Contents
Can a CT urogram detect bladder cancer?
· Can a CT scan miss bladder cancer? CT scans can provide important information about the urinary tract and bladder tumors. However, while some bladder tumors may be seen on a CT scan, others may not be apparent, such as smaller or flatter tumors. What to expect when having a CT scan. A CT scan is a painless procedure that is typically performed on an …
Can an abdomen CAT scan diagnose bladder cancer?
Abdominal CT Scan and the Detection of Bladder Cancer “CT scan is able to detect large bladder irregularities, but not always small lesions,” says Dana Rice, MD, a board certified urologist and creator of the UTI Tracker mobile app, which helps patients catalog daily urinary tract symptoms, medication and behavioral patterns, and offers personalized tips for UTI prevention.
Does cancer always show up in a CT scan?
Computed tomography (CT) scan. A CT scan uses x-rays to make detailed cross-sectional pictures of your body. A CT scan of the kidney, ureters, and bladder is called a CT urogram. It can provide detailed information about the size, shape, and position of any tumors in the urinary tract, including the bladder.
Can a CT scan determine a problem with the gallbladder?
A CT scan is a test that uses x-rays and a computer to create detailed pictures of the inside of your body. It takes pictures from different angles. The computer puts them together to make a 3 dimensional (3D) image. CT (or CAT) stands for computed (axial) tomography. You usually have a CT scan in the x-ray (radiology) department as an outpatient.
Medical History and Physical Exam
Your doctor will want to get your medical history to learn more about your symptoms. The doctor might also ask about possible risk factors, includi…
Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumor (TURBT)
If an abnormal area (or areas) is seen during a cystoscopy, it will be biopsied to see if it is cancer. A biopsy is the removal of small samples of…
Biopsies to Look For Cancer Spread
If imaging tests suggest the cancer might have spread outside of the bladder, a biopsy might be needed to be sure.In some cases, biopsy samples of…
How many people are diagnosed with bladder cancer every year?
If an abdominal CT scan shows a normal bladder, don’t celebrate yet. But if it comes back indicating cancer, don’t panic yet, either. About 80,000 people in the U.S. are diagnosed with bladder cancer every year. The five year survival rate, on average, is about 76.8 percent.
What is the survival rate for bladder cancer?
The five year survival rate, on average, is about 76.8 percent. This not-so-good survival rate is a function of the disease being caught at a later stage than it is of just a hard-to-treat cancer. About four times more men get bladder cancer than do women.
What is a cystoscope?
It’s a diagnostic procedure (performed either under local anesthetic or general anesthesia) during which a doctor inserts a cystoscope (hollow tube) equipped with a lens into the urethra and further into the bladder.

Can a CT scan detect a UTI?
“CT scan is able to detect large bladder irregularities, but not always small lesions,” says Dana Rice, MD, a board certified urologist and creator of the UTI Tracker mobile app, which helps patients catalog daily urinary tract symptoms, medication and behavioral patterns, and offers personalized tips for UTI prevention.
What is the best way to diagnose bladder cancer?
Cystoscopy. If bladder cancer is suspected, most doctors will recommend a cystoscopy. . A urologist uses a cystoscope, which is a long, thin, flexible tube with a light and a lens or a small video camera on the end. For details on how this procedure is done, see Cystoscopy.
What tests are used to check for bladder cancer?
These include the tests called NMP22 ® (or BladderChek ® ), BTA Stat ®, Immunocyt ® , and UroVysion ®, which are discussed in Can Bladder Cancer Be Found Early?
What is the blue light in a cystoscopy?
Fluorescence cystoscopy (also known as blue light cystoscopy) may be done along with routine cystoscopy. For this exam, a light-activated drug is put into the bladder during cystoscopy. It’s taken up by cancer cells. When the doctor then shines a blue light through the cystoscope, any cells containing the drug will glow (fluoresce). This can help the doctor see abnormal areas that might have been missed by the white light normally used.
What is the biopsy for bladder cancer?
A biopsy is when tiny pieces (called samples) of the abnormal-looking tissue are taken out and tested for cancer cells. If bladder cancer is suspected, a biopsy is needed to be sure of the diagnosis.
What is a physical exam for bladder cancer?
A physical exam can provide information about possible signs of bladder cancer and other health problems. The doctor might do a digital rectal exam (DRE), during which a gloved, lubricated finger is put into your rectum. If you are a woman, the doctor might do a pelvic exam as well.

How long does it take for a urine culture to show up?
It can take time for the bacteria to grow, so it may take a few days to get the results of this test.
How does ultrasound help with bladder cancer?
Ultrasound uses sound waves to create pictures of internal organs. It can be useful in determining the size of a bladder cancer and whether it has spread beyond the bladder to nearby organs or tissues. It can also be used to look at the kidneys. This is usually an easy test to have, and it uses no radiation.
What does a CT scan of your pelvis tell you?
You might have a CT scan of your pelvis and tummy (abdomen). It can tell your doctor where the cancer is, how big it is and if the cancer has spread. Knowing this helps your specialist decide on the best treatment for you.

What is a CT scanner?
A CT scanning machine is large and shaped like a doughnut. You might have an injection of a type of dye called a contrast medium through a small tube (cannula) in your arm. You may: feel hot and flushed for a minute or two. have a metallic taste in your mouth.
What is a CT scan of the abdomen?
Knowing this helps your specialist decide on the best treatment for you. A CT scan is a test that uses x-rays and a computer to create detailed pictures of the inside of your body. It takes pictures from different angles.
What is a voiceover CT scan?
Voiceover: A CT scan helps your doctor make a diagnosis, decide about what treatment you need or find out if your treatment is working. This type of scan takes a series of x-rays and uses a computer to put them together. Before your scan you may need to drink either half a litre of water or a type of dye called a contrast medium.

What is the number to call for cancer research?
For information and support, you can call the Cancer Research UK nurses on freephone 0808 800 4040. The lines are open from 9am to 5pm, Monday to Friday.
How to prepare for a CT scan?
You usually receive written instructions on how to prepare for your CT scan. Let the radiology department know if you’re taking a drug called Metformin. The dye (contrast medium or iodine) can interact with the metformin. Also, let them know if you have an allergy to the dye.
How do you talk to a radiographer?
They can see you on a TV screen or through a window from the control room. You can talk to each other through an intercom.

Why do you need a bladder CT scan?
Some reasons to request a bladder CT scan can include incontinence, bladder masses, or signs of blockages. This test can also be requested if a doctor suspects the presence of stones in the bladder. It can be ordered if abnormalities are noticed on another imaging study like an ultrasound or X-ray, or if they are observed during an examination. Interpreting the images may require several days, depending on the staff at a facility.
How to get a picture of bladder?
Images of the bladder can be produced through use of a CT scan.
Can a bladder CT scan be done outpatient?
Imaging centers can usually offer a bladder CT scan as an outpatient procedure. The entire test, including checking in, acquiring the images, and being monitored for initial reactions if contrast was used, may take several hours. If a patient is already hospitalized for an existing medical problem, the test can be offered as an inpatient service, in which case people can transfer to the radiology department for the test and return to their beds when they are finished.

Is a bladder CT scan safe?
Risks associated with a bladder CT scan are low. Patients are exposed to some radiation, but it is kept as low as possible and the benefit of catching a problem outweighs the risk. Pregnant women may be advised to wait for testing if at all possible because of the increased risks for the developing fetuses. Some people experience allergic reactions to contrast agents, and it is important to discuss past allergy and medical history with a medical provider before starting the test. The technician may decide to use a different contrast agent or consider a bladder CT without contrast if this appears necessary.
What is the CT scan used for?
CTU provides imaging of urinary system (the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra) and is especially useful for urinary system pathologies. The second mode of CT scan is the conventional CT; this provides examinations of upper-lower abdomen and pelvis. CT is commonly used and is recommended method for staging BCa (Figure 2) [5, 17, 21, 25, 26].
What is the best way to detect BCa?
White light cystoscopy (WLC), a widely available technique, that allows visualization of the mucosa within the bladder, is considered a gold standard method for detecting BCa [8]. There are two forms of WLC, rigid and flexible cystoscopy (FC). Rigid cystoscopy provides better image quality, enables working with a large lumen, and provides improved flow. FC on the other hand allows alternative patient positioning, easy passage, and enables examination of all parts of the bladder [8]. Therefore, FC is usually applied for initial assessment of patients. However, FC may miss up to 10% of papillary tumors. Furthermore its small working channel lumen does not allow resection of BCa [9]. Although technology has improved the WLC image quality significantly, WLC cannot reliably determine flat and carcinoma in situ (CIS) lesions, and cannot distinguish benign lesions from malignant masses. Such a distingtion is particularly important when Transurethral Resection of Bladder (TURB) is to be performed [9–11]. However, cystoscopy is recommended by national comprehensive cancer network (NCNN) and American urological association (AUA) guidelines for imaging patients with macroscopic hematuria [5, 12].

What is dual energy spectral CT?
Dual energy spectral CT is a relatively new method that provides multiparameteric imaging of the urinary system. On the monochromatic images, a threshold value of 73.4 Hounsfield unit demonstrated high sensitivity (77.0%) and specificity (82.5%) for differentiating posterior wall BCa from benign prostate hypertrophy [35].
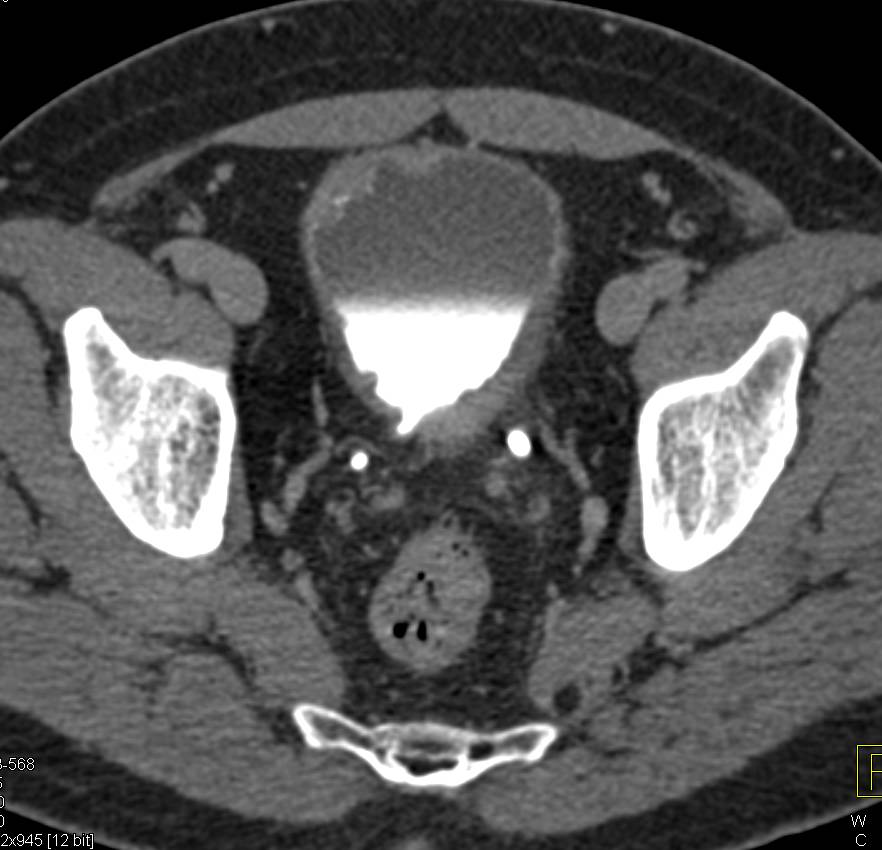
What is the irregular round filling defect in the right posterior aspect of the bladder?
The irregular round filling defect in the right posterior aspect of the bladder (arrow) represents a transitional cell carcinoma. There is thickening of the adjacent bladder wall, but not definite spread beyond the bladder.
How old is microscopic hematuria?
microscopic hematuria (<35 years old): can be performed according to bladder cancer suspicion
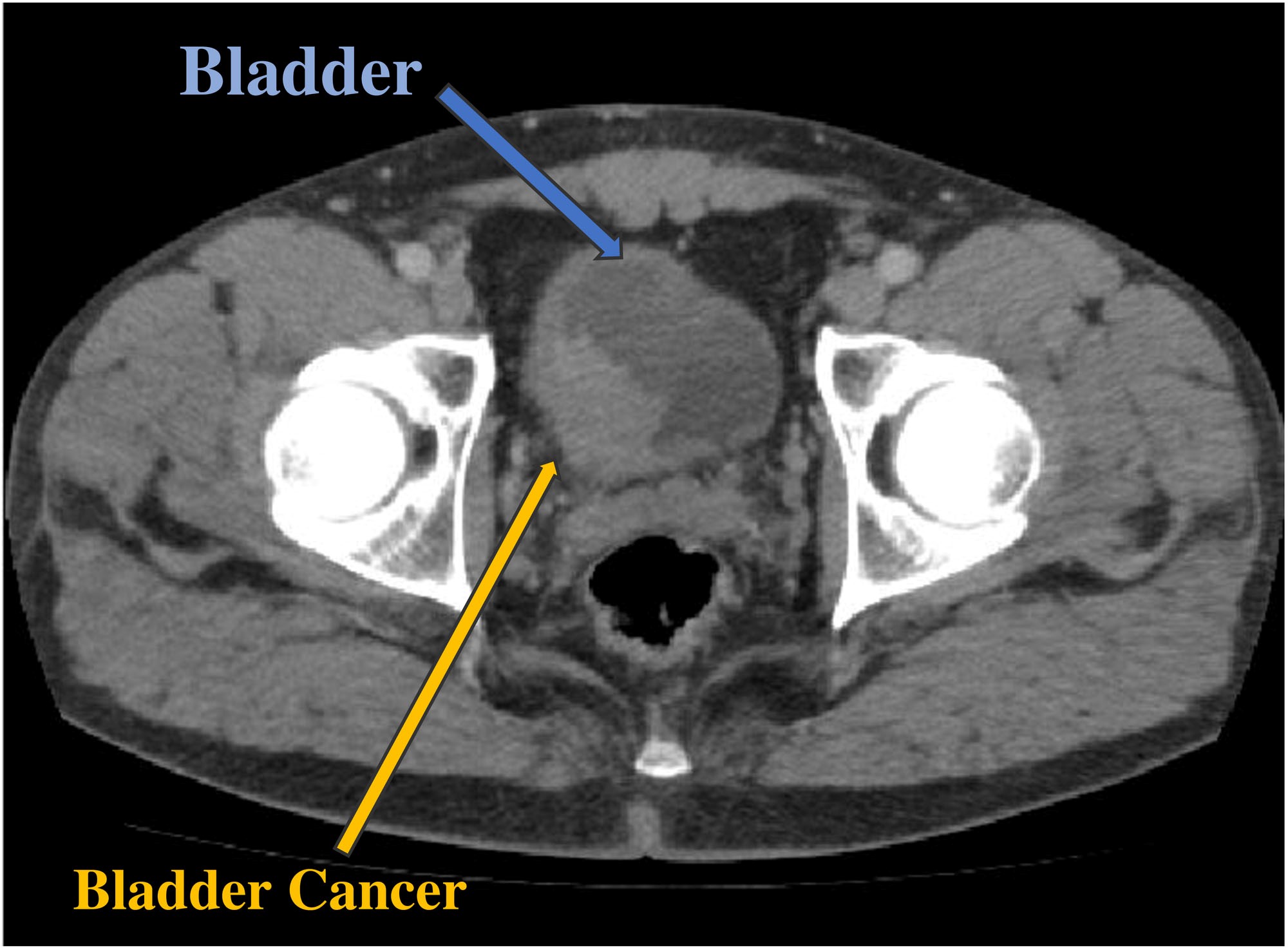
Which is better, CTU or cystoscopy?
Diagnostic performance of CTU was compared with cystoscopy in 177 patients. CTU performed better with 96.3% sensitivity, 86.4% specificity, 92.8% diagnostic accuracy, 92.9% PPV, and 92.7% NPV. The arterial acquisition phase diagnosed the lesions with the highest accuracy, and demonstrated 93.4% of all lesions [31].
Is CT more effective than MRI?
CT is faster and more cost-effective than MRI, but it is associated with the risk of ionizing radiation, high interobserver variability, and can neither differentiate bladder wall muscle layers, nor can it reliably distinguish T1 from T2 disease. Furthermore, its specificity and sensitivity are low for extravesical extension of early stage BCa and small metastatic lesions of BCa.[17, 21, 25, 26, 32–34].
What is a urologic test for cancer?
This test is good at finding tumors of the kidney, renal pelvis, and ureter, as well as other urologic abnormalities. It may identify kidney stones and hydronephrosis (swelling of the kidney that is often due to downstream blockage). In addition, the entire abdomen and pelvis is also imaged. This allows a radiologist to identify other abnormalities in these parts of the body. In patients with cancer, it will help identify signs of spread to lymph nodes or other organs like the liver.

What is the best test for cancer?
MR Urogram. Another option for imaging is MRI of the abdomen and pelvis or MR Urogram. This test is also effective at finding tumors in the kidney and ureters and evidence of spread of cancer. It may be used to avoid radiation or in patients with contrast dye allergies or borderline kidney function.
How long does it take for a cystoscopy to go away?
Patients will go home after the cystoscopy if it is done in the doctor’s office. There may be some bleeding and irritating bladder symptoms following the cystoscopy for a day or two. If the symptoms do not improve within 3-5 days, notify your urologist. Seeing blood in the urine can be very troubling, even small amounts of blood can change the color of the urine dramatically. This should resolve on its own. Make sure to stay hydrated to help keep your urine diluted.
What is urine biopsy?
The biopsy specimen and the urine sample will help the urologist make recommendations about your future care.

Can a urologist do a cystoscopy?
During the cystoscopy, the urologist will look through the cystoscope and make a note of anything in the bladder that may be abnormal. If a tumor or other abnormality is identified, the urologist will likely schedule you for a cystoscopy under anesthesia with bladder biopsy or “transurethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT).”
Can you get a CT scan without contrast?
Your healthcare provider will request blood work to see if you have normal kidney function before you can receive the contrast required for a CT urogram. If the contrast cannot be given, your healthcare provider may decide to perform a CT scan without contrast or other imaging study. A procedure called cystoscopy with retrograde pyelograms may be suggested. The urologist performs x-rays while injecting dye into the ureters. Like a CT urogram, it can help to identify abnormalities of the ureter and renal pelvis.
Does ultrasound show kidney stones?
It may be used in lower risk patients and those with contrast allergies or poor renal function. Unfortunately, it can miss small kidney stones and tumors. Also, it will not detect tumors in the ureter unless they are causing a blockage leading to hydronephrosis