Contents
Symptoms
Bladder cancer can often be found early because it causes blood in the urine or other urinary symptoms that cause a person to see a health care provider. Blood in the urine In most cases, blood in the urine (called hematuria) is the first sign of bladder cancer.
Causes
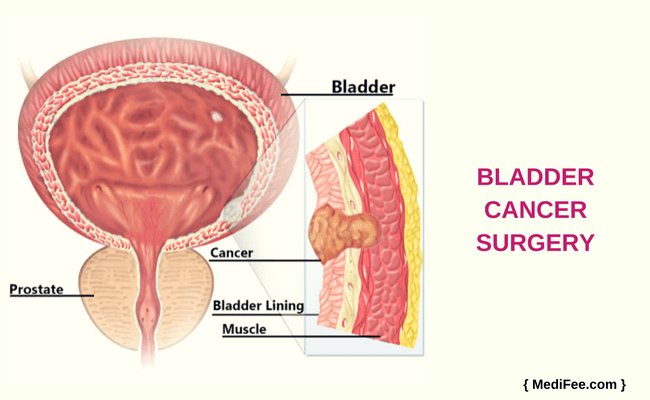
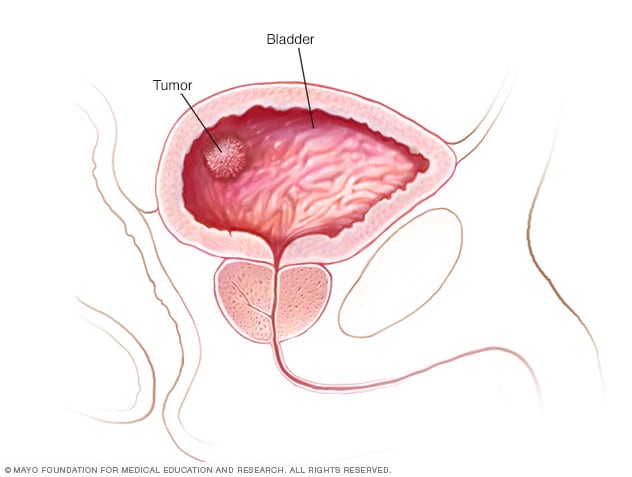
· Bladder cancer is a growth that starts in the inner wall of the bladder, the organ that collects and expels urine created by the kidneys. The bladder has three layers of muscular walls that make up its structure. 1 A cancerous growth in the bladder can grow uncontrollably and start spreading to other parts of the body.
Prevention
However, the most common sites for distant bladder cancer metastases include the: Lungs. Bones. Liver. Metastatic bladder cancer can also spread to other organs in the urinary and reproductive tracts, such as the prostate, uterus and vagina.
Complications
· Bladder cancer usually starts in the innermost lining of the bladder. It can grow into the deeper muscle layers of the bladder and eventually spread to nearby lymph nodes, surrounding tissues, or…
What are the early warning signs of bladder cancer?
At Cancer Treatment Centers of America ® (CTCA), we understand that choosing a treatment approach for bladder cancer should depend as much on the patient’s personal preferences as on the type and stage of the disease. For this reason, you may undergo tests such as a cystoscopy, advanced genomic testing, biopsy and/or X-ray to determine the type and extent of the disease.
Do you know the early signs of bladder cancer?
· Bladder cancer: This is the most common cancer of the urinary system. A biopsy of bladder tissue is required to see how far the cancer has spread, and the spread will determine treatment. In severe cases, the bladder may be removed, with urine diverted to the bowel or collected with an exterior device. 2.
How to diagnose bladder cancer?
· In males, the bladder lies in front of the rectum, above the prostate gland, and behind the pubic symphysis. In women, bladder pain may be referred to the lower sacral vertebrae, resulting in lower back pain. No other symptoms may be present in the lower abdominal or pelvic region.
What is the best test for bladder cancer?

Where does bladder cancer begin?
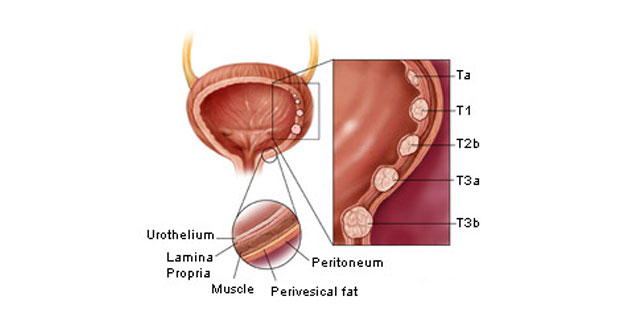
Most bladder cancers start in the innermost lining of the bladder, which is called the urothelium or transitional epithelium. As the cancer grows into or through the other layers in the bladder wall, it has a higher stage, becomes more advanced, and can be harder to treat.
Where is bladder cancer pain located?
Bladder cancer can cause lower back pain when it reaches a more advanced form of the disease. The pain is typically only on one side of the back, but it can be centrally located. Lower back pain might occur once the tumors increase in size or cancer cells start to spread to other parts of your body.
How is bladder cancer usually found?
Bladder cancer can often be found early because it causes blood in the urine or other urinary symptoms that cause a person to see a health care provider. In most cases, blood in the urine (called hematuria) is the first sign of bladder cancer.
What are the warning signs of bladder cancer?
Bladder Cancer: Symptoms and SignsBlood or blood clots in the urine.Pain or burning sensation during urination.Frequent urination.Feeling the need to urinate many times throughout the night.Feeling the need to urinate, but not being able to pass urine.Lower back pain on 1 side of the body.
What is usually the first symptom of bladder cancer?
In most cases, blood in the urine (called hematuria) is the first sign of bladder cancer. There may be enough blood to change the color of the urine to orange, pink, or, less often, dark red.
What are the symptoms of stage 1 bladder cancer?
SymptomsBlood in urine (hematuria), which may cause urine to appear bright red or cola colored, though sometimes the urine appears normal and blood is detected on a lab test.Frequent urination.Painful urination.Back pain.
Does bladder cancer feel like a UTI?
Bladder cancer can be mistaken for a Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) because many of the symptoms overlap. Patients may experience increased frequency and urgency of urination, pain with urination, or urinary incontinence.
How does a urologist check for bladder cancer?
Cystoscopy. If bladder cancer is suspected, most doctors will recommend a cystoscopy. . A urologist uses a cystoscope, which is a long, thin, flexible tube with a light and a lens or a small video camera on the end.
Do you feel bloated with bladder cancer?
Abdominal Pain The types of pains can vary and include: Generalized pain — felt in more than half of the stomach area. Cramp-like pain — less serious and most likely due to bloating and gas.
Does ultrasound show bladder cancer?
Bladder cancer can show up on ultrasound, but ultrasound is infrequently used to help make a diagnosis of a bladder tumor. CAT scans are more often used along with cystoscopy to detect bladder cancers.
Does bladder cancer show up in blood tests?
Tests to diagnose bladder cancer If bladder cancer is suspected, these tests may be performed to diagnose the disease: Physical exam. Blood test: Blood samples are used to measure certain substances released into the blood by organs and tissues in the body.
Which of the following is the most common symptom of cancer of the bladder?
Blood in your urine is the most common symptom of bladder cancer. The medical name for blood in your urine is haematuria and it’s usually painless. You may notice streaks of blood in your urine or the blood may turn your urine brown. The blood isn’t always noticeable and it may come and go.
Where does bladder cancer spread?
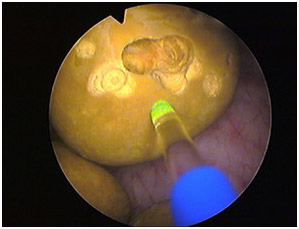
Over time, the cancer might grow outside the bladder and into nearby structures. It might spread to nearby lymph nodes, or to other parts of the body. (When bladder cancer spreads, it tends to go to distant lymph nodes, the bones, the lungs, or the liver.)
What is the name of the cell that starts bladder cancer?
Small cell carcinoma. Less than 1% of bladder cancers are small-cell carcinomas. They start in nerve-like cells called neuroendocrine cells. These cancers often grow quickly and usually need to be treated with chemotherapy like that used for small cell carcinoma of the lung.
What is flat carcinoma?
If a flat tumor is only in the inner layer of bladder cells, it’s known as a non-invasive flat carcinoma or a flat carcinoma in situ (CIS). If either a papillary or flat tumor grows into deeper layers of the bladder, it’s called an invasive urothelial (or transitional cell) carcinoma. Written by. References.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/bodymap-bladder-cancer-03-5ac7bac2c67335003726efc4-2a3ff03ffcb04522a707cb960f8be703.png)
What percentage of bladder cancers are adenocarcinoma?
Adenocarcinoma. Only about 1% of bladder cancers are adenocarcinomas. These cancer cells have a lot in common with gland-forming cells of colon cancers . Nearly all adenocarcinomas of the bladder are invasive.
How does bladder cancer start?
Bladder cancer starts when cells that make up the urinary bladder start to grow out of control. As more cancer cells develop, they can form a tumor and, with time, spread to other parts of the body. (To learn more about how cancers start and spread, see What Is Cancer?)
What is the bladder wall made of?
The wall of the bladder has many several layers. Each layer is made up of different kinds of cells (see Bladder Cancer Stages for details on the different layers). Most bladder cancers start in the innermost lining of the bladder, which is called the urothelium or transitional epithelium. As the cancer grows into or through the other layers in …

Where do papillary tumors grow?
Papillary tumors often grow toward the center of the bladder without growing into the deeper bladder layers. These tumors are called non-invasive papillary cancers.
What is bladder cancer?
Bladder cancer is any of several types of cancer arising from the tissues of the urinary bladder. Symptoms include blood in the urine, pain with urination, and low back pain. It is caused when epithelial cells that line the bladder become malignant.
Where does bladder cancer spread?
Lymph nodes in the pelvis. Bladder cancer commonly spreads to obturator and internal iliac (not labelled)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/bodymap-bladder-cancer-03-5ac7bac2c67335003726efc4-2a3ff03ffcb04522a707cb960f8be703.png)
How to treat non-muscle invasive bladder cancer?
Non-muscle invasive bladder cancer (those not entering the muscle layer of the bladder) can be “shaved off” using an electrocautery device attached to a cystoscope, which in that case is called a resectoscope. The procedure is called transurethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT) and serves primarily for pathological staging. In case of non-muscle invasive bladder cancer the TURBT is in itself the treatment, but in case of muscle invasive cancer, the procedure is insufficient for final treatment. Additionally, blue light cystoscopy with optical-imaging agent Hexaminolevulinate (HAL) is recommended at initial TURBT to increase lesion detection (especially carcinoma in situ) and improve resection quality thereby reducing recurrence. It is important to assess the quality of the resection, if there is evidence of incomplete resection or there is no muscle in the specimen (without which muscle invasiveness cannot be determined) a second TURBT is strongly recommended. Moreover, nearly half of the people with high grade non-invasive disease have residual tumor after primary TURBT, in such cases a second TURBT is important for avoiding under-staging. At this point classifying people into risk groups is recommended. Treatment and surveillance for different risk groups is indicated in the table below.
What are the risk factors for bladder cancer?
Risk factors for bladder cancer include smoking, family history, prior radiation therapy, frequent bladder infections, and exposure to certain chemicals. The most common type is transitional cell carcinoma. Other types include squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. Diagnosis is typically by cystoscopy with tissue biopsies. Staging of the cancer is determined by transurethral resection and medical imaging.
What are the genes that cause bladder cancer?
Mutations in FGFR3, TP53, PIK3CA, KDM6A, ARID1A, KMT2D, HRAS, TERT, KRAS, CREBBP, RB1 and TSC1 genes may be associated with some cases of bladder cancer. Deletions of parts or whole of chromosome 9 is common in bladder cancer. Low grade cancer are known to harbor mutations in RAS pathway and the fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) gene, both of which play a role in the MAPK/ERK pathway. p53 and RB gene mutations are implicated in high-grade muscle invasive tumors. Eighty nine percent of muscle invasive cancers have mutations in chromatin remodeling and histone modifying genes. Deletion of both copies of the GSTM1 gene has a modest increase in risk of bladder cancer. GSTM1 gene product glutathione S-transferase M1 (GSTM1) participates in the detoxification process of carcinogens such as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons found in cigarette smoke. Similarly, mutations in NAT2 ( N-acetyltransferase) is associated with increased risk for bladder cancer. N-acetyltransferase helps in detoxification of carcinogens like aromatic amines (also present in cigarette smoke). Various single-nucleotide polymorphisms in PSCA gene present on chromosome 8 have shown to increase the risk for bladder cancer. PSCA gene promoter region has an androgen response region. Loss of reactivity of this region to androgens is hypothesized as a cause of more number of aggressive tumors in women (unlike in men who have higher amount of androgen).

How long does it take for bladder cancer to go away?
Risk of bladder cancer decreases by 30% within 1–4 years and continues to decrease by 60% at 25 years after smoking cessation. However, former smokers will most likely always be at a higher risk of bladder cancer compared to people who have never smoked. Passive smoking also appear to be a risk.
How many cigarettes a day can you smoke to get bladder cancer?
A risk plateau at smoking about 15 cigarettes a day can be observed (meaning that those who smoke 15 cigarettes a day are approximately at the same risk as those smoking 30 cigarettes a day).
Why is bladder cancer so early?
Bladder cancer can often be found early because it causes blood in the urine or other urinary symptoms that cause a person to see a health care provider.

What are the symptoms of bladder cancer?
Being unable to urinate. Lower back pain on one side. Loss of appetite and weight loss. Feeling tired or weak. Swelling in the feet. Bone pain. Again, many of these symptoms are more likely to be caused by something other than bladder cancer, but it’s important to have them checked.
How long does urine stay clear after bladder cancer?
Blood may be present one day and absent the next, with the urine remaining clear for weeks or even months. But if a person has bladder cancer, at some point the blood reappears.
Can bladder cancer cause a change in urination?
Bladder cancer can sometimes cause changes in urination, such as: Having to urinate more often than usual. Pain or burning during urination. Feeling as if you need to go right away, even when your bladder isn’t full. Having trouble urinating or having a weak urine stream.
Where does bladder cancer start?
Bladder cancer is a growth that starts in the inner wall of the bladder, the organ that collects and expels urine created by the kidneys. The bladder has three layers of muscular walls that make up its structure. 1 A cancerous growth in the bladder can grow uncontrollably and start spreading to other parts of the body.
What are the symptoms of bladder cancer?
The most common symptom of bladder cancer is reddish or brownish-colored urine from blood in the urine. Other symptoms include the frequent urge to urinate, pain while urinating, and pain in the back or pelvis. 4
What is radical cystectomy?
Cases this may be used for include those in which the tumors in the bladder take over a large part of the organ. This surgery removes the bladder and any nearby cancerous lymph nodes or tissues.

What tests are used to diagnose bladder cancer?
These include blood tests, imaging tests that look inside the body, and samples of the tumors called a bladder biopsy, usually taken during surgery.
What does the N number mean in cancer?
N stands for nodes. This number indicates if the tumor has spread to lymph nodes, where the lymph nodes are located, and how many lymph nodes are impacted.
How do doctors diagnose cancer?
When doctors first diagnose a cancerous tumor of any kind, they assess how much it has grown, how far it has spread in the body, and how abnormal, or wild, the cancerous cells in the tumor look. These assessments are used to determine cancer’s stage (0 to IV) and grade. 2

How does cancer spread?
The cancer spreads from the original location through a process called metastasis. When cancer spreads, it’s called metastatic cancer or a metastatic tumor. This spreading can happen between tissues, or through the fluids of the blood or lymphatic systems. 3
How does bladder cancer spread?
Bladder cancer spreads when cancerous cells reproduce and invade surrounding healthy tissues. This is known as metastasis. Usually, metastatic bladder cancer refers to cancer that has spread to distant organs, but metastasis can occur locally in the muscles and connective tissues that are directly adjacent to the bladder as well.
What is the treatment for bladder cancer?
Potential treatment options may include chemotherapy, radiation therapy and clinical trials.

Can bladder cancer be metastasized to lymphatic system?
Once cancerous cells have reached the lymphatic system, they can make their way to almost any part of the body. However, the most common sites for distant bladder cancer metastases include the:
Can bladder cancer spread to other organs?
Metastatic bladder cancer can also spread to other organs in the urinary and reproductive tracts, such as the prostate, uterus and vagina.
Does Moffitt Cancer Center treat bladder cancer?
At Moffitt Cancer Center, we’ve treated many patients with metastatic bladder cancer, creating ta ilored treatment plans for every single one. To help ease the burdens of treatment, we also offer comprehensive supportive care services for patients and their caregivers.

What is the first sign of bladder cancer?
Blood in the urine, either microscopic or visible to the naked eye, is commonly the first sign of bladder cancer. As the cancer grows and spreads to other areas of the body or during treatment for bladder cancer, pain may become a bigger issue. You may experience pain: in the pelvis. in the back.
How to help cancer patients with pain?
Slow, rhythmic breathing and visual concentration on an object are common relaxation techniques that people with cancer can use to reduce pain. They help get rid of muscle tension and soothe the mind.
How to help someone with cancer?
Meditation. Similar to relaxation techniques and distraction, meditation can take your mind off the pain and quiet your thoughts. Some research shows that meditation can ease pain and reduce anxiety and depression among people with cancer, according to the American Cancer Society.
Can bladder cancer be removed?
Early bladder cancer can be managed with a minimally invasive surgery, during which the tumor is scraped off the bladder wall from within. More advanced bladder cancer may require surgery to remove the entire bladder.
Can bladder cancer cause a burning sensation?
Bladder cancer can cause changes in urination. You might experience pain or a burning sensation when you urinate, and you may see blood in your urine. an urge to urinate more frequently than you used to. an urgent need to urinate even if your bladder isn’t full. an urge to urinate often throughout the night.
Can bladder cancer cause lower back pain?
Bladder cancer can cause lower back pain when it reaches a more advanced form of the disease. The pain is typically only on one side of the back, but it can be centrally located.

Can bladder cancer cause mouth sores?
It can also be caused by treatment. Chemotherapy, a common treatment method for bladder cancer, can cause uncomfortable side effects, such as mouth sores.
What is the bladder?
Anatomy. The bladder is a triangle-shaped, hollow organ. In men, it is bordered by the pubic bone at the front of the pelvis and the rectum at the back of the pelvis in the lower abdomen. In women, the bladder is bordered posteriorly by the uterus and vagina. 1 The bladder is supported by ligaments and connects at the top to two ureters …
What is the top part of the bladder?
Apex: This is the top part of the bladder. The apex points forward toward the abdominal wall. Fundus: The base of the bladder. Body: The main portion of the bladder between the apex and fundus. Neck: The narrow part of the bladder that constricts and connects the organ to the urethra.

What organ holds urine until it is ready to be released?
Function. The bladder is the organ that holds urine until it is ready to be released and then helps to expel it from the body. Ureters bring urine to the bladder from the kidneys, passing through an opening to the bladder called the ureterovesical junction.
How much urine can a bladder hold?
When full, the typical adult bladder can hold up to 500 milliliters of urine at a time—or about 2 cups—which must be released every two to five hours. 4
What is the most common cancer of the urinary system?
Verywell. A number of problems can arise both with the bladder or with urination. Bladder cancer: This is the most common cancer of the urinary system. A biopsy of bladder tissue is required to see how far the cancer has spread, and the spread will determine treatment.
What is the function of the bladder?
Function. Associated Conditions. Tests. The bladder collects and expels urine from the body. As urine is made, it moves from the kidneys and down each ureter to the bladder. The bladder’s flexible walls stretch and contract to hold urine until it is expelled from the body through the urethra .
What is the term used to describe inflammation in the bladder?
This problem is most common in children. 2 . Cystitis: This is the term used to describe inflammation in the bladder. Inflammation can occur for a number of reasons, but most commonly from urinary tract or bladder infections. Cystitis can also be caused by other things, including certain drugs or medications.
Where is the urinary bladder located?
In adults, the urinary bladder occupies the lesser pelvis. In children, the urinary bladder lies in the lower part of the abdominal cavity. The pain arising from the bladder may also radiate to other adjacent tissues and organs. In males, the bladder lies in front of the rectum, above the prostate gland, and behind the pubic symphysis.

Where is bladder pain?
The location of the pain is mostly between the umbilicus and the pubic patch in the midline. Pain that emanates from the bladder is usually felt in the lower parts of the trunk. The exact location of the urinary bladder is different in adults and children.
What is the most common cause of bladder pain?
Urinary tract infections (commonly abbreviated as UTI) are the most common causes of bladder inflammation (technically referred to as cystitis) and bladder pain. Urinary tract infections may affect any part of the urinary tract, including the urethra, urinary bladder and the kidneys. Infections and inflammation of the urethra (urethritis) and the urinary bladder (cystitis) are the most common.
What is the pain in the lower back?
In women, bladder pain may be referred to the lower sacral vertebrae, resulting in lower back pain. No other symptoms may be present in the lower abdominal or pelvic region. Infections from the bladder may also ascend up the urinary tract, leading to infection of the kidneys.

Why does the bladder expand after urination?
This can also shift the location of the pain to some degree. After urination, the bladder returns to its original size.
How do you know if you have bladder pain?
The following are the most common signs and symptoms of bladder pain: A burning sensation or pain may be present in the external genitalia along with the bladder pain. The pain may increase during urination, intercourse, or ejaculation (in males). Urine may have a strong smell and be cloudy in color.
How much urine is stored in the bladder?
The urine is stored in the bladder before being expelled through urination. About 300 to 500mL (about 10 to 17 ounces) of urine can be stored in the bladder at any time.
Types of Bladder Cancer
Other Types of Bladder Cancer
Start and Spread of Bladder Cancer
Overview
Signs and symptoms
-
Bladder cancer signs and symptoms may include: 1. Blood in urine (hematuria), which may cause urine to appear bright red or cola colored, though sometimes the urine appears normal and blood is detected on a lab test 2. Frequent urination 3. Painful urination 4. Back pain
Causes
Genetics
Diagnosis
Prevention
- Urothelial carcinoma
Urothelial carcinoma, also known as transitional cell carcinoma(TCC), is by far the most common type of bladder cancer. In fact, if you have bladder cancer it’s almost certain to be a urothelial carcinoma. These cancers start in the urothelial cells that line the inside of the bladder. Urotheli…
Treatment
-
Other types of cancer can start in the bladder, but these are all much less common than urothelial (transitional cell) cancer.
Prognosis
-
The wall of the bladder has many several layers. Each layer is made up of different kinds of cells (see Bladder Cancer Stagesfor details on the different layers). Most bladder cancers start in the innermost lining of the bladder, which is called the urothelium or transitional epithelium. As the cancer grows into or through the other layers in the b…