Contents

Medication
Transurethral resection (TURBT) is often done first to find out how far the cancer has grown into the bladder wall. Chemotherapy followed by radical cystectomy (removal of the bladder and nearby lymph nodes) is then the standard treatment. Partial cystectomy is rarely an option for stage III cancers.
Procedures
Bladder Cancer Surgery. Intravesical Therapy for Bladder Cancer. Chemotherapy for Bladder Cancer. Radiation Therapy for Bladder Cancer. Immunotherapy for Bladder Cancer. Targeted Therapy Drugs for Bladder Cancer.
Therapy
· Treatment of bladder cancer depends on the stage of the cancer. Treatment options include different types of surgery (transurethral resection, radical and partial cystectomy, and urinary diversion), radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy. Learn more about how bladder cancer is treated.
Nutrition
Chemotherapy (chemo) is the use of drugs to treat cancer. Chemo for bladder cancer can be given in 2 different ways: Intravesical chemotherapy For this treatment, the chemo drug is put right into the bladder. This type of chemo is used for …
What is the newest treatment for bladder cancer?
· Drug Combinations Used in Bladder Cancer Drugs Approved for Bladder Cancer Atezolizumab Avelumab Balversa (Erdafitinib) Bavencio (Avelumab) Cisplatin Doxorubicin Hydrochloride Enfortumab Vedotin-ejfv Erdafitinib Jelmyto (Mitomycin) Keytruda (Pembrolizumab) Mitomycin Nivolumab Opdivo (Nivolumab) Padcev (Enfortumab Vedotin …
What are the best treatment centers for bladder cancer?
· Surgery: is part of the treatment for most bladder cancers. The type and extent of the surgery depend on the stage of cancer and other factors such as the longer-term side effects of the procedure. Your doctor may combine treatment approaches.
What are the chances of survival for bladder cancer?
Immunotherapy for Bladder Cancer Immunotherapy is the use of medicines to help a person’s own immune system recognize and destroy cancer cells. This type of treatment is sometimes used to treat bladder cancer. Intravesical BCG BCG is a type of bacteria related to the one that causes tuberculosis.
What is the treatment for Stage 3 bladder cancer?
Bladder cancer can often be cured, or brought into remission, especially if treated early. However, bladder cancer tends to reappear. Overall, the chances of your cancer being cured depend on your type of cancer and how far it has spread. 1 Low grade and high grade bladder cancer
See more
Regional: The cancer has spread from the bladder to nearby structures or lymph nodes. Distant: The cancer has spread to distant parts of the body such as the lungs, liver or bones. 5-year relative survival rates for bladder cancer. Based on people diagnosed with bladder cancer between 2011 and 2017.

Is cancer of the bladder curable?
The prognosis depends on the following: The stage of the cancer (whether it is superficial or invasive bladder cancer, and whether it has spread to other places in the body). Bladder cancer in the early stages can often be cured.
What is the latest treatment for bladder cancer?
Advanced and metastatic bladder cancer treatment A notable new FDA approval in December 2019 was enfortumab vedotin (Padcev), approved for advanced bladder cancer patients who have not responded to chemotherapy or immune checkpoint drugs.
What is the main cause of bladder cancer?
Smoking. Smoking is the single biggest risk factor for bladder cancer. This is because tobacco contains cancer-causing (carcinogenic) chemicals. If you smoke for many years, these chemicals pass into your bloodstream and are filtered by the kidneys into your urine.
How do you get rid of bladder cancer?
When bladder cancer is invasive, all or part of the bladder may need to be removed. This operation is called a cystectomy. Most of the time, chemotherapy is given before cystectomy is done. General anesthesia (where you are in a deep sleep) is used for either type of cystectomy.
Does bladder cancer spread quickly?
They tend to grow and spread slowly. High-grade bladder cancers look less like normal bladder cells. These cancers are more likely to grow and spread.
Can you live without a bladder?
It can affect your body image, and you may worry about its impact on your relationships and sex life. With enough time, you should be able to do almost everything you did before. Even if you now use a urostomy bag (to collect your urine), you can go back to work, exercise, and swim.
What are the 5 warning signs of bladder cancer?
Here are five warning signs to watch for:Blood in the urine (hematuria). This is the most common early symptom of bladder cancer and typically the first sign of bladder cancer that is seen. … UTI-like symptoms. … Unexplained pain. … Decreased appetite. … Postmenopausal uterine bleeding.
What is usually the first symptom of bladder cancer?
In most cases, blood in the urine (called hematuria) is the first sign of bladder cancer. There may be enough blood to change the color of the urine to orange, pink, or, less often, dark red.
Is bladder cancer serious?
The general 5-year survival rate for people with bladder cancer is 77%. However, survival rates depend on many factors, including the type and stage of bladder cancer that is diagnosed. The 5-year survival rate of people with bladder cancer that has not spread beyond the inner layer of the bladder wall is 96%.
What happens if bladder is removed?
After having your bladder removed, your surgeon also needs to create a urinary diversion — a new way to store urine and have it leave your body. There are multiple ways that urine can be stored and eliminated after bladder removal.
How long can you live after bladder removal?
Patients in group 1 achieved a progression-free 5-year survival rate of 77% and an overall survival rate of 63% after 5 years. In group 2 patients achieved a progression-free survival rate of 51% after 5 years and an overall survival rate of 50%.
How long does it take to recover from bladder cancer surgery?
It will take 6 weeks from the date of surgery to fully recover from your operation. This can be divided into two parts — the first 2 weeks and the last 4 weeks. During the first 2 weeks from the date of your surgery, it is important to be “a person of leisure”.
What is the success rate of BCG treatment for bladder cancer 2021?
This method of treatment is considered a form of immunotherapy, which is an emerging form of cancer treatment. The success rate for BCG treatment for bladder cancer is about 90%, which is considered the best life-saving rate by any treatment.
What are the alternatives to BCG treatment for bladder cancer?
If BCG is not available, alternatives to BCG such as gemcitabine, epirubicin, docetaxel, valrubicin, mitomycin, or sequential gemcitabine/docetaxel or gemcitabine/mitomycin may also be considered with an induction and possible maintenance regimen.
What is the best hospital for bladder cancer?
Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., Mayo Clinic in Phoenix/Scottsdale, Ariz., and Mayo Clinic in Jacksonville, Fla., have been ranked among the Best Hospitals for urology and cancer in the nation by U.S. News & World Report.
Can high grade bladder cancer be cured?
Abstract. Context: High-grade T1 (T1HG) bladder cancer (BCa) has a very high likelihood of disease recurrence and progression to muscle invasion. Radical cystectomy is considered the best chance at cure, albeit with a high risk of morbidity, and is overtreatment for some patients.
Treating Stage 0 Bladder Cancer
Stage 0 bladder cancer includes non-invasive papillary carcinoma (Ta) and flat non-invasive carcinoma (Tis). In either case, the cancer has not inv…
Treating Stage I Bladder Cancer
Stage I bladder cancers have grown into the connective tissue layer of the bladder wall but have not reached the muscle layer.Transurethral resecti…
Treating Stage II Bladder Cancer
These cancers have invaded the muscle layer of the bladder wall. Transurethral resection (TURBT) is typically the first treatment for these cancers…
Treating Stage III Bladder Cancer
These cancers have reached the outside of the bladder and might have grown into nearby tissues or organs.Transurethral resection (TURBT) is typical…
Treating Stage IV Bladder Cancer
These cancers have reached the abdominal or pelvic wall (T4b tumors) or have spread to nearby lymph nodes or distant parts of the body. Stage IV ca…
Treating Bladder Cancer That Progresses Or Recurs
If cancer continues to grow during treatment (progresses) or comes back (recurs), your treatment options will depend on where and how much the canc…
Which Treatments Are Used For Bladder Cancer?
Depending on the stage of the cancer and other factors, treatment options for people with bladder cancer can include: 1. Surgery 2. Intravesical th…
Which Doctors Treat Bladder Cancer?
Depending on your options, you can have different types of doctors on your treatment team. The types of doctors who treat bladder cancers include:…
Making Treatment Decisions
It’s important to discuss all of your treatment options, including their goals and possible side effects, with your doctors to help make the decisi…
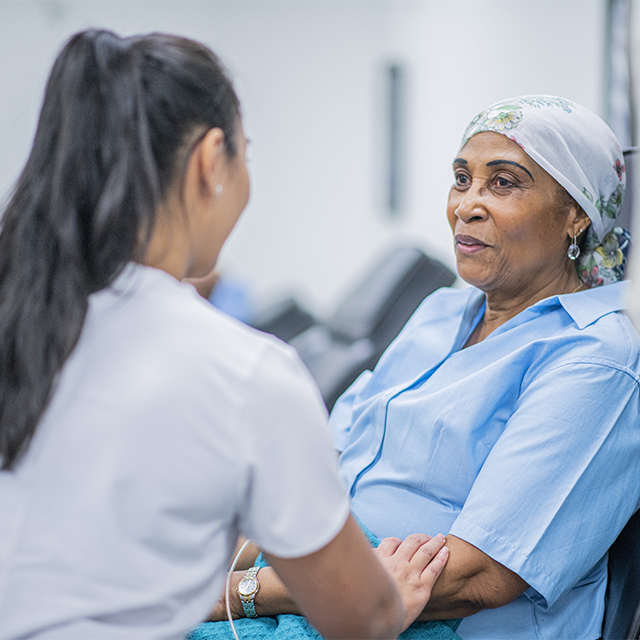
Help Getting Through Treatment
Your cancer care team will be your first source of information and support, but there are other resources for help when you need it. Hospital- or c…
What is the treatment for bladder cancer?
Depending on the stage of the cancer and other factors, treatment options for people with bladder cancer can include: Bladder Cancer Surgery. Intravesical Therapy for Bladder Cancer. Chemotherapy for Bladder Cancer. Radiation Therapy for Bladder Cancer. Immunotherapy for Bladder Cancer. Targeted Therapy Drugs for Bladder Cancer.
Can bladder cancer be removed?
Surgery, alone or with other treatments, is used to treat most bladder cancers. Early-stage bladder tumors can often be removed. But a major concern in people with early-stage bladder cancer is that new cancers often form in other parts of the bladder over time.
What kind of doctor treats cancer?
Based on your treatment options, you might have different types of doctors on your treatment team. These doctors could include: 1 Urologists: surgeons who specialize in treating diseases of the urinary system and male reproductive system 2 Radiation oncologists: doctors who treat cancer with radiation therapy 3 Medical oncologists: doctors who treat cancer with medicines such as chemotherapy and immunotherapy

How to decide on cancer treatment?
It’s important to discuss all of your treatment options, including their goals and possible side effects, with your doctors to help make the decision that best fits your needs. Some important things to consider include: 1 Your age and expected life span 2 Any other serious health conditions you have 3 The stage and grade of your cancer 4 The likelihood that treatment will cure your cancer (or help in some other way) 5 Your feelings about the possible side effects from treatment
What do people with cancer need?
People with cancer need support and information, no matter what stage of illness they may be in. Knowing all of your options and finding the resources you need will help you make informed decisions about your care.
What is the number to call for cancer treatment?
Call our National Cancer Information Center at 1-800-227-2345 and speak with one of our trained specialists. Palliative Care. Find Support Programs and Services in Your Area.
Is treatment information given here official policy of the American Cancer Society?
The treatment information given here is not official policy of the American Cancer Society and is not intended as medical advice to replace the expertise and judgment of your cancer care team. It is intended to help you and your family make informed decisions, together with your doctor.
What is bladder cancer?
Bladder cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the bladder. The bladder is a hollow organ in the lower part of the abdomen. It is shaped like a small balloon and has a muscular wall that allows it to get larger or smaller to store urine made by the kidneys.
What is the treatment for stage IV bladder cancer?
Treatment of stage IV bladder cancer that has spread to other parts of the body, such as the lung, bone, or liver, may include the following: Chemotherapy with or without local treatment ( surgery or radiation therapy ). Immunotherapy ( immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy ).

Does smoking cause bladder cancer?
Smoking can affect the risk of bladder cancer. Signs and symptoms of bladder cancer include blood in the urine and pain during urination. Tests that examine the urine and bladder are used to help diagnose bladder cancer. Certain factors affect prognosis (chance of recovery) and treatment options.
Where is the bladder located?
The bladder is a hollow organ in the lower part of the abdomen. It is shaped like a small balloon and has a muscular wall that allows it to get larger or smaller to store urine made by the kidneys. There are two kidneys, one on each side of the backbone, above the waist.
Where does bladder cancer start?
Most bladder cancers begin in the transitional cells. Transitional cell carcinoma can be low- grade or high-grade: Low-grade transitional cell carcinoma often recurs (comes back) after treatment, but rarely spreads into the muscle layer of the bladder or to other parts of the body.

What is it called when you have cancer in your bladder?
Cancer that is in the lining of the bladder is called superficial bladder cancer. Cancer that has spread through the lining of the bladder and invades the muscle wall of the bladder or has spread to nearby organs and lymph nodes is called invasive bladder cancer. See the following PDQ summaries for more information:
What happens after bladder cancer diagnosis?
After bladder cancer has been diagnosed, tests are done to find out if cancer cells have spread within the bladder or to other parts of the body.
Can bladder cancer recur after treatment?
Bladder cancer may recur, even after successful treatment. Because of this, people with bladder cancer need follow-up testing for years after successful treatment. What tests you’ll have and how often depends on your type of bladder cancer and how it was treated, among other factors.

How does radiation therapy help bladder cancer?
Radiation therapy. Radiation therapy uses beams of powerful energy, such as X-rays and protons, to destroy the cancer cells. Radiation therapy for bladder cancer usually is delivered from a machine that moves around your body, directing the energy beams to precise points.
How to diagnose bladder cancer?
Tests and procedures used to diagnose bladder cancer may include: Using a scope to examine the inside of your bladder (cystoscopy). To perform cystoscopy, your doctor inserts a small , narrow tube (cystoscope) through your urethra. The cystoscope has a lens that allows your doctor to see the inside of your urethra and bladder, …
Can TURBT be used for bladder cancer?
TURBT can also be used to treat bladder cancer. Examining a urine sample (urine cytology). A sample of your urine is analyzed under a microscope to check for cancer cells in a procedure called urine cytology. Imaging tests.

What tests can be done to determine if you have bladder cancer?
Tests may include: CT scan.
What is a low grade bladder cancer?
Low-grade bladder cancer. This type of cancer has cells that are closer in appearance and organization to normal cells (well differentiated). A low-grade tumor usually grows more slowly and is less likely to invade the muscular wall of the bladder than is a high-grade tumor. High-grade bladder cancer.
What is the best treatment for cancer?
Radiation therapy, to destroy cancer cells, often as a primary treatment when surgery isn’t an option or isn’t desired. Immunotherapy, to trigger the body’s immune system to fight cancer cells, either in the bladder or throughout the body. Targeted therapy, to treat advanced cancer when other treatments haven’t helped.

What is the best treatment for bladder cancer?
For those people, treatment with a single drug, such as gemcitabine or cisplatin, may be an option. Other drugs sometimes used alone for bladder cancer include, docetaxel, paclitaxel, doxorubicin, methotrexate, ifosfamide, and pemetrexed. Doctors give chemo in cycles, with each period of treatment followed by a rest period to allow …
Does radiation help bladder cancer?
This can lower the chance that the cancer will come back later. In people getting radiation therapy, to help the radiation work better. As the main treatment for bladder cancers that have spread to distant parts of the body.
What are the side effects of chemo?
The side effects of chemo depend on the type and dose of drugs given and how long they are taken. When chemo and radiation are given at the same time, side effects tend to be worse. Common side effects of chemo include: 1 Nausea and vomiting 2 Loss of appetite 3 Hair loss 4 Mouth sores 5 Diarrhea 6 Constipation 7 Increased risk of infections (because of a shortage of white blood cells) 8 Easy bleeding or bruising, even after minor cuts or injuries (due to a shortage of blood platelets) 9 Fatigue (because of a shortage of red blood cells)
Where is chemo put in the bladder?
For this treatment, the chemo drug is put right into the bladder. This type of chemo is used for bladder cancer that’s only in the lining of the bladder. It’s described in Intravesical Therapy for Bladder Cancer.
How long does bladder cancer last?
Each cycle typically lasts for a few weeks. Most bladder cancers are transitional cell (urothelial) cancers, but there are other types as well, including squamous cell carcinoma, adenocarcinoma, and small cell carcinoma. These rare types of bladder cancer may be treated with drugs different from those listed above.
What type of cancer is bladder cancer?
Most bladder cancers are transitional cell (urothelial) cancers , but there are other types as well, including squamous cell carcinoma, adenocarcinoma, and small cell carcinoma. These rare types of bladder cancer may be treated with drugs different from those listed above.
Does chemo kill cancer cells?
Side effects of chemotherapy. Chemo drugs attack cells that are dividi ng quickly, which is why they work against cancer cells. But other cells in the body, such as those in the bone marrow (where new blood cells are made), the lining of the mouth and intestines, and the hair follicles, also divide quickly.
What is the treatment for bladder cancer?
Radiation therapy: for destroying cancer cells. Radiation therapy is often used as the primary treatment to target localised cancer cells option when surgery isn’t an option. Immunotherapy: to trigger the body’s immune system to fight cancer cells. Surgery: is part of the treatment for most bladder cancers.
Is bladder cancer a treatable disease?
Bladder cancer is usually treatable when caught at an early stage but more challenging to address when found later. Recurrence also poses a risk, even with early-stage tumors, so regular surveillance is essential following treatment or surgery.

How many cases of bladder cancer are there in 2019?
Is Bladder Cancer Curable? Every year, there are around 81,400 new cases of bladder cancer, of which nearly 18,000 are fatal. In 2019, around 4.6% of all new cancer cases were bladder cancer. Bladder cancer is the fourth most common cancer among men, and ninth overall.
What is a low grade bladder tumor?
Low-grade bladder tumor: A type of tumor with cells closer in organization and appearance to healthy cells. They typically grow more gradually and are less likely to invade the bladder’s muscular wall than high-grade tumors.
How long does bladder cancer last?
A particular stage of bladder cancer, for example, may have a 90% five-year relative survival rate. The 90% figure comes from dividing the percentage of people with cancer who are alive after five years by the percentage of people without the disease who are also alive after five years.

Can bladder cancer return?
Even early-stage bladder cancers have a likelihood of returning, so after treatment, you’ll want to continue to see your doctor for follow-up appointments to monitor for recurrence. The types of tests and the frequency of testing depend on the type of cancer and your treatment.
What is a CXbladder test?
Cxbladder is a clinically proven cutting-edge genomic urine test that quickly and accurately detects or rules out bladder cancer in patients presenting with blood in the urine (or hematuria) and those being monitored for recurrence. The test works at a molecular level, measuring five biomarker genes to detect the presence or absence of bladder cancer.
What are the best drugs for bladder cancer?
These drugs can be used in different situations to treat bladder cancer: 1 Any of these checkpoint inhibitors can be used in people with advanced bladder cancer that starts growing again after chemotherapy. 2 Atezolizumab and pembrolizumab can be used in people who can’t get the chemo drug cisplatin (due to things like hearing loss, kidney failure, or heart failure). 3 Avelumab can be used as an additional (maintenance) treatment in people with advanced bladder cancer that did not get worse during their initial chemotherapy treatments. 4 Pembrolizumab can be used to treat certain bladder cancers that are not growing into the muscle wall of the bladder, are not getting smaller with intravesical BCG, and are not being treated with a cystectomy.

Does chemo kill bladder cancer?
The chemo enters the cancer cells and kills them. This drug may be used to treat people with advanced bladder cancer who have already been treated with a platinum chemo drug (such as cisplatin) and immunotherapy (specifically, a PD-1 or PD-L1 inhibitor). Enfortumab vedotin is infused into a vein (IV), once a week for 3 weeks with one week off.
Can checkpoint inhibitors be used for bladder cancer?
These drugs can be used in different situations to treat bladder cancer: Any of these checkpoint inhibitors can be used in people with advanced bladder cancer that starts growing again after chemotherapy.
What is the role of checkpoints in the immune system?
An important part of the immune system is its ability to keep itself from attacking normal cells in the body. To do this, it uses “checkpoints” – proteins on immune cells that need to be turned on (or off) to start an immune response.

What are checkpoint inhibitors?
But newer drugs that target these checkpoints, called checkpoint inhibitors, can help restore the immune response against cancer cells.
What drugs target PD-L1?
Atezolizumab (Tecentriq) and avelumab (Bavencio) are drugs that target PD-L1, a protein on cells (including some cancer cells) that helps keep the immune system from attacking them. By blocking PD-L1, these drugs boost the immune system’s response against the cancer cells. This can shrink some tumors or slow their growth.
Does nivolumab shrink tumors?
This can shrink some tumors or slow their growth. Nivolumab (Opdivo) and pembrolizumab (Keytruda) target PD-1, a protein on certain immune cells (called T cells) that normally helps keep these cells from attacking other cells in the body. Blocking PD-1 can allow the immune system to attack the cancer cells, which can shrink some tumors …

How long does bladder cancer last?
The stage of cancer generally refers to how far it has progressed, and whether it has spread to other parts of the body. For bladder cancer, the 5-year survival rate for people with: 2,3. If you would like to learn more about bladder cancer statistics, consider speaking with someone on your health care team.
What is low grade bladder cancer?
Bladder cancer is called low grade or high grade. Low-grade bladder cancer means the cancer has not invaded the muscles around the bladder (non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer). People rarely die from this type of bladder cancer, it often recurs after treatment.
What is the difference between high grade and low grade bladder cancer?
Low grade and high grade bladder cancer 1 Low-grade bladder cancer means the cancer has not invaded the muscles around the bladder (non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer). People rarely die from this type of bladder cancer, it often recurs after treatment. 2 High-grade bladder cancer also often recurs and has a higher chance of spreading to other parts of the body. Almost all deaths from bladder cancer result this type so it is treated more aggressively.

Is cancer survival based on averages?
It is important to remember that all cancer survival numbers are based on averages across huge numbers of people. These numbers cannot predict what will happen in your individual case.
How long does bladder cancer last?
The SEER database tracks 5-year relative survival rates for bladder cancer in the United States, based on how far the cancer has spread. The SEER database, however, does not group cancers by AJCC TNM stages (stage 1, stage 2, stage 3, etc.). Instead, it groups cancers into localized, regional, and distant stages: 1 Localized: There is no sign that the cancer has spread outside of the bladder. 2 Regional: The cancer has spread from the bladder to nearby structures or lymph nodes. 3 Distant: The cancer has spread to distant parts of the body such as the lungs, liver or bones.
What is the SEER database?
The SEER database tracks 5-year relative survival rates for bladder cancer in the United States, based on how far the cancer has spread.
Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Coping and Support
Treatments include surgery, chemotherapy, and biological therapy.