Contents

What is the role of CT urography in the diagnosis of bladder cancer?
You might have a CT urogram to check: the cause of your symptoms such as where the blood in your urine is coming from. where the cancer is and how big it is (stage) how well your treatment is working. Find out more about staging bladder cancer.
Can a bladder tumor be detected with an ultrasound?
· Imaging Techniques To Detect Bladder Cancer. Imaging techniques, which include ultrasound, computed tomography (or CT) scanning, magnetic resonance imaging (or MRI) and x-ray approaches, provide an important means of assessing the urinary tract, including the kidneys, and play an important role in the detection, diagnosis, and monitoring of bladder cancer.
Can a chest xray show bladder cancer?
· If a person experiences certain urinary tract symptoms, such as pain or blood in the urine, a doctor may recommend a CT urogram. CT urograms use imaging and contrast dye to allow doctors to…
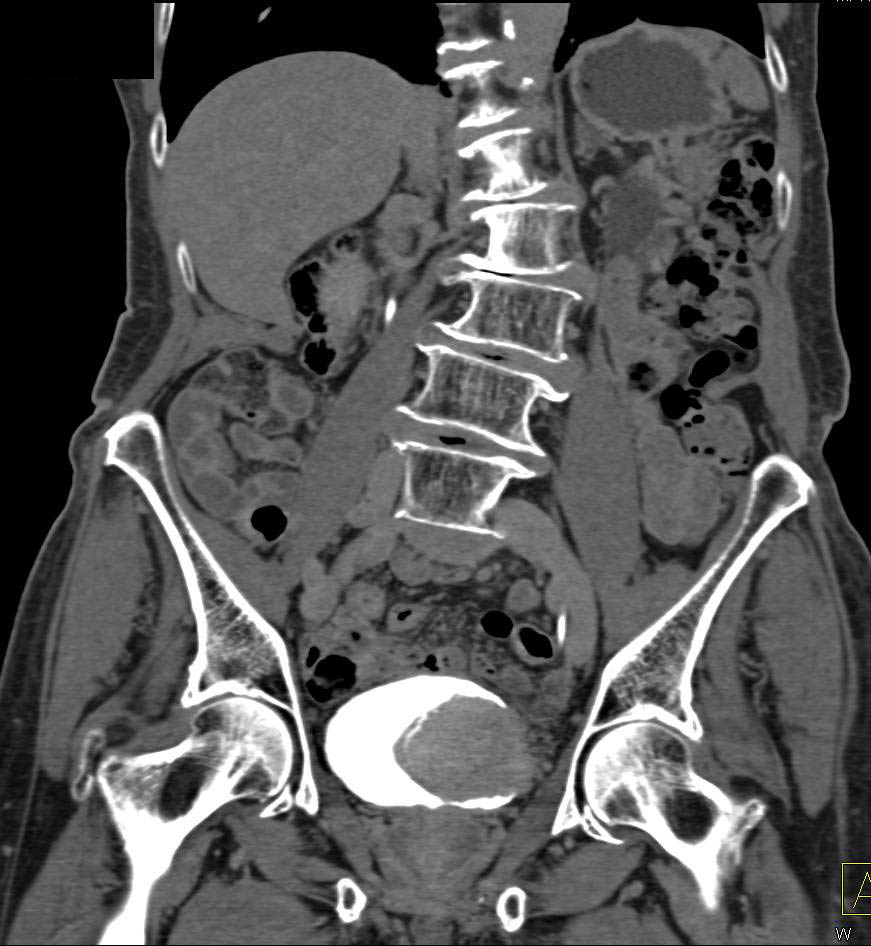
Can CT urogram detect bladder cancer?
In conclusion, CT urography is an accurate, noninvasive test for detecting bladder cancer in patients at risk for the disease. Unlike cystoscopy, CT urography can be used to evaluate the upper tracts concomitantly, an important step in the evaluation of patients with bladder cancer.
What can a CT urogram detect?
A CT urogram may be helpful in diagnosing urinary tract conditions such as: Kidney stones. Bladder stones. Complicated infections.
How accurate is a CT scan for bladder cancer?
Computed tomography (CT) Multidetector (64-slice) CT scanning has provided the mainstay in radiological assessment. It has a reported sensitivity of 85% and specificity of 94% for the diagnosis of bladder cancers [11]. Detection is dependent on the morphology and size of the tumor.
What is the difference between a CT scan and a CT urogram?
A CT urogram is a test that uses a CT scan and a special contrast medium or dye that a doctor injects into a vein. The contrast dye provides a high quality image to allow doctors to look at the urinary system and make a diagnosis.
Is a CT urogram the same as a CT abdomen and pelvis?
A CT (computerised tomography) scan uses x-rays and a computer to create a detailed picture of the inside of the body. A scan of the urinary system may be called a CT urogram, CT IVP (intravenous pyelogram) or a triple-phase abdomen and pelvis CT – these are different names for the same test.
Why do I need a cystoscopy after a CT scan?
While some bladder tumors may be found on a CT urogram or other imaging test, others will not. A urologist will often recommend a cystoscopy to evaluate the lower urinary tract (bladder/urethra) for a source of blood in the urine or to workup other urologic symptoms.
How is bladder cancer detected?
A sample of your urine is analyzed under a microscope to check for cancer cells in a procedure called urine cytology. Imaging tests. Imaging tests, such as computerized tomography (CT) urogram or retrograde pyelogram, allow your doctor to examine the structures of your urinary tract.
Where does it hurt if you have bladder cancer?
Bladder cancer can cause lower back pain when it reaches a more advanced form of the disease. The pain is typically only on one side of the back, but it can be centrally located. Lower back pain might occur once the tumors increase in size or cancer cells start to spread to other parts of your body.
Can CT scan miss cancer?
Imaging tests usually can’t tell if a change has been caused by cancer. CT scans can produce false negatives and false positives. CT scan can miss cancer, or miss tumors in other areas of the body. CT scans are proven to be less effective at diagnosing cancer than PET/CT.
Does CT urogram show pancreas?
The dye makes structures and organs easier to see on the CT pictures. A CT scan can be used to study all parts of your body, such as the chest, belly, pelvis, or an arm or leg. It can take pictures of body organs, such as the liver, pancreas, intestines, kidneys, bladder, adrenal glands, lungs, and heart.
What is a CT urogram with and without contrast?
Urography uses imaging and contrast material to evaluate or detect blood in urine, kidney or bladder stones, and cancer in the urinary tract. Urography with conventional x-ray is known as intravenous pyelogram (IVP). Urography is also often performed using computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
What structures would an intravenous Urogram show?
Intravenous urography (also known as intravenous pyelography) is an X-ray procedure which is used to assess problems in your kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra. These structures make up your urinary tract.
Does CT urogram show pancreas?
The dye makes structures and organs easier to see on the CT pictures. A CT scan can be used to study all parts of your body, such as the chest, belly, pelvis, or an arm or leg. It can take pictures of body organs, such as the liver, pancreas, intestines, kidneys, bladder, adrenal glands, lungs, and heart.
Does CT urogram show urethra?
A computed tomography (CT) urogram is an imaging test used to evaluate the urinary system, which includes the kidneys, ureters (tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to urinary bladder), bladder, and urethra (urinary tract).
What is a CT urogram with and without contrast?
Urography uses imaging and contrast material to evaluate or detect blood in urine, kidney or bladder stones, and cancer in the urinary tract. Urography with conventional x-ray is known as intravenous pyelogram (IVP). Urography is also often performed using computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
How long does a CT urogram with contrast take?
The entire procedure normally takes 5–10 minutes. Contrast studies may take an additional 10–15 minutes. If an oral contrast is required, you will also need an additional 45–50 minutes prior to the test.
Imaging Techniques To Detect Bladder Cancer
Imaging techniques, which include ultrasound, computed tomography (or CT) scanning, magnetic resonance imaging (or MRI) and x-ray approaches, provide an important means of assessing the urinary tract, including the kidneys, and play an important role in the detection, diagnosis, and monitoring of bladder cancer.
Detecting bladder cancer with ultrasound
An ultrasound (which may also be referred to as a sonogram) uses high frequency sound waves to produce images of internal organs. Echoes, which are created as sound waves bounce off organs and tissues, produce computer images that provide information on the structure and movement of organs and the blood flow through vessels.
How do ultrasounds help detect and monitor bladder cancer?
An ultrasound of the urinary tract can help assess the size of a bladder tumor and whether a bladder cancer has spread. Ultrasound is able to differentiate between fluid-filled cysts and solid tumors, however, it cannot determine if a tumor is cancerous. Ultrasound can also be used to guide a biopsy needle to sample a suspected cancer.
Detecting bladder cancer with CT scans
A CT scan uses x-rays to obtain cross-sectional images of the body. Compared to a general x-ray test, which directs a broad x-ray beam from a single angle, the CT scan uses a number of thin beams to produce a series of images from different angles.
Other imaging approaches to detect or monitor bladder cancer
An MRI scan uses radio waves and magnets to produce more detailed pictures of soft tissues. MRI scans can show whether bladder cancer has spread to other tissues or to the lymph nodes. To improve the quality of the images it’s sometimes necessary to administer an intravenous dye.
Can you drink water before a CT urogram?
In order to expand (distend) your bladder, you may be asked to drink water before a CT urogram and not to urinate until after the procedure. However, depending on your condition, guidelines about eating and drinking before your CT urogram may vary.
What position do you lie on for a CT urogram?
For a CT urogram, you usually lie on your back on an exam table, though you may be asked to lie on your side or stomach. Straps and pillows may be used to help you maintain the correct position and keep still during the exam. You may be asked to change positions during the CT urogram.
What is a urogram?
Overview. A computerized tomography (CT) urogram is an imaging exam used to evaluate your urinary tract , including your kidneys, your bladder and the tubes (ureters) that carry urine from your kidneys to your bladder. CT urography uses X-rays to generate multiple images of a slice of the area in your body being studied, including bones, …
Can a CT scan cause cancer?
A single CT urogram carries no risk of developing secondary malignancy, but multiple tests or radiation exposures may cause a slightly increased cancer risk compared with the general population. However, the benefit of an accurate diagnosis far outweighs this risk.
What is a CT urogram?
A CT urogram is a test that uses a CT scan and a special contrast medium or dye that a doctor injects into a vein. The contrast dye provides a high quality image to allow doctors to look at the urinary system and make a diagnosis. A CT scan is a form of medical imaging that allows doctors to see a picture of the inside of the body without …
What is the purpose of a CT urogram?
Considerations. Summary. If a person experiences certain urinary tract symptoms, such as pain or blood in the urine, a doctor may recommend a CT urogram. CT urograms use imaging and contrast dye to allow doctors to diagnose problems such as kidney and bladder stones, certain cancers, and structural irregularities.
Why do doctors use contrast dye?
CT urograms use imaging and contrast dye to allow doctors to diagnose problems such as kidney and bladder stones, certain cancers, and structural irregularities. This article will explore why doctors may recommend a CT urogram, what the procedure involves, and some possible risks. It will also discuss when a person should contact a doctor.
What is contrast dye?
The contrast dye provides a high quality image to allow doctors to look at the urinary system and make a diagnosis. A CT scan is a form of medical imaging that allows doctors to see a picture of the inside of the body without the need for surgery. The CT scanner is a short tunnel that contains a rotating X-ray machine.
What is a CT scan?
A CT scan is a form of medical imaging that allows doctors to see a picture of the inside of the body without the need for surgery . The CT scanner is a short tunnel that contains a rotating X-ray machine. A person lies in the scanner while the inside portion rotates and takes a series of X-rays from various angles.
Why do doctors use CT scans?
Doctors can use CT images to see if the internal structures appear healthy and work correctly and to check for any signs of disease. A doctor may recommend a CT urogram if a person is experiencing blood in the urine, known as hematuria, or pain in the groin or lower back.
Does contrast material affect kidneys?
Kidney problems: The contrast material could negatively impact the kidneys. However, a doctor will check a person’s blood before the procedure to ensure that their kidneys are working well. Radiation: The CT scan involves radiation, which can slightly increase someone’s cancer risk in the future.
What is a CT urography?
CT urography is defined as CT examination of the kidneys, ureters and bladder with at least one series of images acquired during the excretory phase after intravenous contrast administration.
What is urography used for?
Urography uses imaging and contrast material to evaluate or detect blood in urine, kidney or bladder stones, and cancer in the urinary tract. CT and MR urography are painless and proven effective in detecting urinary tract issues. Your preparation may vary depending on whether your exam will use CT or MRI.
Bladder Malignancies on CT: The Underrated Role of CT in Diagnosis
1 Both authors: Department of Radiology, Johns Hopkins University, JHOC 3251, 601 N Caroline St, Baltimore, MD 21287.
Recommended Articles
Structured Review. The “Misty Mesentery”: Mesenteric Panniculitis and Its Mimics
What is a CT scan of the bladder?
A CT scan uses x-rays to make detailed cross-sectional pictures of your body. A CT scan of the kidney, ureters, and bladder is called a CT urogram. It can provide detailed information about the size, shape, and position of any tumors in the urinary tract, including the bladder. It can also help show enlarged lymph nodes that might contain cancer, as well as other organs in the abdomen (belly) and pelvis.
How does ultrasound help with bladder cancer?
Ultrasound uses sound waves to create pictures of internal organs. It can be useful in determining the size of a bladder cancer and whether it has spread beyond the bladder to nearby organs or tissues. It can also be used to look at the kidneys. This is usually an easy test to have, and it uses no radiation.
Why is bladder cancer found?
Bladder cancer is often found because of signs or symptoms a person is having. Or it might be found because of lab tests a person gets for another reason. If bladder cancer is suspected, exams and tests will be needed to confirm the diagnosis. If cancer is found, more tests will be done to help find out the extent ( stage) of the cancer.
Can a urine culture show cancer?
If you’re having urinary symptoms, this test may be done to see if an infection (rather than cancer) is the cause. Urinary tract infections and bladder cancers can cause the same symptoms. For a urine culture, a sample of urine is put into a dish in the lab to allow any bacteria that are present to grow. It can take time for the bacteria to grow, so it may take a few days to get the results of this test.
What type of tube is used for bladder cancer?
If bladder cancer is suspected, most doctors will recommend a cystoscopy. . A urologist uses a cystoscope, which is a long, thin, flexible tube with a light and a lens or a small video camera on the end. For details on how this procedure is done, see Cystoscopy.
What is the biopsy for bladder cancer?
A biopsy is when tiny pieces (called samples) of the abnormal-looking tissue are taken out and tested for cancer cells. If bladder cancer is suspected, a biopsy is needed to be sure of the diagnosis.
Is bladder cancer invasive or noninvasive?
This is very important in deciding treatment. If the cancer stays in the inner layer of cells without growing into the deeper layers, it’s called non-invasive. If the cancer grows into the deeper layers of the bladder, it’s called invasive. Invasive cancers are more likely to spread and are harder to treat.
What is the best way to test for bladder cancer?
Although radiological tests provide important information about the kidneys and the ureters, cystoscopy is the best method of evaluating the bladder and the urethra and diagnosing and monitoring bladder cancer. The cystoscope, a long thin camera, is inserted through the urethra into the bladder.
What is a CT urogram?
A CT urogram examines the upper urinary tract (kidneys and ureters) in detail. This test is good at finding tumors of the kidney, renal pelvis, and ureter, as well as other urologic abnormalities. It may identify kidney stones and hydronephrosis (swelling of the kidney that is often due to downstream blockage).
Can a urologist do a biopsy of the bladder?
Some urologist may have the ability to perform small bladder biopsies in the office. The tissue sample, or biopsy, is then sent to the pathologist for examination. A sample of the urine from the bladder is sent for analysis of the cells (called cytology) to determine if the urine contains any cancer cells.
Can you go home after a cystoscopy?
Patients will go home after the cystoscopy if it is done in the doctor’s office. There may be some bleeding and irritating bladder symptoms following the cystoscopy for a day or two.
Overview
Uses several X-ray images and computer processing to create cross sectional images.
Type: Imaging
Duration: Usually 30-60 mins
Results available: Usually 2-3 days
Conditions it may diagnose: Irritable bowel syndrome · Fatty liver · Gallstones · Lung nodules · Cancer and more
Is Invasive: Noninvasive
Type: Imaging
Duration: Usually 30-60 mins
Results available: Usually 2-3 days
Conditions it may diagnose: Irritable bowel syndrome · Fatty liver · Gallstones · Lung nodules · Cancer and more
Is Invasive: Noninvasive
Ability to confirm condition: High
Ability to rule out condition: High
Why It’s Done
Risks
How You Prepare
What You Can Expect
-
A CTurogram is used to examine the kidneys, ureters and bladder. It lets your doctor see the size and shape of these structures to determine if they’re working properly and to look for any signs of disease that may affect your urinary system. Your doctor may recommend a CTurogram if you have signs and symptoms — such as pain in your side or back or…
Results
-
With a CTurogram, there’s a slight risk of an allergic reaction to the contrast material. Reactions are generally mild and easily managed by medication. They include: 1. A feeling of warmth or flushing 2. Nausea 3. Itching 4. Hives 5. Pain near the injection site A single CT urogram carries no risk of developing cancer after radiation exposure. But, multiple tests or radiation exposures …