Contents
The 3 main types of bladder cancer are:
- Urothelial carcinoma. Urothelial carcinoma (or UCC) accounts for about 90% of all bladder cancers. …
- Squamous cell carcinoma. Squamous cells develop in the bladder lining in response to irritation and inflammation. …
- Adenocarcinoma. This type accounts for about 2% of all bladder cancers and develops from glandular cells.
- Urothelial carcinoma. Urothelial carcinoma (or UCC) accounts for about 90% of all bladder cancers. …
- Squamous cell carcinoma. Squamous cells develop in the bladder lining in response to irritation and inflammation. …
- Adenocarcinoma.
What is the worst type of bladder cancer?
Types of Urothelial Cancer. Precursor lesions ▼. Invasive Urothelial Carcinoma ▼. Morphologic Variants of Urothelial Carcinoma ▼. PD-L1 Testing in Urothelial Carcinoma ▼.
What is the most common type of bladder cancer?
Other types of bladder cancer include: Squamous cell carcinoma Adenocarcinoma Small cell carcinoma Sarcomas
What are the chances of dying from bladder cancer?
· Overall, around 2% of bladder cancers are adenocarcinomas. 2 Small cell carcinoma: Small cell carcinomas of the bladder start in nerve-like cells. This bladder cancer type is rare, accounting for less than 1% of bladder cancers, 4 but can grow rapidly and spread to other parts of the body.

What are the 3 types of bladder cancer?
TypesTransitional cell (urothelial) bladder cancer. About 90 out of 100 bladder cancers in the UK (about 90%) are the transitional cell type. … Squamous cell bladder cancer. About 5 out of every 100 (5%) bladder cancers are squamous cell cancers. … Adenocarcinoma. This is a very rare type of bladder cancer. … Rarer types.
What is the most common bladder cancer?
Urothelial carcinoma, also known as transitional cell carcinoma (TCC), is by far the most common type of bladder cancer. In fact, if you have bladder cancer it’s almost certain to be a urothelial carcinoma.
What is an aggressive form of bladder cancer?
Muscle invasive bladder cancer is a serious and more advanced stage of bladder cancer. MIBC is when the cancer has grown far into the wall of the bladder (Stages T2 and beyond). For patients with MIBC, the overall prognosis (how the disease may progress) is dependent on stage and treatment.
What are the two types of bladder cancer?
Noninvasive bladder cancer: The cancer cells are found only in the innermost layer of the cells of the bladder, called the transitional epithelium. The cancer hasn’t yet grown any deeper than this first layer. Invasive bladder cancer: The cancer cells have grown beyond the first layer of the bladder wall.

What is low grade papillary urothelial carcinoma?
Low-grade papillary urothelial carcinomas are characterized by orderly appearance of cells that are evenly spaced and cohesive. There is minimal but definitive nuclear atypia that is characterized by hyperchromasia, mild variation of nuclear size and mitoses are infrequent.
Is urothelial carcinoma in situ?
Urothelial carcinoma in-situ (CIS): In contrast to papillary carcinomas, CIS is a flat high-grade cancer that is difficult to visualize in cystoscopy. CIS is always high-grade as it has a has a 50% to 75% risk of becoming invasive, if left untreated.
What is a low grade tumor?
Those tumors with mild atypia are called “low-grade”, while those tumors with more pronounced atypia are called “high-grade.”. Both low- and high-grade tumors can be multifocal and frequently recur after resection. Low-grade papillary urothelial carcinomas are characterized by orderly appearance of cells that are evenly spaced and cohesive.
Can PD-L1 be tested for immunotherapy?
With the advent of immunotherapy and FDA approval of immunotherapy in certain patients, testing of PD-L1 expression in urothelial carcinomas has become frequent. PD-L1 expression is tested using immunohistochemistry on the same tissue that has been used for a pathologic diagnosis. Patients with a positive test result are more likely to respond to immunotherapy, but some patients with negative tests can also show some favorable response.
Is a mesenchymal tumor benign?
Mesenchymal tumors arise from the connective tissue cells of the bladder. These tumors are much less common than urothelial tumors and can be benign or malignant. Malignant mesenchymal tumors are termed sarcomas. Sarcomas can become large and have the capacity to invade adjacent organs and give rise to distant metastases. The most common sarcoma of infancy is rhabdomyosarcoma and of adults is leiomyosarcomas.
What is the most significant prognostic factor?
The extent of invasion is the most significant prognostic factor and determines the type of therapy. Understaging a tumor in a bladder biopsy is a common problem. Tumors that invade the lamina propria only are frequently managed conservatively with a combination of transurethral resection and intravesical therapy …
What are the different types of bladder cancer?
There are several different types of bladder cancers. 2 However, one type of bladder cancer—called urothelial carcinoma —is by far the most common in the United States. Other types of bladder cancer include: 1 Squamous cell carcinoma 2 Adenocarcinoma 3 Small cell carcinoma 4 Sarcomas
What is bladder cancer?
What is a bladder tumor? When cancer cells start growing in the bladder, they can form a group of cells called a bladder tumor . A bladder tumor is sometimes called a bladder mass. Bladder tumors made up of cancer cells are called malignant tumors, and these cancer cells can spread to other parts of the body outside of the bladder.
Do cancer cells die off?
Cancer cells grow in an uncontrolled way. New cancer cells keep developing, but the old cancer cells do not die off as they should. The cancer cells can start to crowd out the healthy cells.

What is urothelial carcinoma?
What is a urothelial carcinoma? Around 90% of people who are diagnosed with bladder cancer in the United States have the type called urothelial carcinoma. 2,3 It is called “urothelial” because the cancer cells start out by developing in the lining of the bladder walls, in a layer of cells called the urothelium.
Is bladder cancer invasive?
Bladder cancer can be invasive or non-invasive. If it is non-invasive, then all the cancer cells are still located in the thin layer of cells in the lining of the bladder wall (the urothelium) and have not grown deeper into the bladder. If it is invasive, then the cancer cells have grown deeper into the bladder wall.
Can bladder cancer spread to other areas?
If it is invasive, then the cancer cells have grown deeper into the bladder wall. Bladder cancer that is invasive is more likely to spread into the bladder muscle and on to other areas of the body. The shape of a bladder tumor can be either papillary or flat. Both papillary and flat tumors can be invasive or non-invasive, …

What is a flat tumor?
Papillary or flat tumors. Papillary tumors grow out from the inner lining toward the hollow center of the bladder, in slim finger-shaped growths. These are often non-invasive, because they grow outward from the bladder lining rather than inward deeper into the bladder walls. One type of slow growing, non-invasive papillary bladder cancer is called …
What are the different grades of bladder cancer?
What are the different “grades” for a bladder cancer tumor? Grade is expressed as a number between 1 (low) and 3 (high, i.e. G3); the higher the number the less the tumor resembles a normal cell. In lieu of numbers to grade a bladder cancer tumor, your doctor may refer to the tumor simply as low or high grade.
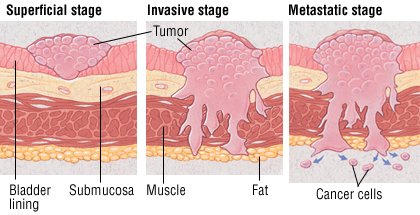
What are the stages of bladder cancer?
Stage suggests the location of the tumor in relation to the inner lining of the bladder. The higher the stage the further the tumor has grown away from its original site on the surface. The following are the stages for bladder tumors: 1 T0: No tumor 2 Ta: Papillary tumor without invading the bladder wall 3 TIS (CIS): Carcinoma in situ (non-invasive flat high- grade (G3) cancer) 4 T1: Tumor invades the connective tissue under the surface lining 5 T2: Tumor invades the muscle layer 6 T3: Tumor penetrates the bladder wall and invades the surrounding fat layer 7 T4: Tumor invades other organs (i.e., prostate, uterus, vagina, pelvic wall)

Where do bladder cancers occur?
While the majority of bladder cancers (approximately 90-95%) arise in the bladder, the urothelial cells that line the bladder are found in other locations in the urinary system. Sometimes these urothelial cancers can occur in the lining of the kidney or in the ureter that connects the kidney to the bladder.
Where do papillary tumors grow?
Papillary tumors stick out from the bladder lining on a stalk. They tend to grow into the bladder cavity, away from the bladder wall, instead of deeper into the layers of the bladder wall. Sessile tumors lie flat against the bladder lining.
What is CIS in a patient?
CIS is a type of nonmuscle-invasive bladder cancer that is of higher grade and increases the risk of recurrence and progression. At diagnosis, approximately 10% of patients with bladder cancer present with CIS.

How many types of bladder cancer are there?
There are four main types of bladder cancer:
What is bladder cancer called?
Bladder cancers are called superficial, or non-invasive, if they stay confined to the bladder tissue in which they began. For example, Urothelial cancer is considered superficial bladder cancer if it has not spread anywhere outside of the bladder lining.
How is bladder cancer determined?
A patient’s specific type of cancer is determined by the type of cell from which the cancer originated, as well as how the tumor cells look under a microscope. There are four main types of bladder cancer: Urothelial or transitional cell carcinoma. Squamous cell carcinoma. Adenocarcinoma.
/GettyImages-1133641181-d459589c88754fec87508d5c021b6d09.jpg)
Is bladder cancer invasive?
Bladder cancer can be invasive or non-invasive, and the type of bladder cancer you have may affect the likelihood of cancer cells traveling to other parts of the body or recurring after treatment.
What is the name of the cancer that starts in the bladder?
Urothelial carcinoma. Urothelial carcinoma — also known as transitional cell carcinoma — is a type of bladder cancer that starts in the surface of the bladder’s lining. It can also be referred to as Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer, or NMIBC.
Where does bladder cancer start?
Almost all bladder cancers start in the urothelium. When the bladder is empty, urothelial cells bunch together. When full, the cells stretch out. The cells can then be reached by urinary chemicals (e.g. from cigarette smoke) that may cause bladder cancer.

What happens when the bladder is empty?
When the bladder is empty, urothelial cells bunch together. When full, the cells stretch out. The cells can then be reached by urinary chemicals (e.g. from cigarette smoke) that may cause bladder cancer. If bladder cancer affects only the urothelium it is called superficial or non-invasive.
What are the different types of bladder cancer?
There are three main types of bladder cancer, and another kind of cancer (the last on the list) that’s rarely but still sometimes seen in the bladder: 1 Urothelial carcinoma, also called transitional cell carcinoma 2 Squamous cell carcinoma 3 Adenocarcinoma 4 Small cell carcinoma
What type of cancer is found in the bladder?
There are three main types of bladder cancer, and another kind of cancer (the last on the list) that’s rarely but still sometimes seen in the bladder: Urothelial carcinoma, also called transitional cell carcinoma. Squamous cell carcinoma. Adenocarcinoma. Small cell carcinoma.

What is the first sign of bladder cancer?
Most often, the first sign that ultimately leads to the diagnosis of bladder cancer is blood in the urine.
How to tell if you have bladder cancer?
Most often, the first sign that ultimately leads to the diagnosis of bladder cancer is blood in the urine. Known as hematuria, the presence of blood in the urine may be noticed by the individual or it may be too minute to see with the naked eye but detected under a microscope during a routine urine test, or urinalysis.
What is it called when you see blood in your urine?
Known as hematuria, the presence of blood in the urine may be noticed by the individual or it may be too minute to see with the naked eye but detected under a microscope during a routine urine test, or urinalysis.
/GettyImages-1133641181-d459589c88754fec87508d5c021b6d09.jpg)
How many people die from bladder cancer?
There are three main types of bladder cancer, and another kind of cancer (the last on the list) that’s rarely but still sometimes seen in the bladder: Annually, about 56,000 men and 18,000 women get bladder cancer, and approximately 12,000 men and 5,000 women die from it, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
What is the second most common form of skin cancer?
Squamous cell carcinoma is the second most common form of skin cancer, accounting for perhaps 1% to 2% of bladder cancers. Viewed under the microscope, squamous cells look similar to the flat cells found on the surface of the skin. Adenocarcinoma accounts for just about 1% of bladder cancer cases, according to the American Cancer Society.
What type of cancer is a bladder cancer?
Less than 1% of bladder cancers are small-cell carcinomas. They start in nerve-like cells called neuroendocrine cells. These cancers often grow quickly and usually need to be treated with chemotherapy like that used for small cell carcinoma of the lung.

What is the most common type of bladder cancer?
Urothelial carcinoma, also known as transitional cell carcinoma (TCC), is by far the most common type of bladder cancer. In fact, if you have bladder cancer it’s almost certain to be a urothelial carcinoma. These cancers start in the urothelial cells that line the inside of the bladder.
Where does cancer spread?
(To learn more about how cancers start and spread, see What Is Cancer?) The bladder is a hollow organ in the lower pelvis. It has flexible, muscular walls that can stretch to hold urine and squeeze to send it out of the body.
What is the function of the bladder?
It has flexible, muscular walls that can stretch to hold urine and squeeze to send it out of the body. The bladder’s main job is to store urine. Urine is liquid waste made by the 2 kidneys and then carried to the bladder through 2 tubes called ureters.

What is the job of the bladder?
The bladder’s main job is to store urine. Urine is liquid waste made by the 2 kidneys and then carried to the bladder through 2 tubes called ureters. When you urinate, the muscles in the bladder contract, and urine is forced out of the bladder through a tube called the urethra.
Can bladder cancer be treated with chemotherapy?
These less common types of bladder cancer (other than sarcoma) are treated a lot like TCCs, especially early-stage tumors, but if chemotherapy is needed, different drugs might be used.
What is the bladder wall made of?
The wall of the bladder has many several layers. Each layer is made up of different kinds of cells (see Bladder Cancer Stages for details on the different layers). Most bladder cancers start in the innermost lining of the bladder, which is called the urothelium or transitional epithelium. As the cancer grows into or through the other layers in …

What is the first treatment for bladder cancer?
Chemo (with or without radiation) is typically the first treatment when bladder cancer has spread to distant parts of the body (M1). After this treatment the cancer is rechecked. If it looks like it’s gone, a boost of radiation to the bladder may be given or cystectomy might be done.
Can bladder cancer be cured?
The outlook for people with stage 0a (non-invasive papillary) bladder cancer is very good. These cancers can be cured with treatment. During long-term follow-up care, more superficial cancers are often found in the bladder or in other parts of the urinary system.
What are the factors that affect cancer treatment?
Other factors, such as the size of the tumor, how fast the cancer cells are growing (grade), and a person’s overall health and preferences, also affect treatment options.

What is stage 0 bladder cancer?
Stage 0 bladder cancer includes non-invasive papillary carcinoma (Ta) and flat non-invasive carcinoma (Tis or carcinoma in situ). In either case, the cancer is only in the inner lining layer of the bladder. It has not invaded (spread deeper into) the bladder wall.
Can stage IV cancer spread to lymph nodes?
These cancers have reached the pelvic or abdominal wall (T4b), may have spread to nearby lymph nodes (any N), and/or have spread to distant parts of the body (M1). Stage IV cancers are very hard to get rid of completely.
How to get rid of stage IV cancer?
The tumor is then rechecked. If it appears to be gone, chemo with or without radiation or cystectomy are options.

What is the treatment for T3 tumors?
An option for some patients with single, small tumors (some T3) might be treatment with a second (and more extensive) transurethral resection (TURBT) followed by a combination of chemo and radiation. If cancer is still found when cystoscopy is repeated, cystectomy might be needed.