Contents

How effective is chemotherapy for bladder cancer?
· Cisplatin-based chemotherapy has been the best standard treatment for bladder cancer since the 1970’s. Based on the results of clinical trials from the 1990s, the two regimens most commonly used are dose-dense (DD) MVAC and …
Does bladder cancer require chemotherapy for treatment?
Chemotherapy before Surgery for Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer. For muscle-invasive bladder cancer, our doctors may recommend chemotherapy before surgery. This treatment approach is called neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Large clinical studies have shown that this method improves cure rates and long-term survival for people with muscle-invasive bladder cancer. We typically …
What is the newest treatment for bladder cancer?
Transurethral resection (TURBT) is often done first to find out how far the cancer has grown into the bladder wall. Chemotherapy followed by radical cystectomy (removal of the bladder and nearby lymph nodes) is then the standard treatment. Partial cystectomy is rarely an option for stage III cancers.
What medications cause bladder cancer?
· The combinations most often used for bladder cancer are: Dose-dense methotrexate, vinblastine, doxorubicin, and cisplatin (called DDMVAC) Cisplatin, methotrexate, and vinblastine (called CMV) Gemcitabine and cisplatin Gemcitabine and carboplatin Carboplatin and paclitaxel Paclitaxel and gemcitabine Chemo is given in cycles.

How many chemo treatments are needed for bladder cancer?
Chemotherapy before surgery or radiotherapy usually 3 cycles. Chemotherapy after surgery or radiotherapy, or alongside radiotherapy, can be 6 or more cycles.
What is the latest treatment for bladder cancer?
Advanced and metastatic bladder cancer treatment A notable new FDA approval in December 2019 was enfortumab vedotin (Padcev), approved for advanced bladder cancer patients who have not responded to chemotherapy or immune checkpoint drugs.
Is bladder cancer treated with chemotherapy?
Intravesical chemotherapy. For this treatment, chemotherapy (chemo) drugs are put right into the bladder through a catheter. These drugs kill actively growing cancer cells. Many of these same drugs can also be given systemically (usually into a vein) to treat more advanced stages of bladder cancer.
Do you always need chemo for bladder cancer?
Chemo (with or without radiation) is typically the first treatment when bladder cancer has spread to distant parts of the body (M1). After this treatment the cancer is rechecked. If it looks like it’s gone, a boost of radiation to the bladder may be given or cystectomy might be done.
Does bladder cancer spread quickly?
They tend to grow and spread slowly. High-grade bladder cancers look less like normal bladder cells. These cancers are more likely to grow and spread.
Are most bladder cancers curable?
What are the most common treatments for bladder cancer? Bladder cancer is highly treatable when it is diagnosed in the early stages.
How long does chemo stay in your bladder?
It generally takes about 48 to 72 hours for your body to break down and/or get rid of most chemo drugs. But it’s important to know that each chemo drug is excreted or passed through the body a bit differently.
Is bladder cancer a terminal?
The general 5-year survival rate for people with bladder cancer is 77%. However, survival rates depend on many factors, including the type and stage of bladder cancer that is diagnosed. The 5-year survival rate of people with bladder cancer that has not spread beyond the inner layer of the bladder wall is 96%.
How do you know if chemo is working for bladder cancer?
The best way to tell if chemotherapy is working for your cancer is through follow-up testing with your doctor. Throughout your treatment, an oncologist will conduct regular visits, and blood and imaging tests to detect cancer cells and whether they’ve grown or shrunk.
Is chemotherapy for bladder cancer painful?
Some chemo drugs can cause other, less common side effects. For example, drugs like cisplatin, docetaxel, and paclitaxel can damage nerves. This can sometimes lead to symptoms (mainly in the hands and feet) such as pain, burning or tingling, sensitivity to cold or heat, or weakness.
What is the main cause of bladder cancer?
Smoking. Smoking is the single biggest risk factor for bladder cancer. This is because tobacco contains cancer-causing (carcinogenic) chemicals. If you smoke for many years, these chemicals pass into your bloodstream and are filtered by the kidneys into your urine.
Is a 5 cm bladder tumor large?
CONCLUSIONS: Larger tumor size (>5 cm) is associated with greater length of stay, reoperation, readmission, and death following TURBT. Patients should be counseled appropriately and likely warrant vigilant observation prior to and following hospital discharge.
Treating Stage 0 Bladder Cancer
Stage 0 bladder cancer includes non-invasive papillary carcinoma (Ta) and flat non-invasive carcinoma (Tis). In either case, the cancer has not inv…
Treating Stage I Bladder Cancer
Stage I bladder cancers have grown into the connective tissue layer of the bladder wall but have not reached the muscle layer.Transurethral resecti…
Treating Stage II Bladder Cancer
These cancers have invaded the muscle layer of the bladder wall. Transurethral resection (TURBT) is typically the first treatment for these cancers…
Treating Stage III Bladder Cancer
These cancers have reached the outside of the bladder and might have grown into nearby tissues or organs.Transurethral resection (TURBT) is typical…
Treating Stage IV Bladder Cancer
These cancers have reached the abdominal or pelvic wall (T4b tumors) or have spread to nearby lymph nodes or distant parts of the body. Stage IV ca…
Treating Bladder Cancer That Progresses Or Recurs
If cancer continues to grow during treatment (progresses) or comes back (recurs), your treatment options will depend on where and how much the canc…

What is the treatment for bladder cancer?
Our standard treatments for bladder cancer that has spread include conventional chemotherapy regimens and immunotherapy treatments as well as approaches that are being tested in clinical trials. These approaches are designed to shrink tumors and relieve symptoms while maintaining quality of life. At MSK, our doctors are continuously seeking out new chemotherapy combinations to provide better outcomes for the people we care for.
How long does intravenous chemo stay in the bladder?
The drug stays in the bladder for one to two hours.
How long does mitomycin stay in the bladder?
The drug stays in the bladder for one to two hours. Then it is drained out through the catheter or in urine. For early-stage (non-muscle-invasive) bladder cancer, we may give intravesical chemotherapy after transurethral resection to reduce the chance that the cancer will return. We typically use the drug mitomycin (Mitosol ®) …
What to look for before starting chemo?
Before beginning chemotherapy, you’ll undergo a comprehensive evaluation to see how well you may tolerate certain treatments. This includes a careful consideration of your age, general health condition, and kidney, heart, and liver function. We also take into account the characteristics of the tumor.
Can you have chemo without neoadjuvant?
Some people may have surgery without neoadjuvant chemotherapy. In this case, chemotherapy after surgery (adjuvant chemotherapy) can kill any remaining cancer cells and reduce the chances that these cancer cells will form new tumors. For adjuvant chemotherapy, we use the same drugs, gemcitabine and cisplatin, that are used for neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
Can you get chemo for bladder cancer?
If you have bladder cancer that has spread , you may receive chemotherapy as the main treatment when surgery is not an option. At MSK, our medical oncologists specialize in chemotherapy for bladder cancer.
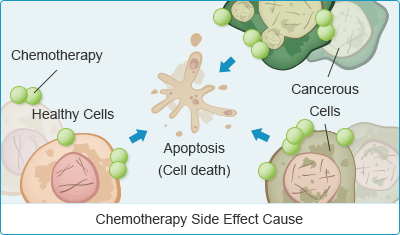
What is the first treatment for bladder cancer?
Chemo (with or without radiation) is typically the first treatment when bladder cancer has spread to distant parts of the body (M1). After this treatment the cancer is rechecked. If it looks like it’s gone, a boost of radiation to the bladder may be given or cystectomy might be done.
What is the treatment for cancer that recurs in distant parts of the body?
Cancers that recur in distant parts of the body can be harder to remove with surgery, so other treatments, such as chemotherapy, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, or radiation therapy , might be needed. For more on dealing with a recurrence, see Understanding Recurrence.
What is the treatment for T3 tumors?
An option for some patients with single, small tumors (some T3) might be treatment with a second (and more extensive) transurethral resection (TURBT) followed by a combination of chemo and radiation. If cancer is still found when cystoscopy is repeated, cystectomy might be needed.
What to do if you have cancer that hasn’t been removed?
(Less often, close follow-up alone might be an option.) If all of the cancer wasn’t removed, options are intravesical BCG or cystectomy (removal of part or all of the bladder).
How to get rid of stage IV cancer?
The tumor is then rechecked. If it appears to be gone, chemo with or without radiation or cystectomy are options.
What is stage 0 bladder cancer?
Stage 0 bladder cancer includes non-invasive papillary carcinoma (Ta) and flat non-invasive carcinoma (Tis or carcinoma in situ). In either case, the cancer is only in the inner lining layer of the bladder. It has not invaded (spread deeper into) the bladder wall.
How long after TA surgery can you get chemo?
For low-grade (slow-growing) non-invasive papillary (Ta) tumors, weekly intravesical chemotherapy may be started a few weeks after surgery. If the cancer comes back, the treatments can be repeated. Sometimes intravesical chemo is repeated over the next year to try to keep the cancer from coming back.
What is chemotherapy?
Chemotherapy (chemo) uses strong medicines to kill cancer cells. Chemo attacks and kills cells that grow quickly, such as cancer cells. But some normal cells also grow quickly. Because of this, chemo can also harm those cells. This can cause side effects.
When might chemo be used for bladder cancer?
These are some of the ways chemo might be used to treat bladder cancer:

How is chemo given for bladder cancer?
The way you get chemo depends on your stage of cancer. There are 2 main ways of chemo to treat bladder cancer:
What are common side effects of chemo?
Side effects depend on the type and dose of medicines you’re taking. They depend on the way you get the medicines (intravesical or systemic). They also depend on if you’re getting radiation at the same time, which can make side effects worse. They vary a lot from person to person.
Working with your healthcare provider
It’s important to know which medicines you’re taking. Write down the names of your medicines. Ask your healthcare team how they work and what side effects they might cause.

What is the treatment for bladder cancer?
Chemotherapy into the bladder. Chemotherapy into the bladder is a treatment for early bladder cancer. You have it through a flexible tube called a catheter, which goes into your bladder. Your doctor may call this treatment intravesical chemotherapy. Having intravesical chemotherapy reduces the chance of the cancer coming back or spreading into …
How long does chemo stay in the bladder?
Your doctor or specialist nurse puts a liquid chemotherapy drug into the catheter. You usually keep the drug in the bladder for 1 or 2 hours. Some hospitals may ask you to change position every now and again to make sure the drug reaches all parts of your bladder. After the time is up your nurse will drain the liquid out through the catheter.
What is the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of your body?
The doctor or nurse puts a catheter through your urethra and into your bladder. The urethra is the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of your body.

How long does it take for doxorubicin to pass through the bladder?
doxorubicin. Your doctor or nurse may then remove the catheter or clamp it. You have to try not to pass any urine for the next 1 to 2 hours. This gives the chemotherapy drugs time to be in contact with the lining of the bladder.
How long does bladder cancer treatment last?
For some people with early bladder cancer, this is all the treatment they need. If you have a moderate risk of your cancer coming back, you have this treatment once a week for 6 weeks. You may also have this treatment if your cancer comes back after the initial surgery and chemotherapy treatment. Find out about having a TURBT.
Why do men pee during chemotherapy?
You have to be careful when you pass urine so that you don’t get it on your skin. Men should sit down to pass urine, to reduce the chance of splashing. The urine contains some chemicals from the chemotherapy which could irritate your skin.

Does intravesical chemotherapy help bladder cancer?
Having intravesical chemotherapy reduces the chance of the cancer coming back or spreading into the deeper layers of the bladder.
How does chemo help cancer?
This can help relieve symptoms from the cancer, for instance, by shrinking tumors that are pressing on nerves and causing pain. Doctors give chemo in cycles, with each period of treatment followed by a rest period to allow the body time to recover.
What is the treatment for gallbladder cancer?
Chemotherapy for Gallbladder Cancer. Chemotherapy (chemo) is treatment with cancer-killing drugs that are usually given into a vein (IV) or taken by mouth. These drugs enter the bloodstream and reach all areas of the body, making this treatment useful for cancers that have spread beyond where they started.

How long does chemo last?
Chemo cycles generally last about 3 to 4 weeks. Chemo usually isn’t recommended for patients in poor health, but advanced age by itself isn’t a barrier to getting chemotherapy.
Which artery is used for gallbladder cancer?
The hepatic artery also supplies most gallbladder tumors, so putting chemo into this artery means more chemo goes to the tumor. The healthy liver then removes most of the remaining drug before it can reach the rest of the body. This can lessen the chemo side effects.
Which vein is used for chemo?
Because giving chemo into a vein (IV) isn’t always helpful for gallbladder cancer, doctors have studied a different way to give it – right into the main artery going into the liver, called the hepatic artery. The hepatic artery also supplies most gallbladder tumors, so putting chemo into this artery means more chemo goes to the tumor.

Does chemo cause cancer?
Possible chemo side effects. Chemo drugs attack cells that are dividing quickly, which is why they work against cancer cells. But other cells in the body, such as those in the bone marrow (where new blood cells are made), the lining of the mouth and intestines, and the hair follicles, also divide quickly.
Does chemo go away?
Side effects can include: These side effects are usually short-term and go away after treatment ends. There are often ways to lessen these side effects or even prevent them.
What are the best drugs for bladder cancer?
These drugs can be used in different situations to treat bladder cancer: 1 Any of these checkpoint inhibitors can be used in people with advanced bladder cancer that starts growing again after chemotherapy. 2 Atezolizumab and pembrolizumab can be used in people who can’t get the chemo drug cisplatin (due to things like hearing loss, kidney failure, or heart failure). 3 Avelumab can be used as an additional (maintenance) treatment in people with advanced bladder cancer that did not get worse during their initial chemotherapy treatments. 4 Pembrolizumab can be used to treat certain bladder cancers that are not growing into the muscle wall of the bladder, are not getting smaller with intravesical BCG, and are not being treated with a cystectomy.

What antibody is used to attach to a bladder cancer cell?
In the case of this ADC, the monoclonal antibody part attaches to the Trop-2 protein on bladder cancer cells and brings the chemo directly to them. (Some bladder cancer cells have too much Trop-2, which helps them grow and spread.)
What is the ADC used for?
This ADC can be used in people with advanced bladder cancer who have already been treated with a platinum chemo drug (such as cisplatin) and immunotherapy (specifically, a PD-1 or PD-L1 inhibitor).
What is the drug ADC?
Enfortumab vedotin (Padcev) Enfortumab vedotin is an antibody-drug conjugate (ADC), which is a monoclonal antibody linked to a chemo drug. Bladder cancer cells usually have the Nectin-4 protein on their surface. Enfortumab vedotin is an anti-Nectin-4 antibody attached to a chemo drug. The antibody part acts like a homing signal, …

How often is pembrolizumab given?
These drugs are given as intravenous (IV) infusions, usually every 2 to 6 weeks, depending on the drug.
What drugs target PD-L1?
Atezolizumab (Tecentriq) and avelumab (Bavencio) are drugs that target PD-L1, a protein on cells (including some cancer cells) that helps keep the immune system from attacking them. By blocking PD-L1, these drugs boost the immune system’s response against the cancer cells. This can shrink some tumors or slow their growth.
What do checkpoints do for cancer?
But newer drugs that target these checkpoints, called checkpoint inhibitors, can help restore the immune response …