Contents
Can a CT urogram detect bladder cancer?
If an abdominal CT scan shows a normal bladder, don’t celebrate yet. But if it comes back indicating cancer, don’t panic yet, either. About 80,000 people in the U.S. are diagnosed with bladder cancer every year. The five year survival rate, on average, is about 76.8 percent. This not-so-good survival rate is a function of the disease being caught at a later stage than it is of just …
Can an abdomen CAT scan diagnose bladder cancer?
· Can a CT scan miss bladder cancer? CT scans can provide important information about the urinary tract and bladder tumors. However, while some bladder tumors may be seen on a CT scan, others may not be apparent, such as smaller or flatter tumors. What to expect when having a CT scan. A CT scan is a painless procedure that is typically performed on an …
Does cancer always show up in a CT scan?
· Mostly, a doctor uses this to trace the tumors in the urinary tract that engulfs the bladder. Moving on, the patient may expect a three-dimensional image through CT Scan. So, a doctor’s usage of a CT Scan to detect bladder cancer may show certain things. This may include the following: The formation of stones in the urinary tract can be seen.
Can a CT scan determine a problem with the gallbladder?
A CT scan is a test that uses x-rays and a computer to create detailed pictures of the inside of your body. It takes pictures from different angles. The computer puts them together to make a 3 dimensional (3D) image. CT (or CAT) stands for computed (axial) tomography. You usually have a CT scan in the x-ray (radiology) department as an outpatient .
How accurate is CT scan for bladder cancer?
Computed tomography (CT) Multidetector (64-slice) CT scanning has provided the mainstay in radiological assessment. It has a reported sensitivity of 85% and specificity of 94% for the diagnosis of bladder cancers [11]. Detection is dependent on the morphology and size of the tumor.
What scans are used to detect bladder cancer?
Cystoscopy. Cystoscopy is the key diagnostic procedure for bladder cancer. It allows the doctor to see inside the body with a thin, lighted, flexible tube called a cystoscope.
How do you rule out bladder cancer?
Tests for bladder cancer look for different substances and/or cancer cells in the urine. Urinalysis: One way to test for bladder cancer is to check for blood in the urine ( hematuria). This can be done during a urinalysis, which is a simple test to check for blood and other substances in a sample of urine.
How would I know if I had bladder cancer?
Having to urinate more often than usual. Pain or burning during urination. Feeling as if you need to go right away, even when your bladder isn’t full. Having trouble urinating or having a weak urine stream.
Do you feel bloated with bladder cancer?
Abdominal Pain The types of pains can vary and include: Generalized pain — felt in more than half of the stomach area. Cramp-like pain — less serious and most likely due to bloating and gas.
Can you have bladder cancer without blood in urine?
Among women with hematuria the rate of cancer was 1.7%, compared with 0.45% among those without hematuria. Among the 10 bladder cancer cases, six had no hematuria.
Can bladder cancer symptoms come and go?
Symptoms often come and go, and are often not severe. The most common symptoms include the following: Hematuria (blood in the urine) — The most common sign of bladder cancer is blood in the urine (hematuria).
Does bladder cancer feel like a UTI?
Bladder cancer can be mistaken for a Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) because many of the symptoms overlap. Patients may experience increased frequency and urgency of urination, pain with urination, or urinary incontinence.
Where does bladder cancer begin?
Most bladder cancers start in the innermost lining of the bladder, which is called the urothelium or transitional epithelium. As the cancer grows into or through the other layers in the bladder wall, it has a higher stage, becomes more advanced, and can be harder to treat.
Which of the following is the most common symptom of cancer of the bladder?
Blood in your urine is the most common symptom of bladder cancer. The medical name for blood in your urine is haematuria and it’s usually painless. You may notice streaks of blood in your urine or the blood may turn your urine brown. The blood isn’t always noticeable and it may come and go.
Do you feel ill with bladder cancer?
Nausea and vomiting. Burning or pain when you urinate, feeling the need to go often, or blood in urine. Diarrhea. Feeling tired.
How does an MRI show bladder cancer?
An MRI scan uses radio waves and magnets to produce more detailed pictures of soft tissues. MRI scans can show whether bladder cancer has spread to other tissues or to the lymph nodes. To improve the quality of the images it’s sometimes necessary to administer an intravenous dye.
Why do we need imaging for bladder cancer?
The use of a specific imaging procedure linked to bladder cancer is dependent on a number of factors including other irregular test results, local access and availability, pre-existing medical conditions , the characteristics of a suspected tumor or unusual growth (e.g. size, location), and possible side effects of the procedure.
What is a CT scan of the kidneys, ureters and bladder called?
A CT scan of the kidneys, ureters and bladder is referred to as a CT urogram.
What is the procedure for a bladder ultrasound?
During a bladder ultrasound, the individual is often lying down while the probe is passed over the skin’s surface. A lubricating gel is administered to the skin which helps the sound waves conduct.
What is ultrasound imaging?
An ultrasound (which may also be referred to as a sonogram) uses high frequency sound waves to produce images of internal organs. Echoes, which are created as sound waves bounce off organs and tissues, produce computer images that provide information on the structure and movement of organs and the blood flow through vessels. An ultrasound does not use radiation or contrast dyes.
How long does it take to get an ultrasound?
Ultrasounds are typically outpatient procedures and usually take 20–30 minutes to complete.
Can ultrasound help with bladder cancer?
An ultrasound of the urinary tract can help assess the size of a bladder tumor and whether a bladder cancer has spread. Ultrasound is able to differentiate between fluid-filled cysts and solid tumors, however, it cannot determine if a tumor is cancerous. Ultrasound can also be used to guide a biopsy needle to sample a suspected cancer.
What tests are used to check for bladder cancer?
These include the tests called NMP22 ® (or BladderChek ® ), BTA Stat ®, Immunocyt ® , and UroVysion ®, which are discussed in Can Bladder Cancer Be Found Early?
What is the best way to diagnose bladder cancer?
Cystoscopy. If bladder cancer is suspected, most doctors will recommend a cystoscopy. . A urologist uses a cystoscope, which is a long, thin, flexible tube with a light and a lens or a small video camera on the end. For details on how this procedure is done, see Cystoscopy.
What is the blue light in a cystoscopy?
Fluorescence cystoscopy (also known as blue light cystoscopy) may be done along with routine cystoscopy. For this exam, a light-activated drug is put into the bladder during cystoscopy. It’s taken up by cancer cells. When the doctor then shines a blue light through the cystoscope, any cells containing the drug will glow (fluoresce). This can help the doctor see abnormal areas that might have been missed by the white light normally used.
What is the biopsy for bladder cancer?
A biopsy is when tiny pieces (called samples) of the abnormal-looking tissue are taken out and tested for cancer cells. If bladder cancer is suspected, a biopsy is needed to be sure of the diagnosis.
What is a physical exam for bladder cancer?
A physical exam can provide information about possible signs of bladder cancer and other health problems. The doctor might do a digital rectal exam (DRE), during which a gloved, lubricated finger is put into your rectum. If you are a woman, the doctor might do a pelvic exam as well.
How long does it take for a urine culture to show up?
It can take time for the bacteria to grow, so it may take a few days to get the results of this test.
How does ultrasound help with bladder cancer?
Ultrasound uses sound waves to create pictures of internal organs. It can be useful in determining the size of a bladder cancer and whether it has spread beyond the bladder to nearby organs or tissues. It can also be used to look at the kidneys. This is usually an easy test to have, and it uses no radiation.
What is the CT scan used for?
CTU provides imaging of urinary system (the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra) and is especially useful for urinary system pathologies. The second mode of CT scan is the conventional CT; this provides examinations of upper-lower abdomen and pelvis. CT is commonly used and is recommended method for staging BCa (Figure 2) [5, 17, 21, 25, 26].
What is the best way to detect BCa?
White light cystoscopy (WLC), a widely available technique, that allows visualization of the mucosa within the bladder, is considered a gold standard method for detecting BCa [8]. There are two forms of WLC, rigid and flexible cystoscopy (FC). Rigid cystoscopy provides better image quality, enables working with a large lumen, and provides improved flow. FC on the other hand allows alternative patient positioning, easy passage, and enables examination of all parts of the bladder [8]. Therefore, FC is usually applied for initial assessment of patients. However, FC may miss up to 10% of papillary tumors. Furthermore its small working channel lumen does not allow resection of BCa [9]. Although technology has improved the WLC image quality significantly, WLC cannot reliably determine flat and carcinoma in situ (CIS) lesions, and cannot distinguish benign lesions from malignant masses. Such a distingtion is particularly important when Transurethral Resection of Bladder (TURB) is to be performed [9–11]. However, cystoscopy is recommended by national comprehensive cancer network (NCNN) and American urological association (AUA) guidelines for imaging patients with macroscopic hematuria [5, 12].
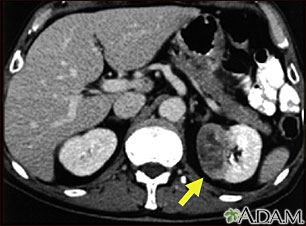
What is the irregular round filling defect in the right posterior aspect of the bladder?
The irregular round filling defect in the right posterior aspect of the bladder (arrow) represents a transitional cell carcinoma. There is thickening of the adjacent bladder wall, but not definite spread beyond the bladder.
Which is better, CTU or cystoscopy?
Diagnostic performance of CTU was compared with cystoscopy in 177 patients. CTU performed better with 96.3% sensitivity, 86.4% specificity, 92.8% diagnostic accuracy, 92.9% PPV, and 92.7% NPV. The arterial acquisition phase diagnosed the lesions with the highest accuracy, and demonstrated 93.4% of all lesions [31].
Is CT more effective than MRI?
CT is faster and more cost-effective than MRI, but it is associated with the risk of ionizing radiation, high interobserver variability, and can neither differentiate bladder wall muscle layers, nor can it reliably distinguish T1 from T2 disease. Furthermore, its specificity and sensitivity are low for extravesical extension of early stage BCa and small metastatic lesions of BCa.[17, 21, 25, 26, 32–34].
Can cystoscopy detect BCa?
For initial diagnosis of BCa, cystoscopy is generally performed. However, cystoscopy can not accurately detect carcinoma insitu (CIS) and can not distinguish benign masses from malignant lesions. CT is used in two modes, CT and computed tomographic urography (CTU), both for dignosis and staging of BCa. However, they cannot differentiate T1 and T2 BCa. MRI is performed to diagnose invasive BCa and can differentiate muscle invasive bladder carcinoma (MIBC) from non-muscle invasive bladder carcinoma (NMIBC). However, CT and MRI have low sensitivity for nodal staging. For nodal staging PET/CT is preferred. PET/MRI provides better differentiation of normal and pathologic structures as compared with PET/CT. Nonetheless none of the approaches can address all issues related for the management of BCa. Novel imaging methods that target specific biomarkers, image BCa early and accurately, and stage the disease are warranted.