Contents

Why does bladder cancer cause hematuria?
Hematuria is the most common presenting symptom in bladder cancer, seen in approximately 85% of patients with the disease [16]. The origin of hematuria in bladder cancer is from direct hemorrhage of the tumor, however minor it may be. Hematuria may be either microscopic or gross.
How do you stop bladder cancer bleeding?
Interventions to stop or slow bleeding may include systemic agents or transfusion of blood products. Noninvasive local treatment options include applied pressure, dressings, packing, and radiation therapy. Invasive local treatments include percutaneous embolization, endoscopic procedures, and surgical treatment.
Does bladder cancer bleed all the time?
Early, small bladder cancers cause blood only detected by lab analysis (microscopic hematuria), while larger tumors cause bleeding that can be seen with urination. Any blood in the urine should be discussed with your doctor and consider evaluation by a urologist. This bleeding may occur only once.
Does bladder cancer bleeding come and go?
Blood in the pee (haematuria) This is the most common symptom of bladder cancer. It can happen suddenly and may come and go. Your pee (urine) may look pink, red or sometimes brown.
How long does bleeding last with bladder cancer?
Blood in the urine Blood may be present one day and absent the next, with the urine remaining clear for weeks or even months. But if a person has bladder cancer, at some point the blood reappears.
What kind of bleeding occurs with bladder cancer?
Hematuria (blood in the urine) — The most common sign of bladder cancer is blood in the urine (hematuria). Hematuria caused by cancer is usually visible (turning the urine pink or red), intermittent, and not painful.
What happens in the final stages of bladder cancer?
When bladder cancer reaches stage 4, the original tumor has often grown and pushed through the wall of the bladder. Cancer cells may have spread to organs close to the bladder or those further away, such as the liver or lungs.
What are the symptoms of advanced bladder cancer?
Symptoms of Advanced Bladder CancerAn inability to urinate.Lower back pain on one side of the body.Loss of appetite.Unintended weight loss.Overwhelming fatigue.Bone pain.Swelling in the feet.
Do benign bladder tumors bleed?
However, some benign masses can bleed or grow very large and cause problems by taking up too much space in your bladder or pressing on other organs in your body. In that case, we usually remove or treat benign masses, using a TURBT procedure.
What does bleeding from the bladder mean?
Hematuria Causes and Risk Factors You might have blood in your urine because of: Urinary tract or kidney infections. Bladder or kidney stones. Certain kidney diseases, such as inflammation in the filtering system (glomerulonephritis) An enlarged prostate (benign prostatic hyperplasia) or prostate cancer.
How do you know if bladder cancer has spread?
Ultrasound: This test uses sound waves to make pictures of the organs inside your body, like your bladder and kidneys. It can help show the size of a bladder cancer and if it has spread. Bone scan: A bone scan can help show if bladder cancer has spread to the bones. This test is not done unless you have bone pain.
What is the life expectancy of someone with bladder cancer?
5-year relative survival rates for bladder cancerSEER Stage5-year Relative Survival RateIn situ alone Localized96% 70%Regional38%Distant6%All SEER stages combined77%Mar 1, 2022

Is cancer a thrombotic event?
Cancer has long been recognized as a risk factor for thrombotic events. While venous thromboembolism (VTE, which includes pulmonary embolism [PE] and deep vein thrombosis [DVT]) is clearly the most common form of malignancy-associated thrombosis, arterial thrombosis and systemic thrombotic syndromes (eg, disseminated intravascular coagulation [DIC]) can also occur. Overall, approximately 2% of patients with bladder cancer (BCa) will experience a VTE event, a rate five times higher than that in the overall population; also, such an event results in a threefold increased risk of death in patients with cancer. [1-3]
Does UPA activate fibrinolysis?
Although its primary role is to activate fibrinolysis, uPA also plays a role in BCa. First, uPA and its receptor are produced by cultured BCa cells and facilitate their invasiveness. [12] Second, uPA and its RNA are elevated in the urine of BCa patients. [13,14] Third, uPA is overexpressed in BCa and associated with a higher recurrence rate and worse survival. [15,16] Interestingly, intravesical uPA has been used (ineffectively) in combination with doxorubicin and thioTEPA as intravesical treatment for BCa. [17-19] Drugs that target uPA and its receptor (uPAR) are being developed. [20]
What is TF in BCa?
TF controls the extrinsic coagulation pathway but also has biologic effects that promote angiogenesis and metastasis. Urinary and serum TF levels are elevated in patients with BCa. [8-10] Importantly, TF is overexpressed in approximately 75% of muscle-invasive BCas and is associated with a threefold increased risk of death. [11]

What is PAI-1 in BCa?
In addition to inhibiting fibrinolysis, PAI-1 (also known as SERPINE1) is involved in angiogenesis, cell migration, and cell adhesion. It is overexpressed in BCa and its levels in urine and serum appear to increase with tumor stage. [21,22] The presence of even a single cell expressing PAI-1 has been shown to increase BCa-specific mortality 4.5-fold. [22] Targeting PAI-1 was shown to be an effective anticancer therapy in a BCa xenograft model. [23]
What is the most important plasminogen activator?
The most important plasminogen activator is tPA, which is slowly released by the endothelium of the injured blood vessel. Once active, plasmin cleaves the fibrin clot into fibrin degradation products (FDPs), the most clinically important of which is the D-dimer. Fibrinolysis is regulated by several mechanisms.
Can bladder cancer cause bleeding?
Usually, the early stages of bladder cancer (when it’s small and only in the bladder) cause bleeding but little or no pain or other symptoms. Blood in the urine doesn’t always mean you have bladder cancer.
What are the symptoms of bladder cancer?
Being unable to urinate. Lower back pain on one side. Loss of appetite and weight loss. Feeling tired or weak. Swelling in the feet. Bone pain. Again, many of these symptoms are more likely to be caused by something other than bladder cancer, but it’s important to have them checked.
How do you know if you have bladder cancer?
Bladder cancers that have grown large or have spread to other parts of the body can sometimes cause other symptoms, such as: Being unable to urinate. Lower back pain on one side. Loss of appetite and weight loss. Feeling tired or weak.
Can bladder cancer spread to other parts of the body?
Bladder cancers that have grown large or have spread to other parts of the body can sometimes cause other symptoms, such as: Again, many of these symptoms are more likely to be caused by something other than bladder cancer, but it’s important to have them checked.
Can bladder cancer cause lower back pain?
Bladder cancers that have grown large or have spread to other parts of the body can sometimes cause other symptoms, such as: Being unable to urinate. Lower back pain on one side. Loss of appetite and weight loss. Feeling tired or weak.
What does it mean when you have blood in your urine?
Blood in the urine. In most cases, blood in the urine (called hematuria) is the first sign of bladder cancer. There may be enough blood to change the color of the urine to orange, pink, or, less often, dark red.
Why do I have trouble peeing?
Having to get up to urinate many times during the night. These symptoms are more likely to be caused by a urinary tract infection (UTI), bladder stones, an overactive bladder, or an enlarged prostate (in men).

Can bladder cancer cause blood in urine?
Most patients with bladder cancer will have blood in the urine, but many patients may have microscopic blood in the urine on routine exam though few will be shown to have bladder cancer. 5.8k views Answered >2 years ago. Thank. 1 thank.
Can you see blood in urine with bladder cancer?
In early stages it may be only microscopic whereas in some cases it may be visible to the naked eye. Most patients with bladder cancer will have blood in the urine, but many patients may have microscopic blood in the urine on routine exam though few will be shown to have bladder cancer. 5.8k views Answered >2 years ago.
Is blood in urine a sign of cancer?
Typically: Specifically, blood in the urine (hematuria) is highly associated with bladder cancer.

How does bladder cancer develop?
Bladder cancer develops when cells in the bladder begin to grow abnormally, forming a tumor in the bladder. Bladder cancer begins when cells in the bladder develop changes (mutations) in their DNA. A cell’s DNA contains instructions that tell the cell what to do.
How do you know if you have bladder cancer?
Bladder cancer signs and symptoms may include: Blood in urine (hematuria), which may cause urine to appear bright red or cola colored, though sometimes the urine appears normal and blood is detected on a lab test. Frequent urination. Painful urination. Back pain.
Where is the bladder located?
Your kidneys, located in the rear portion of your upper abdomen, produce urine by filtering waste and fluid from your blood. Bladder cancer is a common type of cancer that begins in the cells of the bladder. The bladder is a hollow muscular organ in your lower abdomen that stores urine. Bladder cancer most often begins in …

Where does bladder cancer start?
Bladder cancer is a common type of cancer that begins in the cells of the bladder. The bladder is a hollow muscular organ in your lower abdomen that stores urine. Bladder cancer most often begins in the cells (urothelial cells) that line the inside of your bladder. Urothelial cells are also found in your kidneys and the tubes (ureters) …
Where is urothelial cancer found?
Urothelial cells are also found in your kidneys and the tubes (ureters) that connect the kidneys to the bladder. Urothelial cancer can happen in the kidneys and ureters, too, but it’s much more common in the bladder. Most bladder cancers are diagnosed at an early stage, when the cancer is highly treatable.
Can bladder cancer come back?
But even early-stage bladder cancers can come back after successful treatment. For this reason, people with bladder cancer typically need follow-up tests for years after treatment to look for bladder cancer that recurs.
What is the most common type of bladder cancer?
Urothelial carcinoma is the most common type of bladder cancer in the United States. Squamous cell carcinoma. Squamous cell carcinoma is associated with chronic irritation of the bladder — for instance, from an infection or from long-term use of a urinary catheter. Squamous cell bladder cancer is rare in the United States.
Can bladder cancer cause pain?
People with bladder cancer may experience the following symptoms or signs. Sometimes, people with bladder cancer do not have any of these changes. Or, the cause of a symptom may be a different medical condition that is not cancer. Blood or blood clots in the urine. Pain or burning sensation during urination.
How do you know if you have bladder cancer?
Bladder Cancer: Symptoms and Signs 1 Blood or blood clots in the urine 2 Pain or burning sensation during urination 3 Frequent urination 4 Feeling the need to urinate many times throughout the night 5 Feeling the need to urinate, but not being able to pass urine 6 Lower back pain on 1 side of the body

Can hematuria be diagnosed with bladder cancer?
General urine tests are not used to make a specific diagnosis of bladder cancer because hematuria can be a sign of several other conditions that are not cancer, such as an infection or kidney stones.
Can bladder cancer spread to other parts of the body?
Sometimes when the first symptoms of bladder cancer appear, the cancer has already spread to another part of the body. In this situation, the symptoms depend on where the cancer has spread. For example, cancer that has spread to the lungs may cause a cough or shortness of breath, spread to the liver may cause abdominal pain or jaundice …
Can cancer cause shortness of breath?
For example, cancer that has spread to the lungs may cause a cough or shortness of breath, spread to the liver may cause abdominal pain or jaundice (yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes), and spread to the bone may cause bone pain or a fracture (broken bone).

Can bladder cancer cause bleeding?
Passage of tissue fragments in urine (less frequent than other symptoms) The presence of one or all of these signs does not mean you have cancer, but you should be seen by a physician, as these are abnormal bodily functions. Sometimes those diagnosed with bladder cancer do not experience any bleeding or pain.
What is the first symptom of bladder cancer?
Bladder Cancer Symptoms. For most people, the first symptom of bladder cancer is blood in the urine, also called hematuria. Sometimes the blood is visible, prompting the patient to visit a doctor. Other times, blood is microscopic and is only discovered during either a routine lab test or one that was ordered after the patient reported other …
What are the signs of bladder cancer?
Frequent urination. Incomplete emptying of the bladder. Passage of tissue fragments in urine (less frequent than other symptoms) The presence of one or all of these signs does not mean you have cancer, but you should be seen by a physician, as these are abnormal bodily functions. Sometimes those diagnosed with bladder cancer do not experience any …

How do bladder cancer mutations occur?
Some of these acquired gene mutations result from exposure to cancer-causing chemicals or radiation. For example, chemicals in tobacco smoke can be absorbed into the blood, filtered by the kidneys, and end up in urine, where they can affect bladder cells. Other chemicals may reach the bladder the same way. But sometimes, gene changes may just be random events that sometimes happen inside a cell, without having an outside cause.
Can you get bladder cancer from your parents?
Some people inherit gene changes from their parents that increase their risk of bladder cancer. But bladder cancer does not often run in families, and inherited gene mutations are not thought to be a major cause of this disease.
What causes cancer cells to turn on oncogenes?
Cancers can be caused by DNA changes (gene mutations) that turn on oncogenes or turn off tumor suppressor genes. Several different gene changes are usually needed for a cell to become cancer.

What are the genes that cause bladder cancer?
Acquired changes in certain genes, such as the TP53 or RB1 tumor suppressor genes and the FGFR and RAS oncogenes , are thought to be important in the development of some bladder cancers. Changes in these and similar genes may also make some bladder cancers more likely to grow and spread into the bladder wall than others.
Why do we look like our parents?
We usually look like our parents because they are the source of our DNA, but DNA affects more than just how we look . Some genes control when cells grow, divide into new cells, and die: Genes that help cells grow, divide, and stay alive are called oncogenes.
What are the genes that control cell division?
Some genes control when cells grow, divide into new cells, and die: 1 Genes that help cells grow, divide, and stay alive are called oncogenes. 2 Genes that normally help control cell division, repair mistakes in DNA, or cause cells to die at the right time are called tumor suppressor genes.
What is bladder tumor?
What are bladder tumors? Bladder tumors are abnormal growths that occur in the bladder. If the tumor is benign, it’s noncancerous and won’t spread to other parts of your body. This is in contrast to a tumor that’s malignant, which means it’s cancerous.
How to tell if bladder tumor is a tumor?
Bladder tumors are typically diagnosed by a biopsy or a urine analysis. However, certain symptoms can indicate that a tumor or bladder issue is the possible cause, including: blood in the urine. pain while urinating. inability to urinate. having the urge to urinate more frequently. blockage of the urine stream.
What is the most common benign tumor in women?
Leiomyomas . Leiomyomas are the most common benign tumor found in women. That said, they’re rarely located in the bladder: According to a study. on bladder leiomyomas, they account for less than 1 percent of all bladder tumors. Leiomyomas form in the smooth muscle cells.
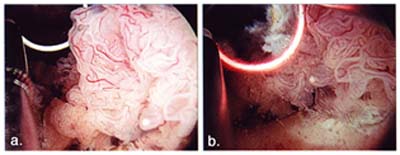
What is a tumor that grows fat cells?
Lipomas are tumor growths of fat cells. They’re often caused by an overgrowth of such cells. Lipomas are fairly common and usually don’t cause any pain unless they press against other organs or nerves.
How to treat a tumor?
Treatment for your tumor will depend on what type of tumor you have. First, your doctor may diagnose the tumor via biopsy or endoscopy. An endoscopy will provide a visual look, while a biopsy will provide a tissue sample of the tumor. After diagnosing the tumor, your doctor will develop a treatment plan that best suits your condition.
How to diagnose a tumor?
First, your doctor may diagnose the tumor via biopsy or endoscopy. An endoscopy will provide a visual look, while a biopsy will provide a tissue sample of the tumor. After diagnosing the tumor, your doctor will develop a treatment plan that best suits your condition.
What to do after a tumor is diagnosed?
After diagnosing the tumor, your doctor will develop a treatment plan that best suits your condition. If the tumor is positioned so the risk of surgery damaging blood vessels, nerves, and the surrounding area is relatively low, they’ll most likely recommend removing the tumor.