancer spreads, it first invades the bladder wall, which is made up of four distinct layers. It can take some time for cancer to penetrate all of these layers, but once it has, it can then spread into the surrounding fatty tissues and lymph nodes.
How long can you live after bladder cancer?
Survival for all stages of bladder cancer almost 55 out of every 100 (almost 55%) survive their cancer for 5 years or more after they are diagnosed. around 45 out of every 100 (around 45%) survive their cancer for 10 years or more after diagnosis.
Can you live 10 years with bladder cancer?
Bladder cancer survival rates by stage According to the American Cancer Society , the relative survival rates for all stages of bladder cancer are: 5 years: 77 percent. 10 years: 70 percent. 15 years: 65 percent.
What are the odds of beating bladder cancer?
This form of cancer resulted in about 17,980 deaths in the same year. While bladder cancer is relatively common, the average five-year survival rate is quite high at 76.9%. This rate has improved over the past several years, and a person’s chance of survival is influenced by many factors.
What is the main cause of bladder cancer?
Smoking. Smoking is the single biggest risk factor for bladder cancer. This is because tobacco contains cancer-causing (carcinogenic) chemicals. If you smoke for many years, these chemicals pass into your bloodstream and are filtered by the kidneys into your urine.
Which Treatments Are Used For Bladder Cancer?
Depending on the stage of the cancer and other factors, treatment options for people with bladder cancer can include: 1. Surgery 2. Intravesical th…
Which Doctors Treat Bladder Cancer?
Depending on your options, you can have different types of doctors on your treatment team. The types of doctors who treat bladder cancers include:…
Making Treatment Decisions
It’s important to discuss all of your treatment options, including their goals and possible side effects, with your doctors to help make the decisi…
Help Getting Through Treatment
Your cancer care team will be your first source of information and support, but there are other resources for help when you need it. Hospital- or c…
Treating Stage 0 Bladder Cancer
Stage 0 bladder cancer includes non-invasive papillary carcinoma (Ta) and flat non-invasive carcinoma (Tis). In either case, the cancer has not inv…
Treating Stage I Bladder Cancer
Stage I bladder cancers have grown into the connective tissue layer of the bladder wall but have not reached the muscle layer.Transurethral resecti…
Treating Stage II Bladder Cancer
These cancers have invaded the muscle layer of the bladder wall. Transurethral resection (TURBT) is typically the first treatment for these cancers…
Treating Stage III Bladder Cancer
These cancers have reached the outside of the bladder and might have grown into nearby tissues or organs.Transurethral resection (TURBT) is typical…
Treating Stage IV Bladder Cancer
These cancers have reached the abdominal or pelvic wall (T4b tumors) or have spread to nearby lymph nodes or distant parts of the body. Stage IV ca…
Treating Bladder Cancer That Progresses Or Recurs
If cancer continues to grow during treatment (progresses) or comes back (recurs), your treatment options will depend on where and how much the canc…

What is the first treatment for bladder cancer?
Chemo (with or without radiation) is typically the first treatment when bladder cancer has spread to distant parts of the body (M1). After this treatment the cancer is rechecked. If it looks like it’s gone, a boost of radiation to the bladder may be given or cystectomy might be done.
What is stage 0 bladder cancer?
Stage 0 bladder cancer includes non-invasive papillary carcinoma (Ta) and flat non-invasive carcinoma (Tis or carcinoma in situ). In either case, the cancer is only in the inner lining layer of the bladder. It has not invaded (spread deeper into) the bladder wall.
What is the treatment for T3 tumors?
An option for some patients with single, small tumors (some T3) might be treatment with a second (and more extensive) transurethral resection (TURBT) followed by a combination of chemo and radiation. If cancer is still found when cystoscopy is repeated, cystectomy might be needed.
What to do if you have cancer that hasn’t been removed?
(Less often, close follow-up alone might be an option.) If all of the cancer wasn’t removed, options are intravesical BCG or cystectomy (removal of part or all of the bladder).
How to get rid of stage IV cancer?
The tumor is then rechecked. If it appears to be gone, chemo with or without radiation or cystectomy are options.
How long after TA surgery can you get chemo?
For low-grade (slow-growing) non-invasive papillary (Ta) tumors, weekly intravesical chemotherapy may be started a few weeks after surgery. If the cancer comes back, the treatments can be repeated. Sometimes intravesical chemo is repeated over the next year to try to keep the cancer from coming back.
What is the treatment for cancer that recurs in distant parts of the body?
Cancers that recur in distant parts of the body can be harder to remove with surgery, so other treatments, such as chemotherapy, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, or radiation therapy , might be needed. For more on dealing with a recurrence, see Understanding Recurrence.
How to diagnose bladder cancer?
Tests and procedures used to diagnose bladder cancer may include: Using a scope to examine the inside of your bladder (cystoscopy). To perform cystoscopy, your doctor inserts a small , narrow tube (cystoscope) through your urethra. The cystoscope has a lens that allows your doctor to see the inside of your urethra and bladder, …
How does radiation therapy help bladder cancer?
Radiation therapy. Radiation therapy uses beams of powerful energy, such as X-rays and protons, to destroy the cancer cells. Radiation therapy for bladder cancer usually is delivered from a machine that moves around your body, directing the energy beams to precise points.
What is a cystoscope?
Cystoscopy allows your doctor to view your lower urinary tract to look for abnormalities, such as a bladder stone. Surgical tools can be passed through the cystoscope to treat certain urinary tract conditions.
How to get a follow up on bladder cancer?
Get a schedule of follow-up tests and go to each appointment. When you finish bladder cancer treatment, ask your doctor to create a personalized schedule of follow- up tests. Before each follow-up cystoscopy exam, expect to have some anxiety. You may fear that cancer has come back or worry about the uncomfortable exam.
What tests can be done to determine if you have bladder cancer?
Tests may include: CT scan.
How is bladder cancer classified?
Bladder cancers are further classified based on how the cancer cells appear when viewed through a microscope. This is known as the grade, and your doctor may describe bladder cancer as either low grade or high grade:
What is a CT urogram?
During a CT urogram, a contrast dye injected into a vein in your hand eventually flows into your kidneys, ureters and bladder.
What is the best test to find out if you have bladder cancer?
Ultrasound: This test uses sound waves to make pictures of the organs inside your body, like your bladder and kidneys. It can help show the size of a bladder cancer and if it has spread. Bone scan: A bone scan can help show if bladder cancer has spread to the bones. This test is not done unless you have bone pain.
What tests are done to check for bladder cancer?
This might include a rectal exam, during which a gloved finger is put into your rectum. If you are a woman, a pelvic exam might also be done.
How do you know if you have bladder cancer?
Signs of bladder cancer are problems peeing, pain when peeing, needing to go more often than normal, and seeing blood in your urine
Why do you need a cystoscope?
More than one sample may be taken because sometimes cancer starts in more than one part of the bladder. Salt water washings of the inside of your bladder may also be collected to look for cancer cells.
What is it called when cancer cells spread to other parts of the body?
For instance, cancer cells in the bladder can travel to the bone and grow there. When cancer cells spread, it’s called metastasis . Cancer is always named for the place where it starts.
Where is the bladder located?
The bladder is a hollow organ that stores urine before it leaves your body. It sits in the lowest part of your belly, called your pelvis. Urine is made in your kidneys. Tubes called ureters connect your kidneys to the bladder. Urine flows through the ureters and into your bladder, where it’s stored. When you urinate (pee), the bladder squeezes the urine out through a tube called the urethra.
Can a test show if bladder cancer is growing?
Tests can show how deeply the cancer has grown into the bladder wall.
How long does bladder cancer last?
A particular stage of bladder cancer, for example, may have a 90% five-year relative survival rate. The 90% figure comes from dividing the percentage of people with cancer who are alive after five years by the percentage of people without the disease who are also alive after five years.
What is the survival rate for bladder cancer?
The five-year relative survival rates for all bladder cancer stages is 77%. Breaking the five-year survival rates down by stage gives you a more detailed picture and illustrates why tracking stage is useful. Between 2008 and 2014, the five-year relative survival rates were:
What is a CXbladder test?
Cxbladder is a clinically proven cutting-edge genomic urine test that quickly and accurately detects or rules out bladder cancer in patients presenting with blood in the urine (or hematuria) and those being monitored for recurrence. The test works at a molecular level, measuring five biomarker genes to detect the presence or absence of bladder cancer.
How long does it take for a CXbladder test to show results?
Cxbladder is discreet, quick, non-invasive and painless, typically giving you meaningful results within five working days.
How many cases of bladder cancer are there in 2019?
Is Bladder Cancer Curable? Every year, there are around 81,400 new cases of bladder cancer, of which nearly 18,000 are fatal. In 2019, around 4.6% of all new cancer cases were bladder cancer. Bladder cancer is the fourth most common cancer among men, and ninth overall.
How can bladder cancer be classified?
Bladder cancer tumors can be classified further based on the way cancer cells look when viewed through a microscope, given this then dictates how they behave. The appearance of the cells contributes to “tumor grade” classification.
Which tumor has a higher chance of spreading to the bladder’s muscular wall and other organs and tissues?
High-grade tumors grow more aggressively than low-grade tumors and have a higher chance of spreading to the bladder’s muscular wall and other organs and tissues. Low-grade bladder tumor: A type of tumor with cells closer in organization and appearance to healthy cells.
What are some ways to make your bladder worse?
You’ll want to stay away from things that can make bladder problems worse. These include caffeine, drinks with alcohol, spicy foods, and tobacco products. Prevent urinary tract infections. Your doctor or nurse will talk with you about ways to lower your chances of getting a urinary tract infection.
How long does it take for a bladder to irritate after radiation?
Radiation therapy to the pelvis (including reproductive organs, the bladder, colon and rectum) can irritate the bladder and urinary tract. These problems often start several weeks after radiation therapy begins and go away several weeks after treatment has been completed. Some types of chemotherapy and immunotherapy can also affect …
What does radiation cystitis mean?
Irritation of the bladder lining ( radiation cystitis ): pain or a burning feeling when you urinate. blood in your urine ( hematuria) trouble starting to urinate. trouble emptying your bladder completely ( urinary retention) feeling that you need to urinate urgently or frequently. leaking a little urine when you sneeze or cough.
What to wear for genital catheterization?
These may include going to the bathroom often, wearing cotton underwear and loose fitting pants, learning about safe and sanitary practices for catheterization, taking showers instead of baths, and checking with your nurse before using products such as creams or lotions near your genital area.
Is it normal for a chemo patient to have a change in their urine?
Talk with your doctor or nurse to learn what symptoms you may experience and ask which ones to call about. Some urinary or bladder changes may be normal, such as changes to the color or smell of your urine caused by some types of chemotherapy.
Do bladder problems go away after treatment?
So talk with them. There may be medicines or exercises to help with some of these problems. And the good news is that most bladder problems go away after treatment.
Can chemo damage the bladder?
Some types of chemotherapy and immunotherapy can also affect or damage cells in the bladder and kidneys. Surgery to remove the prostate ( prostatectomy ), bladder cancer surgery, and surgery to remove a woman’s uterus, the tissue on the sides of the uterus, the cervix, and the top part of the vagina …
What are the best drugs for bladder cancer?
These drugs can be used in different situations to treat bladder cancer: 1 Any of these checkpoint inhibitors can be used in people with advanced bladder cancer that starts growing again after chemotherapy. 2 Atezolizumab and pembrolizumab can be used in people who can’t get the chemo drug cisplatin (due to things like hearing loss, kidney failure, or heart failure). 3 Avelumab can be used as an additional (maintenance) treatment in people with advanced bladder cancer that did not get worse during their initial chemotherapy treatments. 4 Pembrolizumab can be used to treat certain bladder cancers that are not growing into the muscle wall of the bladder, are not getting smaller with intravesical BCG, and are not being treated with a cystectomy.
What antibody is used to attach to a bladder cancer cell?
In the case of this ADC, the monoclonal antibody part attaches to the Trop-2 protein on bladder cancer cells and brings the chemo directly to them. (Some bladder cancer cells have too much Trop-2, which helps them grow and spread.)
Can BCG be put in the bladder?
BCG can be put right into the bladder as a liquid. This activates immune system cells in the bladder, which then attack bladder cancer cells. For more details on this treatment, see Intravesical Therapy for Bladder Cancer.
Can PD-1 block bladder cancer?
Blocking PD-1 can allow the immune system to attack the cancer cells, which can shrink some tumors or slow their growth. These drugs can be used in different situations to treat bladder cancer: Any of these checkpoint inhibitors can be used in people with advanced bladder cancer that starts growing again after chemotherapy.
Does chemo kill bladder cancer?
The chemo enters the cancer cells and kills them. This drug may be used to treat people with advanced bladder cancer who have already been treated with a platinum chemo drug (such as cisplatin) and immunotherapy (specifically, a PD-1 or PD-L1 inhibitor). Enfortumab vedotin is infused into a vein (IV), once a week for 3 weeks with one week off.
What is the treatment for high grade bladder cancer?
High-grade bladder cancer: High-grade cancers that are life-threatening and spread quickly need to be treated with chemotherapy, radiation or surgery.
What is the procedure to remove bladder cancer?
Tumors in the bladder muscle: In case of bladder cancer that has invaded the muscle wall but hasn’t spread to the lymph nodes, the physician recommends radical cystectomy. In this procedure, the physician removes the bladder, nearby lymph nodes and other nearby organs.
What is the first line of treatment for metastatic bladder cancer?
Then, the physician may perform a radical cystectomy to remove cancer that has invaded beyond the bladder wall. Metastatic bladder cancer: Platinum-based chemotherapy is the first line of treatment for this type of bladder cancer.
What is gallbladder cancer?
Gallbladder cancer (GBC) is one of the aggressive cancers of the biliary tract. The gallbladder generates and concentrates bile that aids in the digestion of fats. GBC is a rare, yet deadly cancer of the gastrointestinal tract.
How long do people with bladder cancer live?
Overall, 70 to 90 percent of people with localized bladder cancer will live for at least five years or more . The physician calculates this with the help of survival rates. Survival rates indicate the percentage of people who live with a certain type of cancer for a specific time. The physician often uses an overall five-year survival rate.
Where does bladder cancer start?
Bladder cancer is a tumor (uncontrolled growth of cells) that starts in your urinary bladder. The urinary bladder is a balloon-like organ present in the lower abdomen near the pelvis. Its function is to store urine coming from the kidneys through the ureters (pipe-like passageways for urine) until it is expelled from the body through the tube-like passage called the urethra.
What is SEER in cancer?
The surveillance, epidemiology, and end results (SEER) stages are taken from the SEER database, maintained by the National Cancer Institute. SEER database groups cancers into localized, regional, and distant stages.
What is the diet associated with bladder cancer?
The Western dietary pattern is rich in highly processed foods and low in fruits and vegetables.
How many bladder cancer cases are non-muscle invasive?
Roughly 75 percent of bladder cancer cases are non-muscle invasive. About 60 to 70 percent of cases of this type of cancer will recur. Regular follow-up appointments with your care team are important to monitor your health. There’s no one way of eating that’s proven to reduce the risk of recurrence.
What are some good foods to eat when you have cancer?
Adding a source of protein to meals and snacks can help you meet your daily needs. Whole eggs, fish, nuts, seeds, and Greek yogurt are just a few examples of healthy protein sources.
Does eating fruits and vegetables help with bladder cancer?
Some studies link eating lots of fruits and vegetables to a lower risk of bladder cancer. However, a 2018 review suggested vegetable intake does not play a role in preventing recurrence. A diet high in fruits and vegetables is still recommended for other reasons.
Does bladder cancer reduce vitamin D?
Cancer treatments may reduce other nutrients in the body, including vitamin D and folate. Talk to your healthcare provider if you have questions about nutrient depletions caused by cancer treatments. Summary. Many supplements, including probiotics, may be appropriate for people with bladder cancer.
Can probiotics help with bladder cancer?
Talk to your healthcare team if you have questions about whether any supplements could help you. Certain types of probiotic strains may not be safe for some people with bladder cancer, so it’s important to speak with your doctor before using pro biotics.
Can probiotics help with diarrhea?
Probiotics can increase good bacteria in your digestive system. This may help reduce bloating, gas, and diarrhea. There is also limited evidence that probiotics could play a role in reducing bladder cancer recurrence.
Diagnosis
Treatment
-
Treatment options for bladder cancer depend on a number of factors, including the type of cancer, grade of the cancer and stage of the cancer, which are taken into consideration along with your overall health and your treatment preferences. Bladder cancer treatment may include: 1. Surgery,to remove the cancer cells 2. Chemotherapy in the bladder (i…
Clinical Trials
-
Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Coping and Support
-
Living with the concern that your bladder cancer may recur can leave you feeling as if you have little control over your future. But while there’s no way to ensure that your bladder cancer won’t recur, you can take steps to manage the stress. Over time you’ll find what works for you, but until then, you might: 1. Get a schedule of follow-up tests and go to each appointment.When you finis…
Preparing For Your Appointment
-
Start by seeing your family doctor if you have any signs or symptoms that worry you, such as blood in your urine. Your doctor may suggest tests and procedures to investigate your signs and symptoms. If your doctor suspects that you may have bladder cancer, you may be referred to a doctor who specializes in treating diseases and conditions of the urinary tract (urologist). In so…