Contents
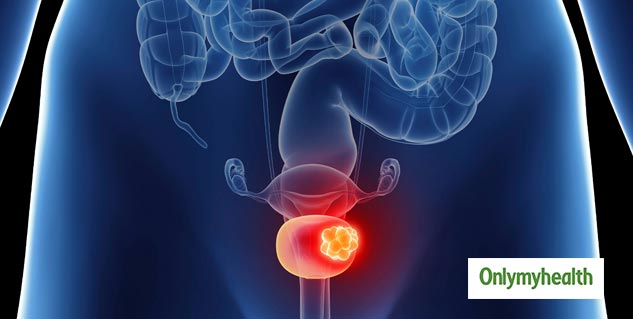
How quickly does bladder cancer grow and spread?
Results: Brain metastases from bladder carcinoma were commonly accompanied by uncontrolled systemic metastases. Multiple brain lesions developed in 14 of the 16 patients. Of the 16 patients 14 received radiation therapy with or without surgery, 1 was treated surgically and 1 did not receive any treatment.
What is the treatment for Stage 3 bladder cancer?
· While bladder cancer can and does metastasize to the brain, the symptoms you describe (a global deficit rather than something that is more focal indicating a specific area of the brain) seems to me to make it unlikely that his symptoms are from metastatic disease to the brain. the confusion and disorientation, I believe, is more likely to be due to some other reason.
What is the progression of bladder cancer?
· Bottom line is that while it is not yet a formal recomendation, there is clearly a growing belief that people with bladder cancer would benefit from genetic testing. As a BRCA+ bladder cancer patient who has been metastatic for 5 years (bones, brain and lung), but current. KenD. 5 Comments – Posted Jan 02.
Is a mass in the bladder always cancer?
· However, brain and skin metastasis is regarded as a late manifestation of systemic spread. The mean survival period of most patients with bladder cancer is relatively too short for manifestations of brain or skin metastatic lesions to develop. Thus, our case suggests that brain or skin may be rare sites for metastatic lesions.

Where does bladder cancer usually metastasize to?
Not all bladder cancers will spread. But If it does it’s most likely to spread to the structures close to the bladder, such as the ureters, urethra, prostate, vagina, or into the pelvis.
What are the signs that cancer has spread to brain?
Brain metastases cause many of the same symptoms as tumors that originate in the brain, such as:Seizures.Numbness.Balance and coordination issues.Headaches that are sometimes accompanied by nausea or vomiting.Dizziness.Cognitive impairment, including confusion, memory loss and personality changes.
Which type of cancer metastasizes most to the brain?
Brain mets are most common in lung cancer. Other cancers that often metastasize to the brain are melanoma, breast cancer, colon cancer, and renal cell (kidney) cancer. There has been a rise in the number of brain metastases in recent years. This could be because we have better tools to diagnose brain metastases.
How much time left when cancer spreads to the brain?
Without treatment, the average survival rate is under 6 months . With treatment, that number can increase slightly. Usually those who develop brain metastases farther out from diagnosis have a slightly higher survival rate than those whose lung cancer metastasizes to the brain earlier.
Can you have a brain tumor for years without knowing?
Some people with a brain or central nervous system tumor have no symptoms. In some cases, doctors discover a tumor during treatment for another issue. As a brain tumor grows and presses on surrounding nerves or blood vessels, it may cause symptoms.
What is the most common primary tumor to metastasize to the brain?
In adults, the most common primary tumors responsible for brain metastases are carcinomas, and include lung, breast, kidney, and colorectal cancers, and melanoma. By contrast, carcinomas of the prostate, esophagus, and oropharynx and non-melanoma skin cancers rarely metastasize to the brain.
How long do you live with brain metastases?
A decade and a half ago, people diagnosed with a brain metastasis survived, on average, less than 6 months. Treatments have improved in the intervening years, and today, people with brain metastases are living longer than ever before.
What happens when cancer moves to the brain?
Brain metastases may form one tumor or many tumors in the brain. As the metastatic brain tumors grow, they create pressure on and change the function of surrounding brain tissue. This causes signs and symptoms, such as headache, personality changes, memory loss and seizures.
How fast does brain metastases grow?
This study demonstrated the mean interval from primary lung cancer diagnosis to brain metastasis was 1.17 years and 4.64 years in the breast cancer group. This is slightly longer than the average time of diagnosis of breast cancer to brain metastasis previously reported of 34 months (2.83 years).
What was your first brain tumor symptoms?
Headaches that gradually become more frequent and more severe. Unexplained nausea or vomiting. Vision problems, such as blurred vision, double vision or loss of peripheral vision. Gradual loss of sensation or movement in an arm or a leg.
What does brain metastases feel like?
Brain metastases may form one tumor or many tumors in the brain. As the metastatic brain tumors grow, they create pressure on and change the function of surrounding brain tissue. This causes signs and symptoms, such as headache, personality changes, memory loss and seizures.
What does a brain cancer headache feel like?
They are often described as dull, “pressure-type” headaches, though some patients also experience sharp or “stabbing” pain. They can be localized to a specific area or generalized. They can be made worse with coughing, sneezing or straining.
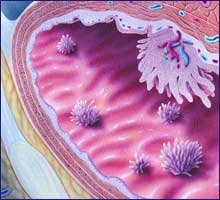
Can bladder cancer spread to other organs?
Metastatic bladder cancer can also spread to other organs in the urinary and reproductive tracts, such as the prostate, uterus and vagina.
How does bladder cancer spread?
Bladder cancer spreads when cancerous cells reproduce and invade surrounding healthy tissues. This is known as metastasis. Usually, metastatic bladder cancer refers to cancer that has spread to distant organs, but metastasis can occur locally in the muscles and connective tissues that are directly adjacent to the bladder as well.
Where does bladder cancer metastasize?
Usually, metastatic bladder cancer refers to cancer that has spread to distant organs, but metastasis can occur locally in the muscles and connective tissues that are directly adjacent to the bladder as well.
Where does bladder cancer occur?
Usually, metastatic bladder cancer refers to cancer that has spread to distant organs, but metastasis can occur locally in the muscles and connective tissues that are directly adjacent to the bladder as well.
Is bladder cancer a secondary tumor?
It’s important to remember that when bladder cancer spreads, the secondary tumors are still considered to be bladder cancer – not lung cancer, liver cancer or any other type of malignancy.
What is the treatment for bladder cancer?
Potential treatment options may include chemotherapy, radiation therapy and clinical trials.
What is the treatment for brain metastases?
For patients with a limited number of brain metastases that are amenable to resection, standard treatment for most solid malignancy histologies is surgery followed by either adjuvant stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) to the surgical cavity or WBRT.
Can UC patients tolerate cisplatin?
Patients who develop UC brain metastases typically have either already received cisplatin-based chemotherapy or cannot tolerate it; only about 50% of mUC patients are eligible for cisplatin-based therapy [ 48 ].
Does RT help with intracranial failure?
The efficacy of RT for primary management of mUC intracranial failure has not been prospectively evaluated. For non-surgical patients with intracranial failure, RT improves LC and palliates neurological symptoms. Patients with multiple unresectable lesions, poor performance status, life expectancy <6 months, and symptomatic UC brain metastases may benefit from WBRT or best supportive care, as extrapolated from the QUARTZ trial where dexamethasone (median 8 mg/day) with WBRT (20 Gy/5 fractions) did not improve OS for NSCLC brain metastases and provided minimal increase in quality-adjusted life years versus optimal supportive care [ 86 ]. On subgroup analysis, patients with better prognosis ( e.g. age < 60) or those with a higher burden of intracranial disease (≥5 brain metastases) had improved OS with WBRT [ 86 ]. These results should be interpreted cautiously since they may not be applicable to UC brain metastases.
Is SRS a good alternative to surgery?
SRS is a reasonable alternative to surgery or WBRT for smaller tumors ≤3 cm that are not resectable and can also be considered for resectable tumors ≤3 cm in patients who are candidates for surgery. Because the risk of both neurotoxicity and local failure after SRS increase with increasing tumor size, surgery is favored for lesions >3 cm. SRS achieves local control rates of ∼70% at 1-year post-treatment in appropriately selected patients [ 71 ]. To-date, no trials of sufficient power comparing SRS alone vs. surgery plus post-operative RT have been completed. Shared decision-making and input from a multi-disciplinary team should help guide the decision on surgery plus adjuvant RT vs. SRS alone. For patients with a limited number of lesions not amenable to surgical resection, SRS (18–24 Gy in 1 fraction based on target size) may be preferable to WBRT for patients with good performance status, since SRS reduces the volume of normal brain irradiated and is associated with less cognitive deterioration at 3 months without compromising OS, although time to intracranial failure outside of the treated lesions is shorter compared to WBRT [ 82, 83 ]. While SRS has been traditionally employed to treat a limited number of tumors (often 4 or fewer), prospective non-randomized data suggest that up to 10 tumors with a cumulative volume ≤15 mL can be treated with SRS in a single treatment session with similar efficacy and no increase in side effects [ 84, 85 ].
Where do brain tumors come from?
Although any type of cancer can spread to the brain, brain metastases most often originate from cancer in the lungs, breasts, kidneys or colon.
What is the term for cancer that spreads to the brain?
When cancer spreads from a different part of the body to the brain, the metastatic tumors are referred to as “brain metastases.”. The brain is a relatively common location for metastasis to occur. In fact, one in four cancer patients experience brain metastasis.
What is the most common type of brain tumor?
The brain is a relatively common location for metastasis to occur. In fact, one in four cancer patients experience brain metastasis. And, brain metastases are the most common type of brain tumor diagnosed among adults.
Is the brain a tumor?
In fact, one in four cancer patients experience brain metastasis. And, brain metastases are the most common type of brain tumor diagnosed among adults.
What are the symptoms of brain metastases?
Brain metastases cause many of the same symptoms as tumors that originate in the brain, such as: Seizures. Numbness. Balance and coordination issues. Headaches that are sometimes accompanied by nausea or vomiting. Dizziness. Cognitive impairment, including confusion, memory loss and personality changes.
What is it called when cancer spreads to another part of the body?
If you or a loved one have been diagnosed with cancer, you’ve probably heard the term “metastasis.”. This refers to when cancer develops in one part of the body and then spreads to another part of the body (for example, when breast cancer spreads to the brain). This generally happens when cancer cells detach from the main tumor …
What is metastatic cancer?
Pinterest. Email. If you or a loved one have been diagnosed with cancer, you’ve probably heard the term “metastasis.”. This refers to when cancer develops in one part of the body and then spreads to another part of the body (for example, when breast cancer spreads to the brain). This generally happens when cancer cells detach from …
Is brain metastasis rare?
Although prostate cancer is currently the most common malignancy among men in the USA with an annual incidence of almost 250 000 cases [5], brain metastasis from prostat e cancer is rare, occurring in only 0.5 to 0.6% of affected men [12]. Some have suggested that the brain may be unusually resistant to metastatic spread from primary prostate cancer …
Is prostate cancer rare?
Although prostate cancer is currently the most common malignancy among men in the USA with an annual incidence of almost 250 000 cases [5], brain metastasis from prostate cancer is rare, occurring in only 0.5 to 0.6% of affected men [12]. Some have suggested that the brain may be unusually resistant to metastatic spread …
What is the treatment for bladder cancer?
Immunotherapy is treatment that boosts your immune system to attack the cancer cells. Different types of immunotherapy can be used to treat bladder cancer. These drugs can be put right into the bladder (as a liquid) or given into a vein.
Can radiation help bladder cancer?
Radiation treatment for bladder cancer can be used: To treat early-stage cancer after surgery. As the main treatment for early-stage cancer if you can’t have surgery. As part of the treatment for advanced bladder cancer. Radiation is often given along with chemo. Certain chemo drugs can help the radiation work better.
Where does cancer start?
Cancer can start any place in the body. Cancer that starts in the bladder is called bladder cancer. It starts when cells in the bladder grow out of control and crowd out normal cells. This makes it hard for the body to work the way it should. Cancer cells can spread to other parts of the body.
What is it called when cancer spreads to the bone?
For instance, cancer cells in the bladder can travel to the bone and grow there. When cancer cells spread, it’s called metastasis . Cancer is always named for the place where it starts. So when bladder cancer spreads to the bone (or any other place), it’s still called bladder cancer.
What is the tube that connects the kidneys to the bladder?
Tubes called ureters connect your kidneys to the bladder. Urine flows through the ureters and into your bladder, where it’s stored. When you urinate (pee), the bladder squeezes the urine out through a tube called the urethra. Bladder cancer usually starts in the lining or inner layer of the bladder wall.
What tests are done to check for bladder cancer?
This might include a rectal exam, during which a gloved finger is put into your rectum. If you are a woman, a pelvic exam might also be done.
What is the test for cancer?
Urine tests: For these tests, you’ll be asked to pee in a cup. Your urine is then tested for cancer cells, blood, or certain proteins (called tumor markers). Cystoscopy: For this exam, a doctor called a urologist looks at the inside of your bladder using a tool called a cystoscope.
Can bladder cancer spread to other parts of the body?
Bladder cancers that have grown large or have spread to other parts of the body can sometimes cause other symptoms, such as: Again, many of these symptoms are more likely to be caused by something other than bladder cancer, but it’s important to have them checked.
Can bladder cancer cause bleeding?
Usually, the early stages of bladder cancer (when it’s small and only in the bladder) cause bleeding but little or no pain or other symptoms. Blood in the urine doesn’t always mean you have bladder cancer.
How do you know if you have bladder cancer?
Bladder cancers that have grown large or have spread to other parts of the body can sometimes cause other symptoms, such as: Being unable to urinate. Lower back pain on one side. Loss of appetite and weight loss. Feeling tired or weak.
Can bladder cancer cause lower back pain?
Bladder cancers that have grown large or have spread to other parts of the body can sometimes cause other symptoms, such as: Being unable to urinate. Lower back pain on one side. Loss of appetite and weight loss. Feeling tired or weak.
What are the symptoms of bladder cancer?
Being unable to urinate. Lower back pain on one side. Loss of appetite and weight loss. Feeling tired or weak. Swelling in the feet. Bone pain. Again, many of these symptoms are more likely to be caused by something other than bladder cancer, but it’s important to have them checked.
What does it mean when you have blood in your urine?
Blood in the urine. In most cases, blood in the urine (called hematuria) is the first sign of bladder cancer. There may be enough blood to change the color of the urine to orange, pink, or, less often, dark red.
Why do I have trouble peeing?
Having to get up to urinate many times during the night. These symptoms are more likely to be caused by a urinary tract infection (UTI), bladder stones, an overactive bladder, or an enlarged prostate (in men).