Contents

What are the final stages of bladder cancer?
12 rows · The stage of bladder cancer is based on the results of physical exams, biopsies, and imaging …
What are the chances of surviving bladder cancer?
Treating stage 0 bladder cancer. Stage 0 bladder cancer includes non-invasive papillary carcinoma (Ta) and flat non-invasive carcinoma (Tis or carcinoma in situ). In either case, the cancer is only in the inner lining layer of the bladder. It …
What happens in end stages of bladder cancer?
There are two types of stages for bladder cancer — the clinical stage and the pathologic stage. The clinical stage is your doctor’s informed opinion of how far your cancer has spread. This is…
What is the prognosis for Stage 1 bladder cancer?
· Stage 0is (flat carcinoma in situ): Cancer grows flat against the bladder’s tissue lining, but it hasn’t spread to the bladder wall’s muscle or connective tissue and hasn’t spread outside the bladder. The TNM characteristics are Tis, N0, M0. Stage 1 Stage 1 bladder cancer doesn’t have substages.
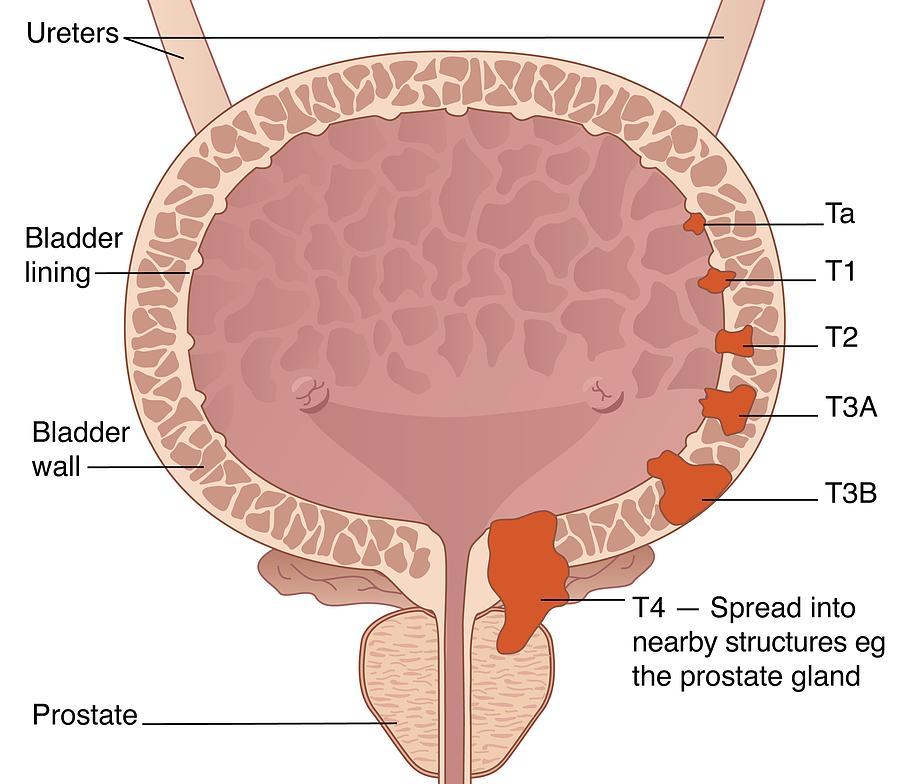
How do I know what stage my bladder cancer is?
The stage of bladder cancer is based on the results of physical exams, biopsies, and imaging tests (CT or MRI scan, x-rays, etc.), which are described in Tests for Bladder Cancer, as well as the results of surgery.
Does bladder cancer spread quickly?
They tend to grow and spread slowly. High-grade bladder cancers look less like normal bladder cells. These cancers are more likely to grow and spread.
Which stage of bladder cancer is curable?
The outlook for people with stage 0a (non-invasive papillary) bladder cancer is very good. These cancers can be cured with treatment. During long-term follow-up care, more superficial cancers are often found in the bladder or in other parts of the urinary system.
How long can you live with Stage 2 Bladder Cancer?
Stage 2. Around 45 out of 100 people (around 45%) survive their cancer for 5 years or more after diagnosis. Stage 2 means that the cancer has grown through the connective tissue layer into the muscle of the bladder wall.
Where is the first place bladder cancer spreads?
When bladder cancer spreads, it first invades the bladder wall, which is made up of four distinct layers. It can take some time for cancer to penetrate all of these layers, but once it has, it can then spread into the surrounding fatty tissues and lymph nodes.
How fast does bladder cancer progress?
As many as 50% of patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer may have occult metastases that become clinically apparent within 5 years of initial diagnosis and around 5% will have distant metastasis at the time of initial diagnosis. Most patients with overt metastatic disease die within 2 years despite chemotherapy.
Is bladder cancer usually fatal?
The general 5-year survival rate for people with bladder cancer is 77%. However, survival rates depend on many factors, including the type and stage of bladder cancer that is diagnosed. The 5-year survival rate of people with bladder cancer that has not spread beyond the inner layer of the bladder wall is 96%.
Can you beat bladder cancer?
Bladder cancer is highly treatable when it is diagnosed in the early stages. The main types of treatments for bladder cancer include: Surgery : Bladder cancer treatment almost always has a surgical component that may be combined with other non-invasive approaches, including those listed below.
How long can someone live with Stage 4 bladder cancer?
The 5-year survival rate is the rate of surviving for 5 years after a cancer diagnosis. For bladder cancer, if the cancer has spread to the regional lymph nodes, the 5-year survival rate is 36.3 percent . If it has spread to a more distant site, the 5-year survival rate is 4.6 percent .
How long can you live with stage 1 bladder cancer?
Among people diagnosed with localized bladder cancer (sometimes called Stage 1) in the United State, the average five-year survival rate is around 70%. This five-year survival rate means that on average, around 70 out of 100 people diagnosed at that stage are alive five years after being diagnosed.
Can Stage 3 bladder cancer be cured?
Though stage 3 bladder cancer is advanced, it can be successfully treated.
What is the life expectancy of someone with bladder cancer?
5-year relative survival rates for bladder cancerSEER Stage5-year Relative Survival RateIn situ alone Localized96% 70%Regional38%Distant6%All SEER stages combined77%Mar 1, 2022
Treating Stage 0 Bladder Cancer
Stage 0 bladder cancer includes non-invasive papillary carcinoma (Ta) and flat non-invasive carcinoma (Tis). In either case, the cancer has not inv…
Treating Stage I Bladder Cancer
Stage I bladder cancers have grown into the connective tissue layer of the bladder wall but have not reached the muscle layer.Transurethral resecti…
Treating Stage II Bladder Cancer
These cancers have invaded the muscle layer of the bladder wall. Transurethral resection (TURBT) is typically the first treatment for these cancers…
Treating Stage III Bladder Cancer
These cancers have reached the outside of the bladder and might have grown into nearby tissues or organs.Transurethral resection (TURBT) is typical…
Treating Stage IV Bladder Cancer
These cancers have reached the abdominal or pelvic wall (T4b tumors) or have spread to nearby lymph nodes or distant parts of the body. Stage IV ca…
Treating Bladder Cancer That Progresses Or Recurs
If cancer continues to grow during treatment (progresses) or comes back (recurs), your treatment options will depend on where and how much the canc…

What are the symptoms of bladder cancer?
The most common symptom of bladder cancer is reddish or brownish-colored urine from blood in the urine. Other symptoms include the frequent urge to urinate, pain while urinating, and pain in the back or pelvis. 4
Where does bladder cancer start?
Bladder cancer is a growth that starts in the inner wall of the bladder, the organ that collects and expels urine created by the kidneys. The bladder has three layers of muscular walls that make up its structure. 1 A cancerous growth in the bladder can grow uncontrollably and start spreading to other parts of the body.
What is radical cystectomy?
Cases this may be used for include those in which the tumors in the bladder take over a large part of the organ. This surgery removes the bladder and any nearby cancerous lymph nodes or tissues.
What tests are used to diagnose bladder cancer?
These include blood tests, imaging tests that look inside the body, and samples of the tumors called a bladder biopsy, usually taken during surgery.
How do doctors diagnose cancer?
When doctors first diagnose a cancerous tumor of any kind, they assess how much it has grown, how far it has spread in the body, and how abnormal, or wild, the cancerous cells in the tumor look. These assessments are used to determine cancer’s stage (0 to IV) and grade. 2
How does cancer spread?
The cancer spreads from the original location through a process called metastasis. When cancer spreads, it’s called metastatic cancer or a metastatic tumor. This spreading can happen between tissues, or through the fluids of the blood or lymphatic systems. 3
How is cancer stage determined?
Cancer staging specifics are determined by guidelines set by the American Joint Committee on Cancer’s system, named the TNM staging system. 2
What is stage 0 bladder cancer?
Stage 0 bladder cancer includes non-invasive papillary carcinoma (Ta) and flat non-invasive carcinoma (Tis or carcinoma in situ). In either case, the cancer is only in the inner lining layer of the bladder. It has not invaded (spread deeper into) the bladder wall.
What is the first treatment for bladder cancer?
Chemo (with or without radiation) is typically the first treatment when bladder cancer has spread to distant parts of the body (M1). After this treatment the cancer is rechecked. If it looks like it’s gone, a boost of radiation to the bladder may be given or cystectomy might be done.
What to do if you have cancer that hasn’t been removed?
(Less often, close follow-up alone might be an option.) If all of the cancer wasn’t removed, options are intravesical BCG or cystectomy (removal of part or all of the bladder).
How to get rid of stage IV cancer?
The tumor is then rechecked. If it appears to be gone, chemo with or without radiation or cystectomy are options.
What is the treatment for cancer that recurs in distant parts of the body?
Cancers that recur in distant parts of the body can be harder to remove with surgery, so other treatments, such as chemotherapy, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, or radiation therapy , might be needed. For more on dealing with a recurrence, see Understanding Recurrence.
Can you get a radical cystectomy before surgery?
Radical cystectomy may be the only treatment for people who are not well enough to get chemo. But most doctors prefer to give chemo before surgery because it’s been shown to help patients live longer than surgery alone. When chemo is given first, surgery is delayed. This is not a problem if the chemo shrinks the bladder cancer, but it might be harmful if the tumor continues to grow during chemo.
Can you get a partial cystectomy for bladder cancer?
Lymph nodes near the bladder are often removed as well. If cancer is in only one part of the bladder, a partial cystectomy may be done instead. But this is possible in only a small number of patients . Radical cystectomy may be the only treatment for people who are not well enough to get chemo.
What are the stages of bladder cancer?
There are two types of stages for bladder cancer — the clinical stage and the pathologic stage. The clinical stage is your doctor’s informed opinion of how far your cancer has spread. This is based on results of a number of tests, including physical exams, imaging tests like MRIs or CT scans, and biopsies. Your doctor will use this information …
What is the difference between stage 1 and stage 2 bladder cancer?
Stage I: The cancer has grown through the inner lining of your bladder, but not the muscle of your bladder wall. Nor has it spread to your lymph nodes or distant organs. Stage I I: The cancer has grown through the connective tissue in your bladder and into the muscle layer of the bladder.
Where is bladder cancer now?
Cancer is now in your lymph nodes or distant sites like your bones, liver, or lungs. The more information you have about the stage of your bladder cancer, the better able you’ll be to choose the right treatment option for you. Pagination. 1. 2.
What is pathologic stage?
The pathologic stage is something your doctor determines after surgery to remove the cancer. They’ll look at previous test results. They’ll also examine what they found during surgery to give you an idea of how far your cancer has spread.
What is the range of cancer stages?
These range from 0 to the Roman numeral IV. Here’s what each stage means:
Where is stage 3 cancer?
Stage III: Cancer is now in the layer of fatty tissue that surrounds your bladder. It may also be in your prostate, uterus, or vagina. But it hasn’t spread to nearby lymph nodes or to distant organs. The cancer has spread from your bladder into your pelvic or abdominal wall.
Does bladder cancer spread to lymph nodes?
The cancer has spread from your bladder into your pelvic or abdominal wall. But it hasn’t spread to lymph nodes or distant organs.
What is stage 1 bladder cancer?
Stage I: The cancer has grown through the inner lining of the bladder and into the lamina propria. It has not spread to the thick layer of muscle in the bladder wall or to lymph nodes or other organs (T1, N0, M0).
How many stages of cancer are there?
There are 5 stages: stage 0 (zero) and stages I through IV (1 through 4). The stage provides a common way of describing the cancer, so doctors can work together to plan the best treatments. Staging can be clinical or pathological.
How is bladder cancer diagnosed?
For bladder cancer, the stage is determined based on examining the sample removed during a TURBT (see Diagnosis) and finding out whether the cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
Where is stage 0 of cancer?
Stage 0is: This stage of cancer, also known as a flat tumor or carcinoma in situ (CIS), is found only on the inner lining of the renal pelvis or ureter (Tis, N0, M0).
What does T0 mean in bladder?
T0 (T plus zero): There is no evidence of a primary tumor in the bladder.
What is pathological staging?
Pathological staging is based on what is found based on the surgery itself (such as removal of the entire bladder), including the results of physical examinations, imaging scans, and biopsies. In general, pathological staging gives the health care team the most amount of information to make a prognosis.
Does bladder cancer come back?
This type of bladder cancer often comes back after treatment, usually as another noninvasive cancer in the bladder. T1: The tumor has spread to the connective tissue (called the lamina propria) that separates the lining of the bladder from the muscles beneath, but it does not involve the bladder wall muscle.
How do doctors determine the stage of bladder cancer?
Doctor s take into account many factors when determin ing the stage of bladder cancer, including how it’s growing in the bladder, where it’s growing in the bladder and where it’s spread, both inside and outside the bladder. They may also consider what the cancer cells look like under a microscope. Results from physical exams, biopsies …
Where does bladder cancer grow?
Different types of bladder cancer grow in different ways, so doctors may discuss a tumor in terms of the direction it’s growing. Papillary carcinomas grow from the bladder’s lining toward the hollow center, while flat carcinomas stay flush against the bladder wall.
What is stage 0a?
Stage 0a (noninvasive papillary carcinoma): Cancer grows toward the center of the bladder, but it hasn’t grown into the connective tissue of the bladder wall or muscle and hasn’t spread outside the bladder. The TNM characteristics are Ta, N0, M0.
What does T1 mean in bladder cancer?
T1 means the tumor has grown from the layer of cells lining the bladder into the connective tissue below. It hasn’t grown into the muscle layer of the bladder. T2 means the tumor has grown into the muscle layer. T2a indicates the tumor is in the inner half of the muscle layer.
How many letters are there in bladder cancer?
The most common way doctors describe bladder cancer stages is using the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) TNM system. This system uses three letters, each of which is assigned a different number. Each letter stands for a specific characteristic of the cancer.
What does it mean when a doctor says a bladder is invasive?
Invasive cancers are deeper in the layers of the bladder wall. If a doctor says the cancer is superficial or non-muscle invasive, that means it isn’t in the bladder’s main muscle layer —though it may still be invasive or noninvasive and have the potential to spread to the muscle.
What does each letter mean in cancer?
Each letter stands for a specific characteristic of the cancer. T is for tumor: How big the primary tumor (the tumor in the bladder) is and where it’s situated in the bladder. N is for nodes: Whether the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes and, if so, how many it has spread to.
How many types of bladder cancer are there?
Three types of bladder cancer may form, and each type of tumor can be present in one or more areas of the bladder, and more than one type can be present at the same time: Papillary tumors stick out from the bladder lining on a stalk. They tend to grow into the bladder cavity, away from the bladder wall, instead of deeper into the layers …
What are the different grades of bladder cancer?
What are the different “grades” for a bladder cancer tumor? Grade is expressed as a number between 1 (low) and 3 (high, i.e. G3); the higher the number the less the tumor resembles a normal cell. In lieu of numbers to grade a bladder cancer tumor, your doctor may refer to the tumor simply as low or high grade.
Where do bladder cancers occur?
While the majority of bladder cancers (approximately 90-95%) arise in the bladder, the urothelial cells that line the bladder are found in other locations in the urinary system. Sometimes these urothelial cancers can occur in the lining of the kidney or in the ureter that connects the kidney to the bladder.
Where is urothelial cancer located?
This is known as upper tract urothelial cancer (UTUC) correspond to a subset of urothelial cancers that arise in the urothelial cells in the lining of the kidney (called the renal pelvis) or the ureter ( the long, thin tube that connects that kidney to the bladder). Learn more about UTUC here.
What is the prognosis of bladder cancer?
Prognosis describes how severe a person’s cancer is and their chances of survival. It is influenced by factors that are not reflected in the SEER survival statistics. Chief among them are the type, stage, and grade of bladder cancer. Other factors also contribute.
How does bladder cancer affect survival?
The factors influencing survival include: 1 Age: Increasing age has been linked to a lower survival rate in people with bladder cancer. 7 2 Sex: A literature review of 27 studies and 23,754 patients found that women had a greater risk for disease recurrence following localized treatment of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. 8 3 Smoking: Smoking increases the risk of recurrence and mortality in people with bladder cancer. 9 4 Recurrence: Recurrence of bladder cancer forebodes a poor prognosis, with a median survival of six months after recurrence. Although people with local recurrence have a slightly better prognosis, those with disease recurrence at local and distant sites perform very poorly.
How many people will die from bladder cancer in 2020?
Bladder cancer is the sixth most common cancer in the United States, representing 4.5% of all new cancer cases in the country. 1 There were an estimated 81,400 new cases of bladder cancer in 2020. This form of cancer resulted in about 17,980 deaths in the same year. While bladder cancer is relatively common, the average five-year survival rate is quite high at 76.9%. This rate has improved over the past several years, and a person’s chance of survival is influenced by many factors.
How many TNM stages are there?
Its purpose is to measure and communicate the extent of tumor growth. There are five TNM stages, from 0 to 4. The lower the stage number, the smaller the spread of cancer. The SEER stages are frequently used by tumor registries but not always understood by physicians.
What is the function of the bladder?
The bladder is flexible, being made of smooth muscle. It works to collect and then eliminate urine from your body. The bladder’s flexible walls are made perfectly to expand and contract as necessary to hold urine until it is expelled from the body.
How many stages of cancer are there in TNM?
Its purpose is to measure and communicate the extent of tumor growth. There are five TNM stages, from 0 to 4. The lower the stage number, the smaller the spread of cancer.
What is the difference between localized and distant cancer?
These rates are classified by stage: localized, regional, and distant. Cancer is considered localized when it is only found in the part of the body where it started. Regional means the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes or organs and tissues, while distant refers to cancer that has metastasized to distant organs or lymph nodes.
Location of bladder cancer tumors
The bladder wall is made up of several layers. From innermost to outermost these are:
Bladder cancer stage groupings
TNM stages can be grouped to provide a simplified, standard description of the cancer that enables the medical team to clearly communicate and plan treatment. In general terms, these stage groupings are:
What does the grade of a bladder cancer refer to?
Cancer grade refers to the appearance of the tumor cells when examined under a microscope.
Why is the staging and grading of bladder cancer important?
Accurate staging and grading of bladder cancer is important as it helps to determine a patient’s most appropriate treatment pathway and provides an indication of their prognosis.
For example, the treatment for non-muscle invasive tumors is usually different to that for muscle invasive tumors:
How successful is bladder cancer treatment?
Bladder cancer can usually be treated effectively, especially when tumors are diagnosed at an early stage. Bladder cancers detected at late stages are often more complex to treat and may have an uncertain prognosis.
Bladder Cancer Detection
Several tests and procedures, including non-invasive genomic urine tests like Cxbladder, are available to determine whether an individual has bladder cancer or to establish an alternative diagnosis. Some of these clarify the presence of symptoms (such as haematuria) and others identify alternative causes of these symptoms (such as an infection).
What type of cancer is bladder cancer?
There are various types of bladder cancer. The type of cancer cell can be temporary or transitional cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, or adenocarcinoma. These terms are named after the types of cells that line the bladder wall where the issues start.
How many types of bladder cancer treatments are there?
There are four kinds of treatments for patients with bladder cancer. Sometimes, doctors use combinations of these procedures to treat your condition.
How do doctors diagnose bladder cancer?
Just like how your doctor checks your mouth when you need to diagnose mouth issues ( just click on this link for more information), a specialist can detect the issue with the bladder by doing imaging and biopsy . In any case, here are the three critical pieces of information to describe how far the disease has spread:
What percentage of bladder cancer is squamous?
On the other hand, squamous cells carcinoma makes up around 5% of bladder cancer. Usually, they are fine-level cells that border the urethra. They can shape in the bladder after long episodes of bladder irritation or inflammation.
How does a doctor check if a tumor has spread?
The doctor checks the tumor by measuring how far the primary tumor develops through the bladder and if cancer has spread into neighboring tissues.
Where does bladder cancer come from?
Over 90% of bladder cancers originate from the transitional cells, which involve the deepest lining of the bladder wall. In some cases, the cancers attack into the more profound layers of the bladder, the thick muscle surface of the bladder. Also, this cancer can invade the fatty tissue of the bladder wall.
Can bladder cancer be treated in clinical trials?
Individuals with bladder cancer of all stages may have the option to join in clinical trials. These are research studies that examine new treatments to check how well they help.