Contents
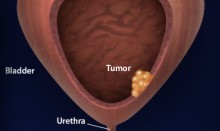
How dangerous is bladder cancer?
What My Bladder Tumor Looked Like. By Editorial Team. October 22, 2019. Many people in the bladder cancer community have described coming face to face with their bladder tumor in the exam room during a cystoscopy. One survivor described the moment by saying, “The first glimpse I had of a tumor of mine, I was struck by how pretty it was.
What are the chances of dying from bladder cancer?
· Bladder Cancer is a type of cancer that affects the urinary bladder. The most common type of bladder cancer, known as urothelial cell carcinoma or transition…
What are the symptoms and signs of bladder cancer?
· Bladder: a hollow organ that stores urine Biopsy (BY-op-see): taking out a tiny piece of tissue to see if there are cancer cells in it. Cystectomy (sis-TEK-tuh-mee): surgery to take out the bladder Cystoscopy (sis-TAH-scuh-pee): a procedure use to look at the inside of the bladder with a thin, lighted tube called a cystoscope (sis-TOE-scope) …
How do you detect bladder cancer?
· This is an examination of the inner lining of the bladder with a cystoscope, a tube with a light and a camera on the end. Other tests can give your doctors more information about the bladder cancer. These may include an ultrasound before the cystoscopy, a biopsy taken during a cystoscopy, and a CT or MRI scan.

How Does The Doctor Know I Have Bladder Cancer?
Bladder cancer might cause symptoms such as: 1. Having trouble peeing 2. Feeling pain when peeing 3. Needing to go more often than normal 4. Seeing…
Tests to Look For Bladder Cancer
Your doctor may do other tests to find out more about the cancer. Some of them are:X-ray: Dye is put into a vein for a special x-ray of the kidneys…
How Serious Is My Cancer?
If you have bladder cancer, the doctor will want to find out how far it has spread. This is called staging. Your doctor will want to find out the s…
What Kind of Treatment Will I Need?
There’s more than one way to treat bladder cancer. You might want to get a second opinion about the best treatment plan for you. Doctors may have d…
What Will Happen After Treatment?
You will be glad when treatment is over. But it’s hard not to worry about cancer coming back. Even when cancer never comes back, people still worry…

How do you know if you have bladder cancer?
Signs of bladder cancer are problems peeing, pain when peeing, needing to go more often than normal, and seeing blood in your urine
What is urine test?
Urine tests: For these tests, you’ll be asked to pee in a cup. Your urine is then tested for cancer cells, blood, or certain proteins (called tumor markers).
What is the blue light on a cystoscopy?
Blue light cystoscopy: Sometimes, special drugs are put into the bladder during the exam. Cancer cells soak up these drugs and then glow when the doctor shines a blue light through the scope. This can help the doctor see cancer cells that might have been missed with the normal light.

Why do you need a cystoscope?
More than one sample may be taken because sometimes cancer starts in more than one part of the bladder. Salt water washings of the inside of your bladder may also be collected to look for cancer cells.
What is the best test to find out if you have bladder cancer?
Ultrasound: This test uses sound waves to make pictures of the organs inside your body, like your bladder and kidneys. It can help show the size of a bladder cancer and if it has spread. Bone scan: A bone scan can help show if bladder cancer has spread to the bones. This test is not done unless you have bone pain.
What tests are done to check for bladder cancer?
This might include a rectal exam, during which a gloved finger is put into your rectum. If you are a woman, a pelvic exam might also be done.

Where does urine go when you pee?
Urine flows through the ureters and into your bladder, where it’s stored. When you urinate (pee), the bladder squeezes the urine out through a tube called the urethra. Bladder cancer usually starts in the lining or inner layer of the bladder wall.
Actos And Bladder Cancer What Does Bladder Cancer Look Like
Ultrasound Video showing a large vesical growth in the urinary bladder.
Endoscopic Teflon Or Deflux Gel Treatment For Vesico
This patient shows an echogenic mound in the left vesico-ureteric junction. The Color Doppler image shows a ureteric jet emerging from this region suggesting that the left distal ureteric orificeis patent. This patient had a history of vesico-ureteric reflux.

Bilharziasis Of The Urinary Bladder
This patient presented with lower urinary symptoms, dysuria and hematuria. Sonography of the pelvis showed thickening of the wall of the urinary bladder with extensive calcification. Theseultrasound images suggest a diagnosis of schistosomiasis or bilharziasis of the wall of the urinary bladder.
If You Have Liver Disease
Certain diseases can make you more likely to get liver cancer, including:
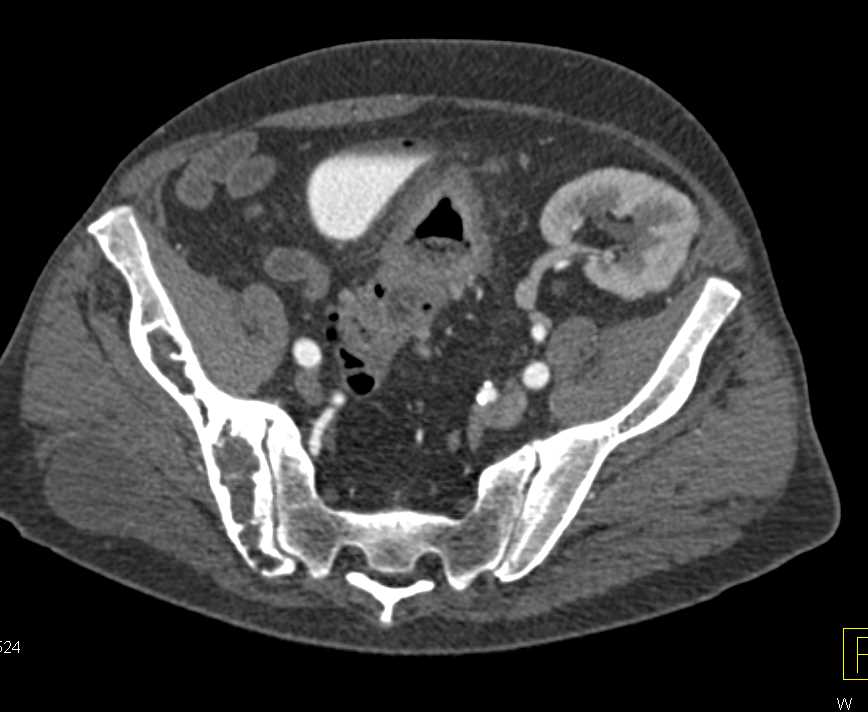
Detecting Bladder Cancer With Ct Scans
A CT scan uses x-rays to obtain cross-sectional images of the body. Compared to a general x-ray test, which directs a broad x-ray beam from a single angle, the CT scan uses a number of thin beams to produce a series of images from different angles.

Screening For Bladder Cancer
Early-stage bladder cancer often shows no symptoms, or symptoms that are similar to those of benign conditions such as bladder stones, an enlarged prostate, or urinary tract infection. For this reason it is important to be examined regularly by a physician.
Can An Ultrasound Tell If An Ovarian Cyst Is Cancerous
Vaginal ultrasound can help to show whether any cysts on your ovaries contain cancer or not. If a cyst has any solid areas it is more likely to be cancer. Sometimes, in women who are past their menopause, the ovaries do not show up on an ultrasound. This means that the ovaries are small and not likely to be cancerous.
What color is the bladder cancer?
In the blue light cystoscopy a fluorescent dye has been used that turns bladder cancer cells pink when they are exposed to blue light.
How long does it take for a cystoscopy to show blood?
For 1 or 2 days after a cystoscopy, patients may notice blood in the urine and/or a burning sensation when passing urine. Drinking plenty of fluids usually helps to minimize these symptoms. Returning to work, physical, and sexual activities is usually quick, for example later the same day after a flexible cystoscopy and 1 to 2 days after a rigid cystoscopy. If discomfort is severe or symptoms do not improve as expected, it is important to promptly seek medical help.
What is rigid cystoscopy?
Rigid cystoscopy uses a hard, straight cystoscope. For this type of cystoscopy, patients are usually under general anesthesia; in some patients, spinal anesthesia that numbs the lower half of the body may be used instead. Rigid cystoscopy is performed when tissue samples (biopsies) and/or removal of small bladder tumors are required. Long, small-diameter instruments can be passed down the cystoscope to take biopsies from the bladder lining, and a tool called a resectoscope that has a cutting wire loop at the end may be used to remove abnormal tissue or small tumors. This procedure is referred to as ‘transurethral resection of a bladder tumor’ or ‘TURBT’.
What is a flexible cystoscope?
Flexible cystoscopy uses a flexible cystoscope tube that is able to bend easily as it passes through the urethra. This procedure can be carried out under local anesthetic while the patient is awake and is commonly used for simple visual examination of the inside of the bladder, although the collection of bladder washings (for cytology testing) or small tissue samples may be undertaken.

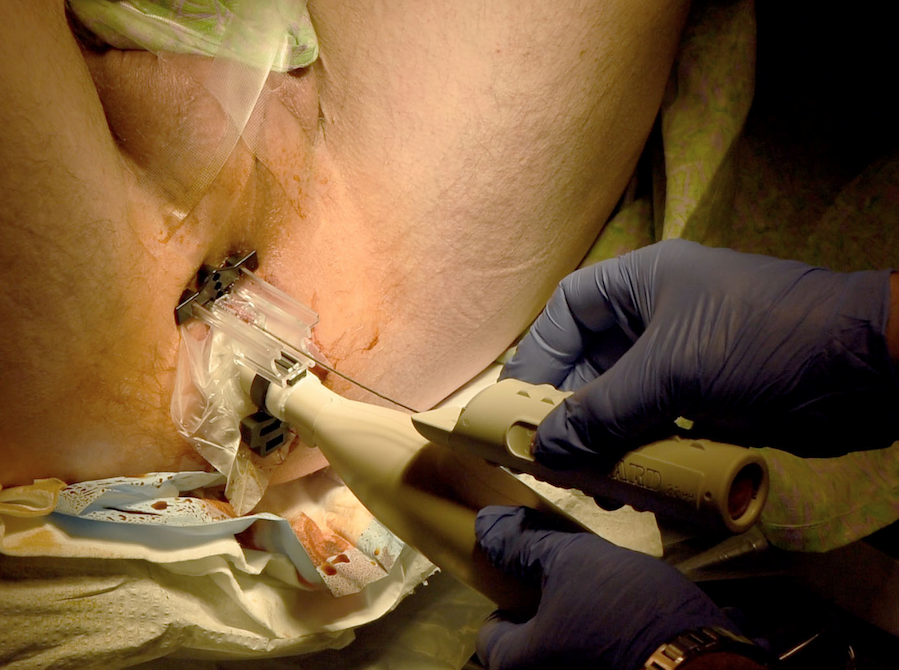
What is a thin tube with a light and camera attached to the end?
A cystoscope is a thin tube with a light and camera attached to the end. During a cystoscopy, the cystoscope is passed through the urethra (the tube through which urine leaves the bladder) into the bladder. The two main types of cystoscopy are termed flexible and rigid:
What is cystoscopy used for?
Alongside urine testing and diagnostic imaging procedures, cystoscopy is used in both the initial diagnosis of bladder cancer and in ongoing surveillance for recurrence. In addition, cystoscopy-based procedures are commonly used to remove or treat small bladder tumors.
What is the most common light source used for cystoscopy?
A white light source or blue light source may be used for flexible and rigid cystoscopy procedures. White light cystoscopy is traditionally the most commonly used technique for the detection of bladder cancer. Blue light cystoscopy (sometimes referred to as ‘photodynamic diagnosis’) has been developed more recently, and while not as common, its use in clinical settings is increasing. For this procedure, a fluorescent dye is injected into the bladder through a catheter in the urethra. The dye is absorbed by cancer cells, which then appear red or pink when examined under the blue light of the cystoscope.

What is bladder cancer?
Cancer: It is a cancer involving the lining of the bladder that will spread into the muscle layers of the bladder if left untreated. It is a malignant conditi … Read More
What is the treatment for bladder cancer?
Surgery or Radiation: The 2 mainstay forms of muscle invasive bladder cancer treatment includes radical surgery or radiation with chemotherapy. If there is no muscle invasi… Read More
What is the function of the bladder?
The bladder collects: And eliminates waste produced by kidneys. The lining cells are suceptible to toxins, and those from cigarette smoking can cause the cells to mutate, b … Read More
Can bladder cancer recur?
Yes: Bladder cancers can very aggressive and recur despite treatment with radical surgery and/or chemotherapy. There is no way to be sure who will develop … Read More
Is bladder cancer painful?
Maybe: Bladder cancer is generally not painful until it has spread to local organs and structures. If it contained to the superficial lining of the bladder w … Read More
Can you die from bladder cancer?
Serious: One can die from bladder cancer if that helps you understand it’s gravity. The most common risk factor for bladder cancer is smoking. Do not smoke!
Is bladder cancer a result of smoking?
Usually not. : The vast majority of bladder cancers are linked with environmental factors, especially smoking. Many epidemiologic studies have looked at the role of … Read More
How to treat bladder cancer?
Bladder Treatments. Cystoscopy: A narrow tube is passed through the urethra into the bladder. A light, camera, and tools allow a doctor to diagnose and treat bladder problems. Surgery: Bladder cancer generally requires surgery. Some cases of urinary incontinence and cystocele may also be treated with surgery.
What is the bladder anatomy page?
WebMD’s Bladder Anatomy Page provides a detailed image and definition of the bladder and describes its function, location in the body, and conditions that affect the bladder.

Why does urine not exit the bladder?
Urinary retention: Urine does not exit the bladder normally due to a blockage or suppressed bladder muscle activity. The bladder may swell to hold more than a quart of urine. Cystocele: Weakened pelvic muscles (usually from childbirth) allow the bladder to press on the vagina. Problems with urination can result.
What causes pain in the bladder?
Cystitis: Inflammation or infection of the bladder causing acute or chronic pain, discomfort, or urinary frequency or hesitancy. Urinary stones: Stones (calculi) may form in the kidney and travel down to the bladder. If kidney stones block urine flow to or from the bladder, they can cause severe pain.
Why does my urine leak out?
Urinary incontinence can result from many causes. Overactive bladder: The bladder muscle (detrusor) squeezes uncontrollably, causing some urine to leak out. Detrusor overactivity is a common cause of urinary incontinence. Hematuria: Blood in the urine.
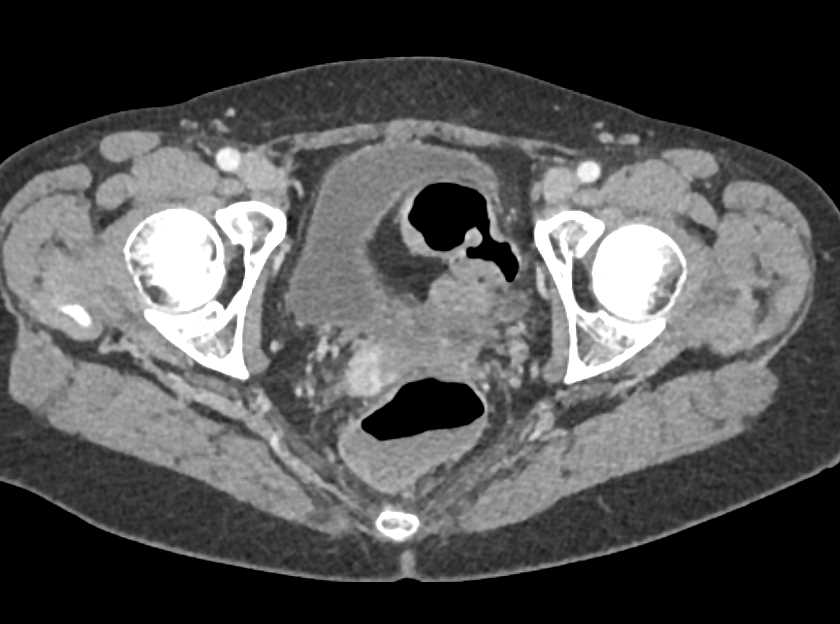
How many ml of urine does the bladder hold?
The bladder is lined by layers of muscle tissue that stretch to hold urine. The normal capacity of the bladder is 400-600 mL. During urination, the bladder muscles squeeze, and two sphincters (valves) open to allow urine to flow out. Urine exits the bladder into the urethra, which carries urine out of the body.
What is the first part of a urine test?
The first part of the test is a dipstick. If this is abnormal the urine should be looked at under a microscope. Cystoscopy: A narrow tube is passed through the urethra and into the bladder. A light, camera, and tools allow a doctor to diagnose and treat bladder problems.