Contents

Medication
Tests for Bladder Cancer Medical history and physical exam. Your doctor will want to get your medical history to learn more about your symptoms. Urine lab tests. This is a simple lab test to check for blood and other substances in a sample of …
Procedures
Although radiological tests provide important information about the kidneys and the ureters, cystoscopy is the best method of evaluating the bladder and the urethra and diagnosing and monitoring bladder cancer. The cystoscope, a long thin camera, is inserted through the urethra into the bladder.
Therapy
· What Are The Typical Results For Urine Test For Cancer If the urine sample was collect accurately, avoiding interference of certain foods, medications, and dietary… In general, yellow-brown or greenish-brown urine may be a sign of bilirubin leaking from the liver into the urine. It… Blood test, …
Nutrition
An ultrasound uses sound waves to create a picture of the inside of the body, which can be used to see if bladder cancer has spread to the kidneys or areas near the bladder. Bone scan. A bone scan is a procedure that is used to check whether bladder cancer has spread to the bones.
What is the best test for bladder cancer?
Imaging such as an ultrasound, X-ray, computed tomography (CT) scan or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to view detailed images of the bladder. Cystoscopy to closely examine the bladder and remove a small piece of abnormal tissue for biopsy, if necessary, using a …
How to recognize the signs of bladder cancer?
Two tests may be used to screen for bladder cancer in patients who have had bladder cancer in the past: Cystoscopy Cystoscopy is a procedure to look inside the bladder and urethra to check for abnormal areas. A cystoscope (a thin, lighted tube) is inserted through the urethra into the bladder. Tissue samples may be taken for biopsy. Enlarge
How can urine tests detect bladder cancer?
A cystoscopy is a test to check the health of your urethra and bladder. You might also hear it called a cystourethroscopy or, more simply, a bladder scope. It’s …
How to diagnose bladder cancer?
Stages and Outlook (Prognosis) After a cancer diagnosis, staging provides important information about the extent (amount) of cancer in the body and the likely response to treatment. Bladder Cancer Stages. Survival Rates for Bladder Cancer.
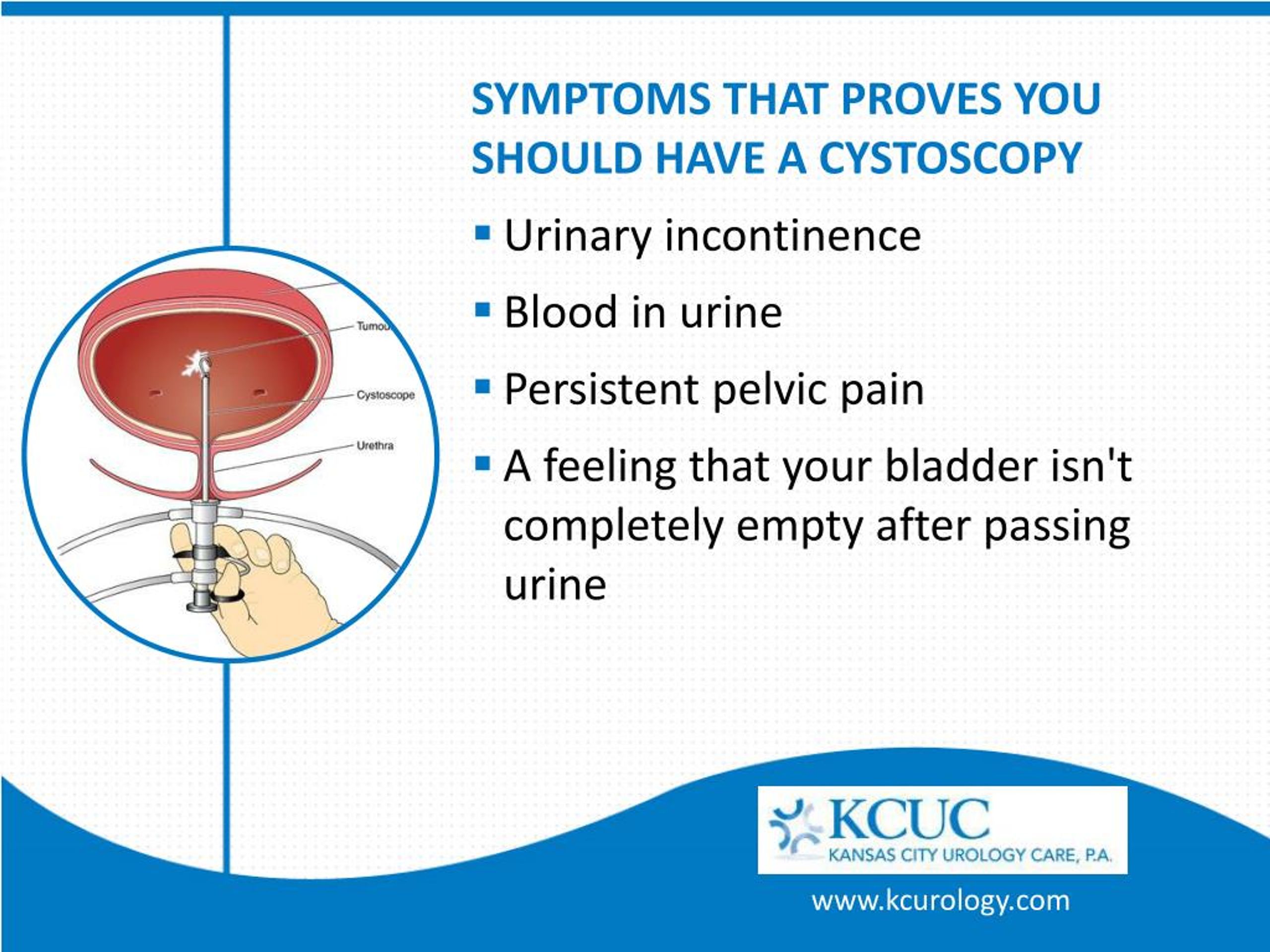
How can a doctor tell if you have bladder cancer?
A sample of your urine is analyzed under a microscope to check for cancer cells in a procedure called urine cytology. Imaging tests. Imaging tests, such as computerized tomography (CT) urogram or retrograde pyelogram, allow your doctor to examine the structures of your urinary tract.
Does bladder cancer show up in blood work?
Tests to diagnose bladder cancer If bladder cancer is suspected, these tests may be performed to diagnose the disease: Physical exam. Blood test: Blood samples are used to measure certain substances released into the blood by organs and tissues in the body.
What is usually the first symptom of bladder cancer?
For most people, the first symptom of bladder cancer is blood in the urine, also called hematuria. Sometimes the blood is visible, prompting the patient to visit a doctor.
Does bladder cancer feel like a UTI?
Bladder cancer can be mistaken for a Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) because many of the symptoms overlap. Patients may experience increased frequency and urgency of urination, pain with urination, or urinary incontinence.
How painful is a cystoscopy?
People often worry that a cystoscopy will be painful, but it does not usually hurt. Tell your doctor or nurse if you feel any pain during it. It can be a bit uncomfortable and you may feel like you need to pee during the procedure, but this will only last a few minutes.
Do you feel ill with bladder cancer?
Nausea and vomiting. Burning or pain when you urinate, feeling the need to go often, or blood in urine. Diarrhea. Feeling tired.
What are the signs that something is wrong with your bladder?
Some common signs and symptoms of bladder issues include:Bladder leakage.Pain or a burning sensation during urination.Cloudy urine.Persistent, strong urge to urinate.Urinating frequently in small amounts.Frequent urination (more than eight times during the day or more than two times at night)Urine that smells strong.More items…
Who is at high risk for bladder cancer?
Age: Most people who get bladder cancer are older in age. The average age at diagnosis is 73, and 90 percent of patients are over age 55. Race: Bladder cancer is twice as common among Caucasians as African Americans. This disease is less common among Hispanics, Asians and Native Americans.

How to diagnose bladder cancer?
Tests and procedures used to diagnose bladder cancer may include: Using a scope to examine the inside of your bladder (cystoscopy). To perform cystoscopy, your doctor inserts a small , narrow tube (cystoscope) through your urethra. The cystoscope has a lens that allows your doctor to see the inside of your urethra and bladder, …
What tests can be done to determine if you have bladder cancer?
Tests may include: CT scan.
Can TURBT be used for bladder cancer?
TURBT can also be used to treat bladder cancer. Examining a urine sample (urine cytology). A sample of your urine is analyzed under a microscope to check for cancer cells in a procedure called urine cytology. Imaging tests.

What is a low grade bladder cancer?
Low-grade bladder cancer. This type of cancer has cells that are closer in appearance and organization to normal cells (well differentiated). A low-grade tumor usually grows more slowly and is less likely to invade the muscular wall of the bladder than is a high-grade tumor. High-grade bladder cancer.
What is the best treatment for cancer?
Radiation therapy, to destroy cancer cells, often as a primary treatment when surgery isn’t an option or isn’t desired. Immunotherapy, to trigger the body’s immune system to fight cancer cells, either in the bladder or throughout the body. Targeted therapy, to treat advanced cancer when other treatments haven’t helped.
How does radiation therapy help bladder cancer?
Radiation therapy. Radiation therapy uses beams of powerful energy, such as X-rays and protons, to destroy the cancer cells. Radiation therapy for bladder cancer usually is delivered from a machine that moves around your body, directing the energy beams to precise points.

Can bladder cancer recur after treatment?
Bladder cancer may recur, even after successful treatment. Because of this, people with bladder cancer need follow-up testing for years after successful treatment. What tests you’ll have and how often depends on your type of bladder cancer and how it was treated, among other factors.
What is the best way to test for bladder cancer?
Although radiological tests provide important information about the kidneys and the ureters, cystoscopy is the best method of evaluating the bladder and the urethra and diagnosing and monitoring bladder cancer. The cystoscope, a long thin camera, is inserted through the urethra into the bladder.
Can a urologist do a biopsy of the bladder?
Some urologist may have the ability to perform small bladder biopsies in the office. The tissue sample, or biopsy, is then sent to the pathologist for examination. A sample of the urine from the bladder is sent for analysis of the cells (called cytology) to determine if the urine contains any cancer cells.

What is a CT urogram?
A CT urogram examines the upper urinary tract (kidneys and ureters) in detail. This test is good at finding tumors of the kidney, renal pelvis, and ureter, as well as other urologic abnormalities. It may identify kidney stones and hydronephrosis (swelling of the kidney that is often due to downstream blockage).
Can you go home after a cystoscopy?
Patients will go home after the cystoscopy if it is done in the doctor’s office. There may be some bleeding and irritating bladder symptoms following the cystoscopy for a day or two.
What is a CT scan for bladder cancer?
To check if bladder cancer has spread, CT scans may be used to create images of the entire urinary tract (including the kidneys) as well as lymph nodes, other organs in the abdomen, and the lungs.
Can a chest x-ray detect bladder cancer?
If healthcare providers suspect that the bladder cancer may have spread to the patient’s lungs, then a chest x-ray may be used.
What is it called when bladder cancer spreads?
1,2 Bladder cancer that has spread ( metastasized) is called metastatic bladder cancer.
How does bladder cancer spread?
It can also spread through the lymph system, by traveling through lymph vessels to lymph nodes in different parts of the body. It can also spread through the body’s blood vessels and form tumors in other parts of the body, …

What is a CAT scan?
Computed tomography (CT or CAT) scans use computer technology to combine multiple x-rays into a more detailed, three-dimensional image of the inside of the body. To check if bladder cancer has spread, CT scans may be used to create images of the entire urinary tract (including the kidneys) as well as lymph nodes, other organs in the abdomen, and the lungs.
What is ultrasound used for?
An ultrasound uses sound waves to create a picture of the inside of the body, which can be used to see if bladder cancer has spread to the kidneys or areas near the bladder.
Can a biopsy confirm cancer?
Biopsies can confirm if cancer has spread. If imaging shows that there are tumors in other organs, for example, then biopsies can be used to confirm the diagnosis. 1,2 Biopsies are small samples of tissue taken from the body and then analyzed in a laboratory to check for the presence of cancer cells.
Where does bladder cancer start?
Most bladder cancers begin in the transitional cells. Squamous cell carcinoma: Cancer that forms in squamous cells (thin, flat cells that line the bladder). Cancer may form after long-term infection or irritation. Adenocarcinoma: Cancer that begins in glandular cells.
Is bladder cancer more common in men than women?
Bladder and other urothelial cancers are diseases in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the urothelium. Bladder cancer is more common in men than women. Smoking can affect the risk of bladder cancer.
What is the urothelium?
The urothelium is a layer of tissue that lines the urethra, bladder, ureters, prostate, and renal pelvis. Cancer that begins in the urothelium of the bladder is much more common than cancer that begins in the urothelium of the urethra, ureters, prostate, or renal pelvis. Because it is the most common form of urothelial cancer, …

What is screening for cancer?
Screening is looking for cancer before a person has any symptoms. This can help find cancer at an early stage. When abnormal tissue or cancer is found early, it may be easier to treat. By the time symptoms appear, cancer may have begun to spread.
Can cancer be found early?
This can help find cancer at an early stage. When abnormal tissue or cancer is found early, it may be easier to treat. By the time symptoms appear, cancer may have begun to spread. Scientists are trying to better understand which people are more likely to get certain types of cancer.
Do doctors think you have cancer?
It is important to remember that your doctor does not necessarily think you have cancer if he or she suggests a screening test. Screening tests are given when you have no cancer symptoms. If a screening test result is abnormal, you may need to have more tests done to find out if you have cancer.

Where is the bladder located?
The bladder is a hollow organ in the lower part of the abdomen. It is shaped like a small balloon and has a muscle wall that allows it to get larger or smaller to store urine made by the kidneys. There are two kidneys, one on each side of the backbone, above the waist.
What happens when your bladder is full?
When your bladder is full of water, it stretches. This lets the doctor see your entire bladder wall. They’ll ask you how it feels when it’s full. The doctor takes tissue samples. If an area looks abnormal, the doctor will use the cystoscope to cut a small piece that they can send to the lab for analysis.
What is a cystoscopy?
A cystoscopy is a test to check the health of your urethra and bladder. You might also hear it called a cystourethroscopy or, more simply, a bladder scope. It’s an outpatient test, which means you can get it at your doctor’s office, a hospital, or clinic and go home the same day. The doctor inserts a tube into your urethra.

How long does it take to get a cystoscopy?
What to Expect During Cystoscopy. The procedure generally takes about 15 to 20 minutes. You’ll need to pee first. The test is done with an empty bladder. You’ll lie down. The position depends on the type of scope your doctor uses: Standard rigid cystoscope. You’ll lie on your back with your knees up and apart.
How does a cystoscope work?
The cystoscope has a lens on the end that works like a telescope. It makes it easier for the doctor to see inside your body. They might put a video camera over the lens to project images onto a screen. The doctor fills your bladder. They put water or saline in through the cystoscope.
What is staging after cancer diagnosis?
After a cancer diagnosis, staging provides important information about the extent (amount) of cancer in the body and the likely response to treatment.

Why is it important to find cancer early?
Finding cancer early, when it’s small and hasn’t spread, often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can be noticed, but that’s not always the case.
How to check for cancer in urine?
When you pee in a cup at your doctor’s office, there are a number of things they and other health professionals can look for: 1 Urinalysis. Your doctor will check to see if there’s any blood, or other substances, in your urine. 2 Urine cytology. Your doctor will use a microscope to check your urine for cancer cells. 3 Urine culture. Your doctor will send your urine to a lab. After a few days, lab technicians will check to see what kinds of germs grow in it. These results will tell your doctor if you have a bladder infection. 4 Urine tumor marker tests. These look for substances that are released by bladder cancer cells. Your doctor may use one or more of these along with a urine cytology to see if you have the disease.
What does MRI show?
This will give your doctor an image of your kidney, bladder, and ureters (tubes that carry pee from your kidneys to your bladder). It’ll show tumors in your urinary tract. It can also show lymph nodes that contain cancer. MRI. This test uses radio waves and sound magnets to create images of your urinary tract.

What is a TURBT?
Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumor (TURBT) If your doctor finds something that doesn’t look right during your cystoscopy, they’ll take a sample of it ( biopsy) to see whether it’s cancer. During a TURBT, your surgeon will remove the tumor and some of the bladder muscle near it.
Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Coping and Support
Treatments include surgery, chemotherapy, and biological therapy.
Specialist to consult
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Diagnosing bladder cancer
Tests and procedures used to diagnose bladder cancer may include: 1. Using a scope to examine the inside of your bladder (cystoscopy).To perform cystoscopy, your doctor inserts a small, narrow tube (cystoscope) through your urethra. The cystoscope has a lens that allows your doct… - Determining the extent of the cancer
After confirming that you have bladder cancer, your doctor may recommend additional tests to determine whether your cancer has spread to your lymph nodes or to other areas of your body. Tests may include: 1. CTscan 2. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) 3. Positron emission tomog…