Contents

How can urine tests detect bladder cancer?
Urine cytology tests to detect cancer cells. In a urine cytology test, a sample of the patient’s urine is analyzed under a microscope. 1,2 This test can reveal the presence of cancer cells or cells that are pre-cancerous, meaning that they are more likely to become cancer cells later. However, this test is not enough to provide a definite diagnosis on its own—it is possible for cancer cells to …
What if cancer cells found in urine cytology?
A urine cytology test can only help diagnose cancer. Healthcare providers don’t use it solely to diagnose urinary system cancers. If you have atypical, suspicious or cancer cells in your urine, your healthcare provider will likely want you to have further testing such as a cystoscopy or a CT scan to examine your bladder and urinary tract.
What is the recovery time for bladder cancer surgery?
Urinary cytology is increasingly accepted as a diagnostic tool in the detection and follow-up of patients with bladder cancer. Its potential value has been reduced, however, by the relative inexperience of most pathologists in the examination of urinary specimens, and by the lack of cellular criteria specifically reflecting the morphology of low-grade papillary and flat lesions of …
Can cancer be detected in urine?
Urinary cytology has its place as an additive diagnostic tool to cystoscopy. None of the currently available urinary markers can replace cystoscopy but are helpful for specific diagnostic problems. The role of urinary cytology for detection of bladder cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol.

How accurate is urine cytology for bladder cancer?
Urine cytology is associated with a significant false-negative rate, especially for low-grade carcinoma (10-50% accuracy rate). The false-positive rate is 1-12%, although cytology has a 95% accuracy rate for diagnosing high-grade carcinoma and CIS. Urine cytology is often the test used for diagnosis of CIS.
Can bladder cancer be detected with a urine test?
Urinalysis can help find some bladder cancers early, but it has not been shown to be useful as a routine screening test. Urine cytology: In this test, a microscope is used to look for cancer cells in urine. Urine cytology does find some cancers, but it’s not reliable enough to make a good screening test.
What does a urine cytology show?
Cytology is the examination of cells from the body under a microscope. In a urine cytology exam, a doctor looks at cells collected from a urine specimen to see how they look and function. The test commonly checks for infection, inflammatory disease of the urinary tract, cancer, or precancerous conditions.
What is the best scan to detect bladder cancer?
Cystoscopy. Cystoscopy is the key diagnostic procedure for bladder cancer. It allows the doctor to see inside the body with a thin, lighted, flexible tube called a cystoscope. Flexible cystoscopy is performed in a doctor’s office and does not require anesthesia, which is medication that blocks the awareness of pain.
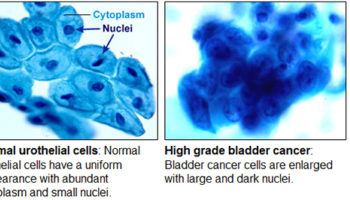
What is cytology in bladder cancer?
Urinary cytology is increasingly accepted as a diagnostic tool in the detection and follow-up of patients with bladder cancer. Its potential value has been reduced, however, by the relative inexperience of most pathologists in the examination of urinary specimens, and by the lack of cellular criteria specifically reflecting the morphology of low-grade papillary and flat lesions of bladder epithelium. The cytologic features of urothelial lesions, including papillary transitional cell carcinomas and flat urothelial dysplasias have been studied in both experimental systems and clinical situations and their application to a selected patient population is presented. Overall, the cytohistologic correlation for patients with bladder cancer was 92%. Positive cells reflecting the morphology of the tumor occurred in 62% of patients with grade I transitional cell carcinomas, and cells suspicious for malignancy were identified in an additional 14% of these individuals. Using the criteria presented, a positive cytology can correlate with a papillary grade I bladder tumor, and should not necessarily indicate the presence of another neoplasm. Dysplastic cells in cytologic specimens are often identified in patients having urothelial dysplasia as the most serious bladder lesion, but the cytologic diagnosis of dysplasia may represent an under-interpretation of a low-grade papillary bladder tumor. The cells of urothelial neoplasms, including low-grade transitional cell carcinomas and dysplasias, differ morphologically both from normal and reactive/reparative elements, and can be detected in cytologic samples. The changes are often subtle and require experience and a cautious approach for accurate interpretation.
Is urinary cytology a diagnostic tool?
The cellular features of transitional cell neoplasms. Urinary cytology is increasingly accepted as a diagnostic tool in the detection and follow-up of patients with bladder cancer. Its potential value has been reduced, however, by the relative inexperience of most pathologists in the examination …
What is the cytology of urine?
Presently the cytological examination of urine or other fluid samples from the urinary tract is a routine non-invasive diagnostic procedure to detect cancer of the urinary tract , especially in patients with painless haematuria. It is also used in the follow-up of patients previously treated for bladder cancer to detect recurrence or a new primary. It is a highly specific method for the diagnosis of invasive and in situ urothelial carcinoma and high-grade papillary carcinoma. However, it is unreliable for the detection of low-grade papillary neoplasms. Malignant cytomorphological characteristics of the exfoliated cells in urine or bladder washing can facilitate the diagnosis of bladder cancer. The Paris System (TPS) Working Group has proposed. The Paris System (TPS) authorities have proposed a standard reporting stem which includes specified diagnostic categories and cytomorphologic criteria for diagnosis of High-grade Urothelial Carcinoma (HGUC).
How to detect urinary tract malignancies?
Dr. George Papanicolaou hypothesized more than five decades ago; the urinary tract malignancies can be detected by evaluation of exfoliated cells in urine [1]. Microscopic evaluation of stained cellular smears from the urine is termed as urinary cytology. Urinary cytology is not a laboratory test and needs a pathologist’s interpretation of the morphologic features of shed urothelial cells. However, urinary tract cytology has been plagued with poor sensitivity, accuracy, and reproducibility. Several factors such as the low sensitivity in detecting low-grade non-invasive lesions, lack of standardized diagnostic criteria, and wide inter-observer variability are particularly worrisome [2]. Urine cytology samples constitute a significant percentage of daily case volume in any cytopathology practice. Although the numbers of urinary cytology are significantly less when compared to the gynaecologic cases, it is a more difficult specimen that pathologists encounter. Problems encountered by cytopathologists include inadequate cellularity of samples, cellular degeneration prior to fixation in cytology for diagnosis of Low-grade urothelial neoplasms (LGUN). 70% of the bladder tumors encountered via cystoscopy are LGUN [1, 3].
What is the Bethesda system for cytology?
It is well known that the Bethesda System (TBS) for reporting Cervical Cytology terminology, which was initiated in 1988, has led the way for standardized reporting in cytopathology [4]. However, there has been a lack of a standardized/comprehensive reporting system for urinary cytology, which is based on the current understanding of urothelial carcinoma (UC). An international panel of cytopathologists met in Paris in May 2013 on the occasion of the 18th International Congress of Cytology organized by the International Academy of Cytology, to set a standard reporting protocol of urinary cytology [1]. The value of ancillary tests in the screening and diagnosis of urinary neoplasms was also considered during this meet.
How to obtain a bladder wash sample?
The bladder wash sample is obtained during or before cystoscopy and is an invasive diagnostic procedure. First, the bladder is emptied using a catheter and then 50 to 100ml of normal saline is instilled and recovered for three times. The bladder cells get exfoliated into the washings and are used for microscopic examination. These bladder washing samples are highly cellular and contain well-preserved cells. In cases wherein the urinary sample cannot be delivered to the cytology laboratory within three hours after they have been obtained, then it needs to be prefixed with a mixture of 2% polyethylene glycol and 50% to 70% ethanol [9]. Several different techniques are used for the cytopathological preparation of the fluid samples. Centrifugation of fluid is used by some laboratories to obtain a pellet, which is then directly smeared onto the glass slide. While some laboratories use the commercially available ThinPrep TM technique for the preparation of samples from the urinary tract [9, 10]. The majority of erythrocytes and leukocytes are removed because the gentle negative pressure that is applied to assist filtration, usually deforms these cells and they pass through the filter. A single layer of cells (monolayer) is obtained by gently imprinting the filter onto a pair of glass slides. The cell sample on the slide is fixed by and the cell preparations are subsequently stained by the Papanicolaou method [9].
Why is urine cytology important?
Urine cytology also represents important means to survey the upper tracts and urethra in case of radical cystectomy with urinary diversions. Urinary cytology has its limitations. Studying morphology under the microscope is not a perfect reflection of biologic behaviour.
What should be included in a urine cytology evaluation?
An initial evaluation in patients at higher risk for bladder cancer (older age, male, smoking history, occupational exposures) and those with unexplained irritative urinary symptoms (potentially due to carcinoma in situ) should include urine cytology.
What is the most common sample sent for cytopathological examination?
Spontaneously voided urine is the most common sample sent for cytopathological examination. Apart from that, bladder wash samples catheterized urine samples or urine obtained by retrograde catheterization of the ureters or renal pelvis are occasionally sent for the cytopathological examination.
What is the best way to check for cancerous bladder?
If atypical or cancerous cells are detected, your doctor will likely recommend a cystoscopy procedure and a CT scan to further examine your bladder and urinary tract. By Mayo Clinic Staff.
Why do we do urine cytology?
Why it’s done. Urine cytology is used with other tests and procedures to diagnose cancers of the urinary tract , including: It’s generally used for people who have signs or symptoms of urinary tract cancer, such as blood in the urine. Urine cytology can best detect larger and more-aggressive urinary tract cancers.
How to do a cytology test?
In some cases, a urine sample is collected using a thin, hollow tube (catheter) that’s inserted into your urethra and moved up to your bladder.
What is the male urinary system?
Male urinary system. Your urinary system — which includes your kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra — removes waste from your body through urine. Your kidneys, located in the rear portion of your upper abdomen, produce urine by filtering waste and fluid from your blood. Urine cytology is a test to look for abnormal cells in your urine.
What does it mean when a urine sample is unsatisfactory?
Unsatisfactory specimen. This can mean that not enough cells or the wrong types of cells were found in your urine sample. You may need to repeat the test.
What is the name of the doctor who examines urine?
Your urine sample is sent to a lab for testing by a doctor who specializes in examining body tissues (pathologist). The pathologist analyzes cells from the urine sample under a microscope, notes the types of cells and looks for signs in the cells that might indicate cancer.
Can cytology detect urinary cancer?
Urine cytology can best detect larger and more-aggressive urinary tract cancers. It might not detect small urinary tract cancers that grow more slowly.
How to detect bladder cancer?
Urine tests: A urine test can help detect bladder cancer in a small number of cases. A urine routine and microscopic test may reveal the presence of blood in the urine. Further, a urine cytology test can be ordered. This test involves testing samples of urine for three consecutive days and is called three-day urine cytology test. The urine samples are examined under a microscope to look for the presence of cancerous cells.
What is the test for bladder cancer called?
This test involves testing samples of urine for three consecutive days and is called three-day urine cytology test. The urine samples are examined under a microscope to look for the presence of cancerous cells. Cystoscopy: If urine cytology does not make the diagnosis of bladder condition clear, doctors perform a procedure known as cystoscopy.
What is the procedure to remove a tumor from the bladder called?
The surgical procedure to remove the tissue for biopsy is called a transurethral bladder tumor resection or TURBT. The procedure is used to diagnose bladder cancer, identify the type of tumor and know how deeply cancer has grown into the layers of the bladder.
What is the purpose of a urine cytology test?
The test helps the doctor to look for any suspicious growths in the bladder. Urine could also be collected from the bladder during this procedure for a urine cytology test. Ultrasound: An ultrasound of the pelvis uses a sound probe to reveal any blockages in the kidneys or ureters that are causing the urinary symptoms.
What is a TURBT biopsy?
Biopsy/transurethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT): Biopsy is a procedure that involves removing a small tissue of the suspicious part (tumor) of the bladder to examine it under a microscope. It is done when an abnormal growth is found during cystoscopy.
What tests can be done to find out if bladder cancer has spread?
The doctor may order additional tests to find out if the bladder cancer has spread elsewhere in the body. These include. Computed tomography (CT) scan: CT scan uses multiple X-rays to give detailed, cross-sectional images of bladder cancer from different angles.
When is bladder cancer detected?
Bladder cancer is often detected when a person develops signs and symptoms. Bladder cancer is often detected when a person develops signs and symptoms. It is a highly treatable type of cancer when detected early. Although screening tests for bladder cancer are not conducted routinely, the following tests may be used to diagnose …
How to test for bladder cancer?
Urinalysis: One way to test for bladder cancer is to check for blood in the urine ( hematuria ). This can be done during a urinalysis, which is a simple test to check for blood and other substances in a sample of urine. This test is sometimes done as part of a general health check-up.
What is the best test to check for bladder cancer?
Urine cytology: In this test, a microscope is used to look for cancer cells in urine. Urine cytology does find some cancers, but it’s not reliable enough to make a good screening test. Urine tests for tumor markers: Newer tests look for certain substances in urine that might be a sign of bladder cancer. These include:
Why do we need to do a bladder screening?
This is because no screening test has been shown to lower the risk of dying from bladder cancer in people who are at average risk.
What is UroVysion test?
UroVysion™: This test looks for chromosome changes that are often seen in bladder cancer cells.
What causes blood in urine?
This test is sometimes done as part of a general health check-up. Blood in the urine is usually caused by benign (non-cancer) problems, like infections, but it also can be the first sign of bladder cancer. Large amounts of blood in urine can be seen if the urine turns pink or red, but a urinalysis can find even small amounts.
What is the test that looks for mucin in urine?
ImmunoCyt™: This test looks at cells in the urine for the presence of substances such as mucin and carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), which are often found on cancer cells.
Can urine be found with cancer?
Large amounts of blood in urine can be seen if the urine turns pink or red, but a urinalysis can find even small amounts. Urinalysis can help find some bladder cancers early, but it has not been shown to be useful as a routine screening test. Urine cytology: In this test, a microscope is used to look for cancer cells in urine.
What is the gold standard for bladder cancer screening?
Urine cytology remains the gold standard for bladder cancer screening. It is the test against which all others are compared when evaluating potential bladder tumor markers. The answer to whether urine cytology possess the optimal combination of sensitivity and specificity to retain consideration as the best screening device depends on the goals …
Why are TCC patients monitored?
Because patients with low-grade TCC are at low risk for progression, they are monitored primarily for the development of a subsequent tumor. One might argue that the detection of new low-grade lesions is of secondary importance to the early detection of disease progression.
Does urine cytology increase sensitivity?
Although adding urine cytology has not increased the sensitivity of some point-of-service tests, few studies have addressed the effect on specificity. Until an obvious winner is declared in the race to find a bladder tumor marker, urine cytology will remain the gold standard screening method because of its comfortable familiarity.
What tests are used to check for bladder cancer?
These include the tests called NMP22 ® (or BladderChek ® ), BTA Stat ®, Immunocyt ® , and UroVysion ®, which are discussed in Can Bladder Cancer Be Found Early?
What is the best way to diagnose bladder cancer?
Cystoscopy. If bladder cancer is suspected, most doctors will recommend a cystoscopy. . A urologist uses a cystoscope, which is a long, thin, flexible tube with a light and a lens or a small video camera on the end. For details on how this procedure is done, see Cystoscopy.
What is the blue light in a cystoscopy?
Fluorescence cystoscopy (also known as blue light cystoscopy) may be done along with routine cystoscopy. For this exam, a light-activated drug is put into the bladder during cystoscopy. It’s taken up by cancer cells. When the doctor then shines a blue light through the cystoscope, any cells containing the drug will glow (fluoresce). This can help the doctor see abnormal areas that might have been missed by the white light normally used.
What is the biopsy for bladder cancer?
A biopsy is when tiny pieces (called samples) of the abnormal-looking tissue are taken out and tested for cancer cells. If bladder cancer is suspected, a biopsy is needed to be sure of the diagnosis.
What is a physical exam for bladder cancer?
A physical exam can provide information about possible signs of bladder cancer and other health problems. The doctor might do a digital rectal exam (DRE), during which a gloved, lubricated finger is put into your rectum. If you are a woman, the doctor might do a pelvic exam as well.
How long does it take for a urine culture to show up?
It can take time for the bacteria to grow, so it may take a few days to get the results of this test.
How does ultrasound help with bladder cancer?
Ultrasound uses sound waves to create pictures of internal organs. It can be useful in determining the size of a bladder cancer and whether it has spread beyond the bladder to nearby organs or tissues. It can also be used to look at the kidneys. This is usually an easy test to have, and it uses no radiation.