Contents

- Smoking. Smoking cigarettes, cigars or pipes may increase the risk of bladder cancer by causing harmful chemicals to accumulate in the urine. …
- Increasing age. …
- Being male. …
- Exposure to certain chemicals. …
- Previous cancer treatment. …
- Chronic bladder inflammation. …
- Personal or family history of cancer.
Symptoms
Some genes control when cells grow, divide into new cells, and die: Genes that help cells grow, divide, and stay alive are called oncogenes. Genes that normally help control cell division, repair mistakes in DNA, or cause cells to die at the right time are called tumor suppressor genes.
Causes
· Symptoms of bladder cancer include: Blood in the urine ( hematuria) Usually the first sign of bladder cancer. Urine may appear orange, pink, or, less often, dark red. Changes in bladder habits. Bladder irritation. Urinary frequency. Pain or burning during urination. Feeling as if you need to go …
Prevention
The main cause of bladder cancer, or most common risk factor in the United States, is smoking. The second group of exposure risk factors include exposures to carcinogens or a history of radiation therapy for another cancer (for example, prostate cancer), or chemotherapy agents, mainly cyclophosphamide.
Complications
· What Is the Main Cause of Bladder Cancer? Chronic urinary infections (such as cystitis) Schistosomiasis (a parasitic infection) Previous cancer therapy.
What are the chances of having bladder cancer?
The main cause of bladder cancer, or most common risk factor in the United States, is smoking. The second group of exposure risk factors include exposures to carcinogens or a history of radiation therapy for another cancer (for example, prostate cancer), or chemotherapy agents, mainly cyclophosphamide.
How dangerous is bladder cancer?
Learn about the risk factors for bladder cancer and what you might be able to do to help lower your risk. … From basic information about cancer and its causes to in-depth information on specific cancer types – including risk factors, early detection, diagnosis, and treatment options – you’ll find it here. Explore Cancer A-Z; Breast …
What are the early warning signs of bladder cancer?
Bladder Cancer Bladder cancer originates within the bladder, and may have several different causes, including smoking, workplace chemical exposures, diet, and the herb Aristolochia fangchi. Though there are several types of bladder cancer, cancer is most likey to develop in the interior lining of the bladder.
What are the risk factors for bladder cancer?
· It is unknown what causes most cases of bladder cancer, but genetic changes are thought to play a role. Risk factors for developing bladder cancer include: Smoking The main risk factor for bladder cancer Accounts for about half of all bladder cancers in both men and women Certain medicines or herbal supplements
See more
Blood in the urine doesn’t always mean you have bladder cancer. More often it’s caused by other things like an infection, benign (not cancer) tumors, stones in the kidney or bladder, or other benign kidney diseases. Still, it’s important to have it checked by a doctor so the cause can be found. Changes in bladder habits or symptoms of irritation
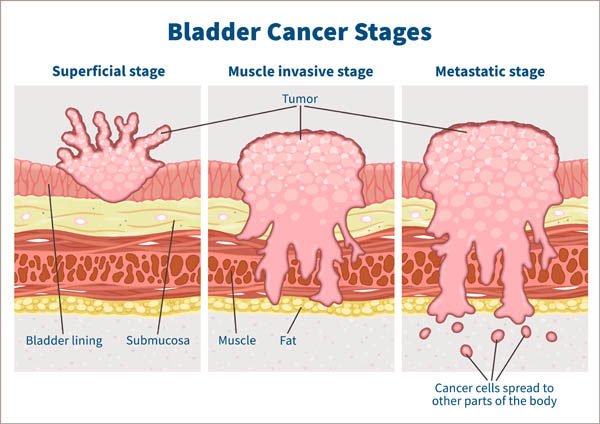
Why does bladder cancer happen?
Bladder cancer forms when the DNA in cells in the bladder mutate or change, disabling the functions that control cell growth. In many cases, these mutated cells die or are attacked by the immune system. But some mutated cells may escape the immune system and grow out of control, forming a tumor in the bladder.
How can bladder cancer be prevented?
Can Bladder Cancer Be Prevented?Don’t smoke. Smoking is thought to cause about half of all bladder cancers. … Limit exposure to certain chemicals in the workplace. Workers in industries that use certain organic chemicals have a higher risk of bladder cancer. … Drink plenty of liquids. … Eat lots of fruits and vegetables.
What are the 3 types of bladder cancer?
The 3 main types of bladder cancer are:Urothelial carcinoma. Urothelial carcinoma (or UCC) accounts for about 90% of all bladder cancers. … Squamous cell carcinoma. Squamous cells develop in the bladder lining in response to irritation and inflammation. … Adenocarcinoma.
Who is more at risk for bladder cancer?
The risk of developing bladder cancer increases with age. It usually occurs in people older than 65 years of age. Bladder cancer is most common in Caucasians, and men develop this disease more often than women.
Does coffee cause cancer of the bladder?
In summary, findings from this large meta-analysis of prospective studies suggest that coffee consumption was not significantly associated with long-term risk of bladder cancer. Such a null association was similar for men and women, and was confirmed in never smokers.
Which of the following is usually the first symptom of bladder cancer?
For most people, the first symptom of bladder cancer is blood in the urine, also called hematuria. Sometimes the blood is visible, prompting the patient to visit a doctor.
Do you feel ill with bladder cancer?
Nausea and vomiting. Burning or pain when you urinate, feeling the need to go often, or blood in urine. Diarrhea. Feeling tired.
Does bladder cancer spread fast?
It is an early stage cancer but is always high grade. This means it can grow quickly and might spread. If you have bladder carcinoma in situ your doctor will start treatment straight away.
Does alcohol cause bladder cancer?
Conclusion: No significant association between alcohol consumption and bladder cancer risk was found in the entire population, but there was a linear dose-response relation in those who consume alcohol from liquor or spirits. Alcohol may elevate the risk of bladder cancer in males in a dose-independent way.
Can Tea cause bladder cancer?
[6] found no association between tea consumption and bladder cancer risk. The authors reported that the consumption of tea seems not to be related to an increased risk of urinary tract cancer.
Is bladder cancer curable?
Bladder cancer is highly treatable when it is diagnosed in the early stages. The main types of treatments for bladder cancer include: Surgery : Bladder cancer treatment almost always has a surgical component that may be combined with other non-invasive approaches, including those listed below.
How is bladder cancer detected?
A sample of your urine is analyzed under a microscope to check for cancer cells in a procedure called urine cytology. Imaging tests. Imaging tests, such as computerized tomography (CT) urogram or retrograde pyelogram, allow your doctor to examine the structures of your urinary tract.

How does bladder cancer develop?
Bladder cancer develops when cells in the bladder begin to grow abnormally, forming a tumor in the bladder. Bladder cancer begins when cells in the bladder develop changes (mutations) in their DNA. A cell’s DNA contains instructions that tell the cell what to do.
Where does bladder cancer start?
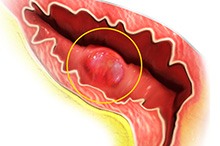
Bladder cancer is a common type of cancer that begins in the cells of the bladder. The bladder is a hollow muscular organ in your lower abdomen that stores urine. Bladder cancer most often begins in the cells (urothelial cells) that line the inside of your bladder. Urothelial cells are also found in your kidneys and the tubes (ureters) …
Where is the bladder located?
Your kidneys, located in the rear portion of your upper abdomen, produce urine by filtering waste and fluid from your blood. Bladder cancer is a common type of cancer that begins in the cells of the bladder. The bladder is a hollow muscular organ in your lower abdomen that stores urine. Bladder cancer most often begins in …

Where is urothelial cancer found?
Urothelial cells are also found in your kidneys and the tubes (ureters) that connect the kidneys to the bladder. Urothelial cancer can happen in the kidneys and ureters, too, but it’s much more common in the bladder. Most bladder cancers are diagnosed at an early stage, when the cancer is highly treatable.
Can bladder cancer come back?
But even early-stage bladder cancers can come back after successful treatment. For this reason, people with bladder cancer typically need follow-up tests for years after treatment to look for bladder cancer that recurs.
How do you know if you have bladder cancer?
Bladder cancer signs and symptoms may include: Blood in urine (hematuria), which may cause urine to appear bright red or cola colored, though sometimes the urine appears normal and blood is detected on a lab test. Frequent urination. Painful urination. Back pain.

What is the most common type of bladder cancer?
Urothelial carcinoma is the most common type of bladder cancer in the United States. Squamous cell carcinoma. Squamous cell carcinoma is associated with chronic irritation of the bladder — for instance, from an infection or from long-term use of a urinary catheter. Squamous cell bladder cancer is rare in the United States.
What causes bladder cancer?
Causes of bladder cancer are often genetic, and risk factors include smoking, chemical exposure, race, age and other variables. Bladder cancer is a type of cancer that occurs when cells in the bladder become abnormal and grow out of control. Types of bladder cancers include:
What is the most common type of bladder cancer?
Types of bladder cancers include: Urothelial carcinoma , also known as transitional cell carcinoma (TCC): the most common type of bladder cancer. Squamous cell carcinoma: only about 1% to 2% of bladder cancers are squamous cell …
What causes a swollen bladder?
Chronic bladder irritation and infections. Urinary infections ( UTIs ), kidney and bladder stones, bladder catheters left in place a long time, and other causes of chronic bladder irritation. Schistosomiasis ( bilharziasis ), parasitic worm infection that can get into the bladder.
What is the procedure for removing the bladder?
Surgical removal of all or part of the bladder (radical or partial cystectomy): for invasive bladder cancer. Reconstructive surgery after radical cystectomy: if the entire bladder is removed, patients need another way to store urine and pass it out of the body.
How long do you live with bladder cancer?
Life expectancy for bladder cancer is often expressed in 5-year survival rates, that is, how many people will be alive 5 years after diagnosis. Bladder cancer 5-year survival rates: In situ (cancer is still confined to the cells in which it initially started and has not spread into any nearby tissue): 96%.
What does it mean when you have blood in your urine?
Blood in the urine ( hematuria) Usually the first sign of bladder cancer . Urine may appear orange, pink, or, less often, dark red. Changes in bladder habits. Bladder irritation. Urinary frequency. Pain or burning during urination. Feeling as if you need to go right away, even when the bladder isn’t full.
Why does my urine turn red?
Bladder irritation. Urinary frequency. Pain or burning during urination. Feeling as if you need to go right away, even when the bladder isn’t full. Difficulty urinating or having a weak urine stream .
Can you prevent bladder cancer?
There is no sure way to prevent bladder cancer. But you can take certain measures to lower your risk of developing it. These include the following:

Top What Is the Main Cause of Bladder Cancer? Related Articles
Bladder cancer occurs when cancerous cells, often from the lining of the bladder, begin to multiply. Find more information about bladder cancer, the stages of bladder cancer, and available treatment options.
Risk Factors
A risk factor is anything that affects your chance of getting a disease such as cancer. Learn more about the risk factors for bladder cancer.
Prevention
There’s no way to completely prevent cancer. But there are things you can do that might help lower your risk. Learn more.

What Causes Bladder Cancer?
It is unknown what causes most cases of bladder cancer, but genetic changes are thought to play a role.
How Is Bladder Cancer Diagnosed?
Bladder cancer is diagnosed with a physical examination which may involve a digital rectal exam (DRE) and in women, a pelvic exam.
What Is the Treatment for Bladder Cancer?
Treatment for bladder cancer may involve one or more of the following:

Can bladder cancer cause bleeding?
Usually, the early stages of bladder cancer (when it’s small and only in the bladder) cause bleeding but little or no pain or other symptoms. Blood in the urine doesn’t always mean you have bladder cancer.
What are the symptoms of bladder cancer?
Being unable to urinate. Lower back pain on one side. Loss of appetite and weight loss. Feeling tired or weak. Swelling in the feet. Bone pain. Again, many of these symptoms are more likely to be caused by something other than bladder cancer, but it’s important to have them checked.
How do you know if you have bladder cancer?
Bladder cancers that have grown large or have spread to other parts of the body can sometimes cause other symptoms, such as: Being unable to urinate. Lower back pain on one side. Loss of appetite and weight loss. Feeling tired or weak.
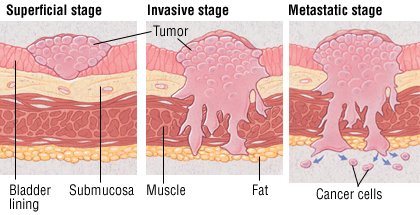
Can bladder cancer spread to other parts of the body?
Bladder cancers that have grown large or have spread to other parts of the body can sometimes cause other symptoms, such as: Again, many of these symptoms are more likely to be caused by something other than bladder cancer, but it’s important to have them checked.
Can bladder cancer cause lower back pain?
Bladder cancers that have grown large or have spread to other parts of the body can sometimes cause other symptoms, such as: Being unable to urinate. Lower back pain on one side. Loss of appetite and weight loss. Feeling tired or weak.
What does it mean when you have blood in your urine?
Blood in the urine. In most cases, blood in the urine (called hematuria) is the first sign of bladder cancer. There may be enough blood to change the color of the urine to orange, pink, or, less often, dark red.
Why do I have trouble peeing?
Having to get up to urinate many times during the night. These symptoms are more likely to be caused by a urinary tract infection (UTI), bladder stones, an overactive bladder, or an enlarged prostate (in men).