Contents

How does bladder cancer effect the human body?
A malignant epithelial neoplasm arising in the transitional epithelium of the renal pelvis, ureter and urinary bladder; it is the 5th most common cancer of men in developed nations. Statistics. ±55,000 new cases/year (US); 90% 5-year survival; 9% if distant metastasis when diagnosed. Clinical findings.
What are the risks of bladder cancer?
You get bladder cancer when bladder cells become abnormal and grow out of control. Over time, a tumor forms. Over time, a tumor forms. It can spread to nearby lymph nodes and other organs.
How is bladder cancer identified on an ultrasound?
What is Bladder Cancer? Bladder cancer is marked by the formation of malignant cells in the tissues of the bladder, the organ where urine is stored. Learn more > What are the symptoms and risk factors of bladder cancer? Bladder cancer symptoms may include blood in the urine, frequent urination and pain during urination. Bladder cancer symptoms, risk factors and prevention >
What is the diagnosis for bladder cancer?
· Bladder cancer: A common form of cancer that begins in the lining of the bladder. The most common warning sign is blood in the urine. Symptoms include pain during urination, frequent urination, and feeling the need to urinate without results. A diagnosis of bladder cancer is supported by findings in the medical history, physical examination, examination of the urine, …
See more
bladder cancer. Cancer that forms in tissues of the bladder (the organ that stores urine). Most bladder cancers are transitional cell carcinomas (cancer that begins in cells that normally …
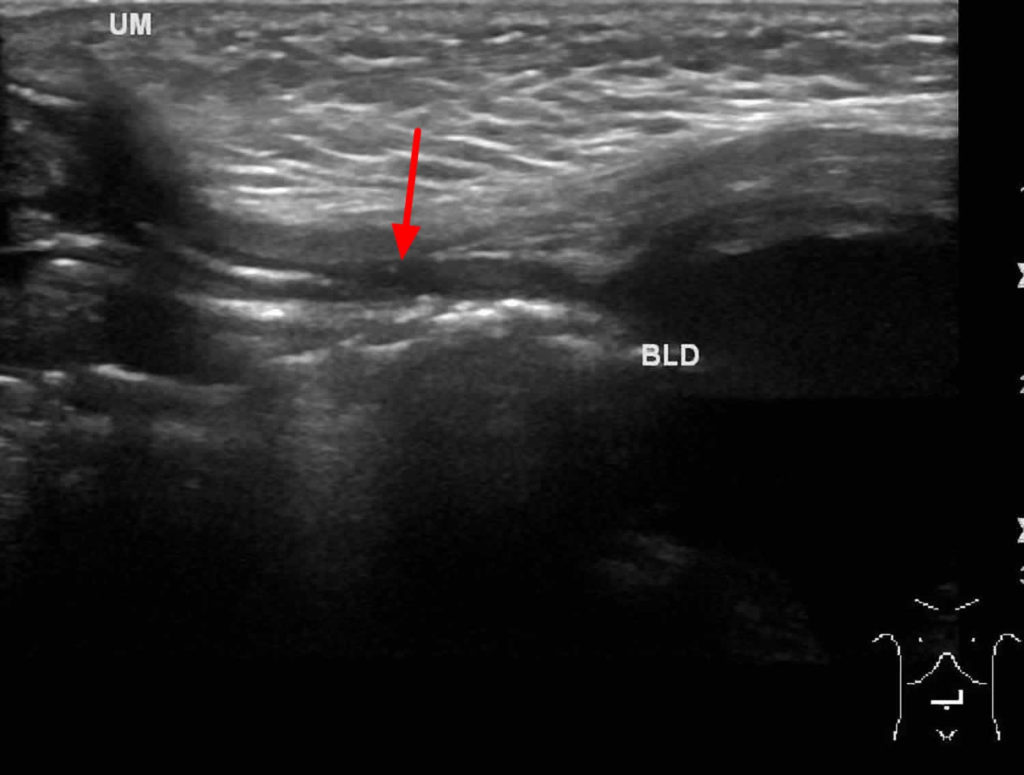

What is the most common type of bladder cancer?
Urothelial carcinoma is the most common type of bladder cancer in the United States. Squamous cell carcinoma. Squamous cell carcinoma is associated with chronic irritation of the bladder — for instance, from an infection or from long-term use of a urinary catheter. Squamous cell bladder cancer is rare in the United States.
How does bladder cancer develop?
Bladder cancer develops when cells in the bladder begin to grow abnormally, forming a tumor in the bladder. Bladder cancer begins when cells in the bladder develop changes (mutations) in their DNA. A cell’s DNA contains instructions that tell the cell what to do.
Where is the bladder located?
Your kidneys, located in the rear portion of your upper abdomen, produce urine by filtering waste and fluid from your blood. Bladder cancer is a common type of cancer that begins in the cells of the bladder. The bladder is a hollow muscular organ in your lower abdomen that stores urine. Bladder cancer most often begins in …
Where does bladder cancer start?
Bladder cancer is a common type of cancer that begins in the cells of the bladder. The bladder is a hollow muscular organ in your lower abdomen that stores urine. Bladder cancer most often begins in the cells (urothelial cells) that line the inside of your bladder. Urothelial cells are also found in your kidneys and the tubes (ureters) …
Where is urothelial cancer found?
Urothelial cells are also found in your kidneys and the tubes (ureters) that connect the kidneys to the bladder. Urothelial cancer can happen in the kidneys and ureters, too, but it’s much more common in the bladder. Most bladder cancers are diagnosed at an early stage, when the cancer is highly treatable.
Can bladder cancer come back?
But even early-stage bladder cancers can come back after successful treatment. For this reason, people with bladder cancer typically need follow-up tests for years after treatment to look for bladder cancer that recurs.
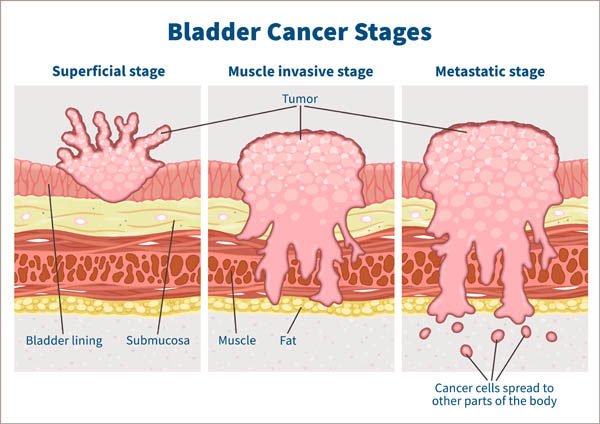
How do you know if you have bladder cancer?
Bladder cancer signs and symptoms may include: Blood in urine (hematuria), which may cause urine to appear bright red or cola colored, though sometimes the urine appears normal and blood is detected on a lab test. Frequent urination. Painful urination. Back pain.
What is the first sign of bladder cancer?
One of the first warning signals of bladder cancer is blood in the urine. Sometimes, there is enough blood to change the color of the urine to a yellow-red or a dark red. At other times, the color of the urine appears normal but chemical testing of the urine reveals the presence of blood cells.
Does bladder cancer recur?
The urethra carries the urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. Bladder cancer has a very high rate of recurrence. Even after superficial tumors are completely removed, there is a 75% chance that new tumors will develop in other areas of the bladder. Hence, patients need frequent and thorough follow-up care.

Is bladder cancer a risk factor for smokers?
Although the exact cause of bladder cancer is not known, smokers are twice as likely as nonsmokers to get the disease . Hence, smoking is considered the greatest risk factor for bladder cancer. Workers who are exposed to certain chemicals used in the dye industry and in the rubber, leather, textile, and paint industries are believed to be at a higher risk for bladder cancer. The disease also is three times more common in men than in women; caucasians also are at an increased risk. The risk of bladder cancer increases with age. Most cases are found in people who are 50-70 years old. In 2003, studies showed that hormone replacement therapy (HRT), a treatment used by many postmenopausal women, significantly increased the risk of bladder and other cancers.
Is smoking a cause of bladder cancer?
Hence, smoking is considered the greatest risk factor for bladder cancer. Workers who are exposed to certain chemicals used in the dye industry and in the rubber, leather, textile, and paint industries are believed to be at a higher risk for bladder cancer.
How old do you have to be to get bladder cancer?
The risk of bladder cancer increases with age. Most cases are found in people who are 50-70 years old. In 2003, studies showed that hormone replacement therapy (HRT), a treatment used by many postmenopausal women, significantly increased the risk of bladder and other cancers.

Can bladder cancer be removed?
Cancer that is not very large can be removed by partial cystectomy, a procedure where a part of the bladder is removed. If the cancer is large or is present in more than one area of the bladder, a radical cystectomy is done. In this operation, the entire bladder and adjoining organs also may be removed.
What is the procedure to look inside the bladder?
Cystoscopy — A diagnostic procedure where a hollow lighted tube, (cystoscope) is used to look inside the bladder and the urethra. Electrofulguration — A procedure where a high-energy laser beam is used to burn the cancerous tissue. Immunotherapy — Treatment of cancer by stimulating the body’s immune defense system.
What causes bladder cancer?
Research shows that smoking is the cause of about 50% of all bladder cancers. Working around harmful chemicals. People who work in certain industries (painters, machinists, printers, hairdressers, and truck drivers, among others) may be exposed to harmful chemicals for long periods of time.

How to get rid of bladder cancer?
Doctors believe tobacco products cause about half of all bladder cancer cases. Drink lots of fluids. When you pee, you get rid of harmful chemicals that build up in your bladder. So drink up — especially water. It may lower your cancer risk. Eat more fruits and veggies.
What is the purpose of the bladder?
The bladder is a hollow, flexible pouch in your pelvis. Its main job is to store urine before it leaves your body. Your kidneys make pee. Tubes called ureters carry the pee from your kidneys to your bladder. When you use the bathroom, the muscles in your bladder push the urine out through a tube called the urethra.
Where does bladder cancer spread?
It can spread to nearby lymph nodes and other organs. In severe cases, it can spread to distant parts of your body, including your bones, lungs, or liver. Bladder cancer is rare. It accounts for just 5% of all new cancers in the U.S.

Can bladder cancer spread to other organs?
You get bladder cancer when bladder cells become abnormal and grow out of control. Over time, a tumor forms. It can spread to nearby lymph nodes and other organs. In severe cases, it can spread to distant parts of your body, including your bones, lungs, or liver. Bladder cancer is rare.
What is bladder cancer?
Bladder cancer is marked by the formation of malignant cells in the tissues of the bladder, the organ where urine is stored. Learn more >.
What are the symptoms of bladder cancer?
What are the symptoms and risk factors of bladder cancer? Bladder cancer symptoms may include blood in the urine, frequent urination and pain during urination. Bladder cancer symptoms, risk factors and prevention >.

Overview and Types
If you’ve been diagnosed with bladder cancer or are worried about it, you likely have a lot of questions. Learning some basics is a good place to start..
Research and Statistics
See the latest estimates for new cases of and deaths linked to bladder cancer in the US and what research is currently being done.
What are the symptoms of bladder cancer?
Being unable to urinate. Lower back pain on one side. Loss of appetite and weight loss. Feeling tired or weak. Swelling in the feet. Bone pain. Again, many of these symptoms are more likely to be caused by something other than bladder cancer, but it’s important to have them checked.
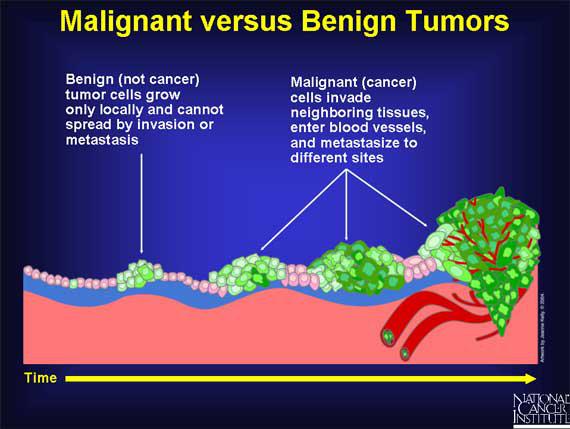
Can bladder cancer cause bleeding?
Usually, the early stages of bladder cancer (when it’s small and only in the bladder) cause bleeding but little or no pain or other symptoms. Blood in the urine doesn’t always mean you have bladder cancer.
How do you know if you have bladder cancer?
Bladder cancers that have grown large or have spread to other parts of the body can sometimes cause other symptoms, such as: Being unable to urinate. Lower back pain on one side. Loss of appetite and weight loss. Feeling tired or weak.
Can bladder cancer spread to other parts of the body?
Bladder cancers that have grown large or have spread to other parts of the body can sometimes cause other symptoms, such as: Again, many of these symptoms are more likely to be caused by something other than bladder cancer, but it’s important to have them checked.

Can bladder cancer cause lower back pain?
Bladder cancers that have grown large or have spread to other parts of the body can sometimes cause other symptoms, such as: Being unable to urinate. Lower back pain on one side. Loss of appetite and weight loss. Feeling tired or weak.
What does it mean when you have blood in your urine?
Blood in the urine. In most cases, blood in the urine (called hematuria) is the first sign of bladder cancer. There may be enough blood to change the color of the urine to orange, pink, or, less often, dark red.
Is urine a normal color?
Sometimes, the color of the urine is normal but small amounts of blood are found when a urine test (urinalysis) is done because of other symptoms or as part of a general medical check-up. Blood may be present one day and absent the next, with the urine remaining clear for weeks or even months.