Contents
Medication
Tests for Bladder Cancer Medical history and physical exam. Your doctor will want to get your medical history to learn more about your symptoms. Urine lab tests. This is a simple lab test to check for blood and other substances in a sample of …
Procedures
These tests often include: Urinalysis to observe the levels of protein, sugar and red and white blood cells in the urine, which can signal the… Urine cytology to look for abnormal cells in the urine under a microscope. Imaging such as an ultrasound, …
Therapy
Stages and Outlook (Prognosis) After a cancer diagnosis, staging provides important information about the extent (amount) of cancer in the body and the likely response to treatment. Bladder Cancer Stages. Survival Rates for Bladder Cancer.
Nutrition
Screening for Bladder and Other Urothelial Cancers Tests are used to screen for different types of cancer when a person does not have symptoms.. Scientists study screening… Hematuria tests have been studied as a way to screen for bladder cancer.. Hematuria ( red …
What is the best test for bladder cancer?
A variety of tests may be used to make an exact diagnosis of bladder cancer. Pathology Tests. Screening typically begins with pathology tests, where samples of fluid and tissue are examined by a pathologist in a laboratory. The most efficient, noninvasive and inexpensive test is a urinalysis/cytology. Here, a sample of urine is taken from the patient and evaluated for cancer …
How to recognize the signs of bladder cancer?
· Notably, no single test is best able to detect bladder cancer, and usually different types of tests (i.e., urine tests, cystoscopy, and imaging techniques) are used in combination. For example, the Cxbladder genomic urine test in combination with ultrasound or computed tomography (CT) imaging has been shown to identify the presence or absence of bladder …
How bad is bladder cancer?
An ultrasound uses sound waves to create a picture of the inside of the body, which can be used to see if bladder cancer has spread to the kidneys or areas near the bladder. Bone scan. A bone scan is a procedure that is used to check whether bladder cancer has spread to the bones.
What are the symptoms and signs of bladder cancer?
Urinalysis can detect very small amounts of blood in the urine, which can sometimes help to diagnose bladder cancer at an earlier stage, if bladder cancer is present. Urinalysis can also be used to check the levels of other substances, such as …

Medical History and Physical Exam
Your doctor will want to get your medical history to learn more about your symptoms. The doctor might also ask about possible risk factors, includi…
Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumor (TURBT)
If an abnormal area (or areas) is seen during a cystoscopy, it will be biopsied to see if it is cancer. A biopsy is the removal of small samples of…
Biopsies to Look For Cancer Spread
If imaging tests suggest the cancer might have spread outside of the bladder, a biopsy might be needed to be sure.In some cases, biopsy samples of…
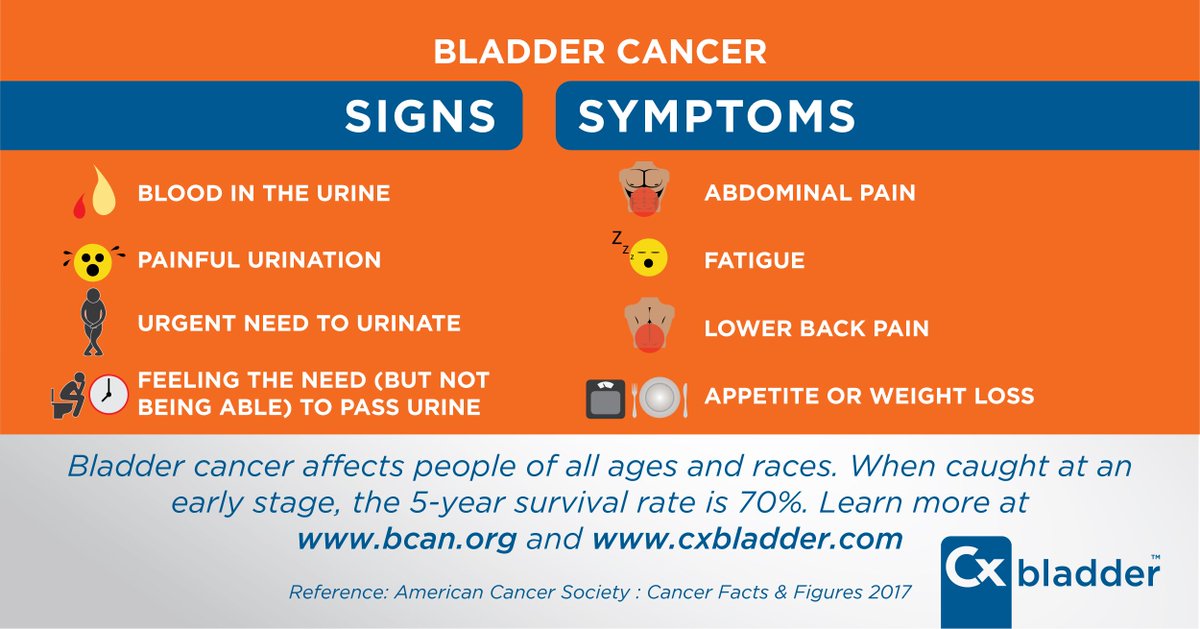
How to diagnose bladder cancer?
Tests and procedures used to diagnose bladder cancer may include: Using a scope to examine the inside of your bladder (cystoscopy). To perform cystoscopy, your doctor inserts a small , narrow tube (cystoscope) through your urethra. The cystoscope has a lens that allows your doctor to see the inside of your urethra and bladder, …
What tests can be done to determine if you have bladder cancer?
Tests may include: CT scan.
Can TURBT be used for bladder cancer?
TURBT can also be used to treat bladder cancer. Examining a urine sample (urine cytology). A sample of your urine is analyzed under a microscope to check for cancer cells in a procedure called urine cytology. Imaging tests.

What is a low grade bladder cancer?
Low-grade bladder cancer. This type of cancer has cells that are closer in appearance and organization to normal cells (well differentiated). A low-grade tumor usually grows more slowly and is less likely to invade the muscular wall of the bladder than is a high-grade tumor. High-grade bladder cancer.
What is the best treatment for cancer?
Radiation therapy, to destroy cancer cells, often as a primary treatment when surgery isn’t an option or isn’t desired. Immunotherapy, to trigger the body’s immune system to fight cancer cells, either in the bladder or throughout the body. Targeted therapy, to treat advanced cancer when other treatments haven’t helped.
How does radiation therapy help bladder cancer?
Radiation therapy. Radiation therapy uses beams of powerful energy, such as X-rays and protons, to destroy the cancer cells. Radiation therapy for bladder cancer usually is delivered from a machine that moves around your body, directing the energy beams to precise points.

Can bladder cancer recur after treatment?
Bladder cancer may recur, even after successful treatment. Because of this, people with bladder cancer need follow-up testing for years after successful treatment. What tests you’ll have and how often depends on your type of bladder cancer and how it was treated, among other factors.
What is staging after cancer diagnosis?
After a cancer diagnosis, staging provides important information about the extent (amount) of cancer in the body and the likely response to treatment.
Why is it important to find cancer early?
Finding cancer early, when it’s small and hasn’t spread, often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can be noticed, but that’s not always the case.
Where does bladder cancer start?
Most bladder cancers begin in the transitional cells. Squamous cell carcinoma: Cancer that forms in squamous cells (thin, flat cells that line the bladder). Cancer may form after long-term infection or irritation. Adenocarcinoma: Cancer that begins in glandular cells.
Is bladder cancer more common in men than women?
Bladder and other urothelial cancers are diseases in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the urothelium. Bladder cancer is more common in men than women. Smoking can affect the risk of bladder cancer.
What is the urothelium?
The urothelium is a layer of tissue that lines the urethra, bladder, ureters, prostate, and renal pelvis. Cancer that begins in the urothelium of the bladder is much more common than cancer that begins in the urothelium of the urethra, ureters, prostate, or renal pelvis. Because it is the most common form of urothelial cancer, …

What is screening for cancer?
Screening is looking for cancer before a person has any symptoms. This can help find cancer at an early stage. When abnormal tissue or cancer is found early, it may be easier to treat. By the time symptoms appear, cancer may have begun to spread.
Can cancer be found early?
This can help find cancer at an early stage. When abnormal tissue or cancer is found early, it may be easier to treat. By the time symptoms appear, cancer may have begun to spread. Scientists are trying to better understand which people are more likely to get certain types of cancer.
Do doctors think you have cancer?
It is important to remember that your doctor does not necessarily think you have cancer if he or she suggests a screening test. Screening tests are given when you have no cancer symptoms. If a screening test result is abnormal, you may need to have more tests done to find out if you have cancer.

Where is the bladder located?
The bladder is a hollow organ in the lower part of the abdomen. It is shaped like a small balloon and has a muscle wall that allows it to get larger or smaller to store urine made by the kidneys. There are two kidneys, one on each side of the backbone, above the waist.
What is the best imaging for bladder tumors?
MRI is another imaging form that creates very high-quality and detailed images of bladder tumors in addition to adjacent organs, such as the chest, pelvis and abdomen, to locate any metastasis. Ultrasound imaging, without side effects or radiation, is noninvasive and looks primarily at the bladder and kidneys.
What is the purpose of an intravenous pyelogram?
Imaging tests may be used to locate blockages and tumors, and determine whether cancer has spread to other organs. An intravenous pyelogram is an imaging test during which the patient is injected with dye and the radiologist observes with an X-ray the movement of that dye through the urinary tract.

Detecting Bladder Cancer with a Urine Test
Urine is made up of several components including water and waste materials filtered from the blood by the kidneys, as well as small numbers of cells such as epithelial cells shed from the lining of the urinary tract and possibly red and white blood cells.
What can be detected in a urine test?
Urine testing can assist in diagnosing many different disorders including kidney disease, diabetes, liver disorders, urinary tract infections (UTIs), and bladder cancer.
How are samples collected?
Requirements for urine sampling vary depending on the test/s being performed. Often the timing of collection is random, as dictated by the logistics of a doctor consult or access to a laboratory service. However, depending on the purpose of the test, certain urine voids of the day (e.g., the first or second void) may be preferred.
Can a urine test detect bladder cancer?
Several types of urine test have an important role in the overall process of diagnosing bladder cancer. Among these tests, urine cytology and urine tumor marker tests are used to detect the presence or absence of bladder cancer.
Urine-based tests used in the diagnosis of bladder cancer
Urinalysis#N#Urinalysis examines several physical, chemical, and microscopic features of urine samples.
Cxbladder is a genomic urine test for bladder cancer that improves overall detection accuracy
Cxbladder is a non-invasive and easy-to-use genomic urine test that quickly and accurately detects or rules out bladder cancer. The test combines clinical risk factor markers with genetic information, measuring five biomarker genes to detect the presence or absence of bladder cancer.

General Sources
American Cancer Society. Tests for Bladder Cancer. Accessed April 21, 2021.
What is a CT scan for bladder cancer?
To check if bladder cancer has spread, CT scans may be used to create images of the entire urinary tract (including the kidneys) as well as lymph nodes, other organs in the abdomen, and the lungs.
Can a chest x-ray detect bladder cancer?
If healthcare providers suspect that the bladder cancer may have spread to the patient’s lungs, then a chest x-ray may be used.

What is it called when bladder cancer spreads?
1,2 Bladder cancer that has spread ( metastasized) is called metastatic bladder cancer.
How does bladder cancer spread?
It can also spread through the lymph system, by traveling through lymph vessels to lymph nodes in different parts of the body. It can also spread through the body’s blood vessels and form tumors in other parts of the body, …
What is a retrograde pyelogram?
For example, intravenous or retrograde pyelograms are types of x-rays that use a special dye to highlight the organs of the urinary tract. This can make it possible to detect cancer that has spread to the kidneys, ureters, or other parts of the urinary tract.

What is ultrasound used for?
An ultrasound uses sound waves to create a picture of the inside of the body, which can be used to see if bladder cancer has spread to the kidneys or areas near the bladder.
Can a biopsy confirm cancer?
Biopsies can confirm if cancer has spread. If imaging shows that there are tumors in other organs, for example, then biopsies can be used to confirm the diagnosis. 1,2 Biopsies are small samples of tissue taken from the body and then analyzed in a laboratory to check for the presence of cancer cells.
How to diagnose bladder cancer?
If the healthcare provider thinks that bladder cancer may be the cause of the symptoms, the patient may be asked to provide a urine sample for analysis in the laboratory. Several types of urine lab tests may be used to help make a diagnosis of bladder cancer, including: 1 Urinalysis testing 2 Urine cytology testing 3 Urine culture testing 4 Urine tests for tumor markers

What is the test for bladder cancer?
A test that can detect substances often found on cancer cells, called mucin and carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) A test that can detect a protein (called NMP22) that is often elevated in patients with bladder cancer.
Why do people go to the doctor for bladder cancer?
Some patients visit their healthcare providers because they have symptoms such as visible blood in the urine or other urinary symptoms.
Can bladder cancer be diagnosed in urine?
If the healthcare provider thinks that bladder cancer may be the cause of the symptoms, the patient may be asked to provide a urine sample for analysis in the laboratory. Several types of urine lab tests may be used to help make a diagnosis of bladder cancer, including:

What is the medical term for blood in urine?
1-3 The medical term for the symptom of blood in the urine is hematuria.
Can you see blood in urine?
Many patients diagnosed with bladder cancer have the symptom of blood in the urine that is easily visible, but in some patients the amount of blood is so small that it is not visible to the naked eye. Urinalysis can detect very small amounts of blood in the urine, which can sometimes help to diagnose bladder cancer at an earlier stage, …
What is urine cytology?
Urine cytology tests to detect cancer cells. In a urine cytology test, a sample of the patient’s urine is analyzed under a microscope. 1,2 This test can reveal the presence of cancer cells or cells that are pre-cancerous, meaning that they are more likely to become cancer cells later.

What happens when your bladder is full?
When your bladder is full of water, it stretches. This lets the doctor see your entire bladder wall. They’ll ask you how it feels when it’s full. The doctor takes tissue samples. If an area looks abnormal, the doctor will use the cystoscope to cut a small piece that they can send to the lab for analysis.
What is a cystoscopy?
A cystoscopy is a test to check the health of your urethra and bladder. You might also hear it called a cystourethroscopy or, more simply, a bladder scope. It’s an outpatient test, which means you can get it at your doctor’s office, a hospital, or clinic and go home the same day. The doctor inserts a tube into your urethra.
How does a cystoscope work?
The cystoscope has a lens on the end that works like a telescope. It makes it easier for the doctor to see inside your body. They might put a video camera over the lens to project images onto a screen. The doctor fills your bladder. They put water or saline in through the cystoscope.

How long does it take to get a cystoscopy?
What to Expect During Cystoscopy. The procedure generally takes about 15 to 20 minutes. You’ll need to pee first. The test is done with an empty bladder. You’ll lie down. The position depends on the type of scope your doctor uses: Standard rigid cystoscope. You’ll lie on your back with your knees up and apart.
Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Coping and Support
Treatments include surgery, chemotherapy, and biological therapy.
Specialist to consult
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Diagnosing bladder cancer
Tests and procedures used to diagnose bladder cancer may include: 1. Using a scope to examine the inside of your bladder (cystoscopy).To perform cystoscopy, your doctor inserts a small, narrow tube (cystoscope) through your urethra. The cystoscope has a lens that allows your doct… - Determining the extent of the cancer
After confirming that you have bladder cancer, your doctor may recommend additional tests to determine whether your cancer has spread to your lymph nodes or to other areas of your body. Tests may include: 1. CTscan 2. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) 3. Positron emission tomog…