Contents

Symptoms
· What is bladder cancer? Cancer can start any place in the body. Cancer that starts in the bladder is called bladder cancer. It starts when cells in the bladder grow out of control and crowd out normal cells. This makes it hard for the body to work the way it should. Cancer cells can spread to other parts of the body.
Causes
To find out whether you have bladder cancer, the first thing your doctor probably will do is a complete medical history. They’ll ask you about your overall health, as well as anything that…
Prevention
Bladder cancer can often be found early because it causes blood in the urine or other urinary symptoms that cause a person to see a health care provider. Blood in the urine. In most cases, blood in the urine (called hematuria) is the first sign of bladder cancer. There may be enough blood to change the color of the urine to orange, pink, or, less often, dark red.
Complications
Bladder Cancer. If you have bladder cancer or are close to someone who does, knowing what to expect can help you cope. Here you can find out all about bladder cancer, including risk factors, symptoms, how it’s found, and how it’s treated.
What are the early warning signs of bladder cancer?
The outlook for people with stage 0a (non-invasive papillary) bladder cancer is very good. These cancers can be cured with treatment. During long-term follow-up care, more superficial cancers are often found in the bladder or in other parts of the urinary system.
What are the chances of dying from bladder cancer?
Bladder cancer can sometimes be found early — when it’s small and hasn’t spread beyond the bladder. Finding it early improves your chances that treatment will work. Screening for bladder cancer Screening is the use of tests or exams to look for a …
Do you know the early signs of bladder cancer?
· The urinary bladder is a hollow muscular organ in the lower abdomen that is responsible for the storage of urine filtered by the kidneys. Bladder cancer is a common urologic cancer that has the highest recurrence rate of any malignancy. Bladder cancer is more common in men compared to women.
How bad is bladder cancer?
· 5 weeks ago i noticed for 2 whole days that i was passing blood in my urine enough to turn it bright red. Couple of days later i started to experience UTI syptoms-burning when peeing and only being able to pass small volumes. I thought i may have been passing a kidney stone so flushed by self out. Couple days passed and i rang my GP and was …
See more
2 days ago · Bladder cancer is any of several types of cancer arising from the tissues of the urinary bladder. Symptoms include blood in the urine, pain with urination, and low back pain. It is caused when epithelial cells that line the bladder become malignant.
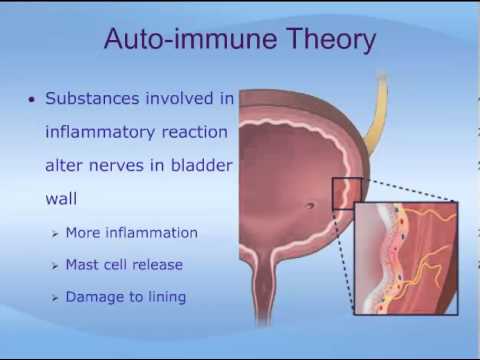
What is usually the first symptom of bladder cancer?
In most cases, blood in the urine (called hematuria) is the first sign of bladder cancer. There may be enough blood to change the color of the urine to orange, pink, or, less often, dark red.
What are the 5 warning signs of bladder cancer?
Here are five warning signs to watch for:Blood in the urine (hematuria). This is the most common early symptom of bladder cancer and typically the first sign of bladder cancer that is seen. … UTI-like symptoms. … Unexplained pain. … Decreased appetite. … Postmenopausal uterine bleeding.
Which is the most common symptom of bladder cancer?
Blood in your urine is the most common symptom of bladder cancer. The medical name for blood in your urine is haematuria and it’s usually painless. You may notice streaks of blood in your urine or the blood may turn your urine brown. The blood isn’t always noticeable and it may come and go.
How do you determine if a person has bladder cancer?
Tests for bladder cancer look for different substances and/or cancer cells in the urine.Urinalysis: One way to test for bladder cancer is to check for blood in the urine ( hematuria). … Urine cytology: In this test, a microscope is used to look for cancer cells in urine.More items…•
What are the signs that something is wrong with your bladder?
Some common signs and symptoms of bladder issues include:Bladder leakage.Pain or a burning sensation during urination.Cloudy urine.Persistent, strong urge to urinate.Urinating frequently in small amounts.Frequent urination (more than eight times during the day or more than two times at night)Urine that smells strong.More items…
Does bladder cancer show up in blood tests?
Tests to diagnose bladder cancer If bladder cancer is suspected, these tests may be performed to diagnose the disease: Physical exam. Blood test: Blood samples are used to measure certain substances released into the blood by organs and tissues in the body.
Can you have bladder cancer for years and not know it?
It may be seen as a symptom of post-menopausal bleeding, simple cystitis or a urinary tract infection. As a result, a bladder cancer diagnosis can be overlooked for a year or more.
Where does bladder cancer begin?
Most bladder cancers start in the innermost lining of the bladder, which is called the urothelium or transitional epithelium. As the cancer grows into or through the other layers in the bladder wall, it has a higher stage, becomes more advanced, and can be harder to treat.
Who is at high risk for bladder cancer?
Age: Most people who get bladder cancer are older in age. The average age at diagnosis is 73, and 90 percent of patients are over age 55. Race: Bladder cancer is twice as common among Caucasians as African Americans. This disease is less common among Hispanics, Asians and Native Americans.
How does a urologist check for bladder cancer?
Cystoscopy. If bladder cancer is suspected, most doctors will recommend a cystoscopy. . A urologist uses a cystoscope, which is a long, thin, flexible tube with a light and a lens or a small video camera on the end.
Do you feel bloated with bladder cancer?
Abdominal Pain The types of pains can vary and include: Generalized pain — felt in more than half of the stomach area. Cramp-like pain — less serious and most likely due to bloating and gas.
Is there pain with bladder cancer?
Bladder cancer can cause changes in urination. You might experience pain or a burning sensation when you urinate, and you may see blood in your urine. You may also feel: an urge to urinate more frequently than you used to.
Where do you feel pain with bladder cancer?
Bladder cancer can cause lower back pain when it reaches a more advanced form of the disease. The pain is typically only on one side of the back, but it can be centrally located. Lower back pain might occur once the tumors increase in size or cancer cells start to spread to other parts of your body.
Can you have bladder cancer for years and not know it?
It may be seen as a symptom of post-menopausal bleeding, simple cystitis or a urinary tract infection. As a result, a bladder cancer diagnosis can be overlooked for a year or more.
Where does bladder cancer begin?
Most bladder cancers start in the innermost lining of the bladder, which is called the urothelium or transitional epithelium. As the cancer grows into or through the other layers in the bladder wall, it has a higher stage, becomes more advanced, and can be harder to treat.
How quickly does bladder cancer spread?
As many as 50% of patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer may have occult metastases that become clinically apparent within 5 years of initial diagnosis and around 5% will have distant metastasis at the time of initial diagnosis. Most patients with overt metastatic disease die within 2 years despite chemotherapy.

How to see if you have tumors in your bladder?
Retrograde pyelogram. Your doctor will insert a thin tube (catheter) into your urethra and bladder. They’ll inject dye through the catheter so they can see the lining of the bladder. If there are any tumors in your urinary tract, they’ll show up here.
What tests can be used to check for bladder cancer?
They’ll be sent to the lab to check for cancer. Imaging Tests. These use X-rays, magnetic fields, sound waves, or radioactive substances to create pictures of what’s happening inside your body. Here are just a few of the imaging tests your doctor may use to see if you have bladder cancer: Intravenous pyelogram (IVP).
How to check for cancer in urine?
When you pee in a cup at your doctor’s office, there are a number of things they and other health professionals can look for: 1 Urinalysis. Your doctor will check to see if there’s any blood, or other substances, in your urine. 2 Urine cytology. Your doctor will use a microscope to check your urine for cancer cells. 3 Urine culture. Your doctor will send your urine to a lab. After a few days, lab technicians will check to see what kinds of germs grow in it. These results will tell your doctor if you have a bladder infection. 4 Urine tumor marker tests. These look for substances that are released by bladder cancer cells. Your doctor may use one or more of these along with a urine cytology to see if you have the disease.
What is a urine tumor test?
Urine tumor marker tests. These look for substances that are released by bladder cancer cells. Your doctor may use one or more of these along with a urine cytology to see if you have the disease.
What test can show if you have a bladder tumor?
Ultrasound. Sound waves create pictures of your urinary tract. It allows your doctor to see how big a bladder tumor is. Chest X-ray. If cancer in your bladder spread to your lungs, this test will allow your doctor to see it.
What do doctors look for when you pee in a cup?
When you pee in a cup at your doctor’s office, there are a number of things they and other health professionals can look for: Urinalysis. Your doctor will check to see if there’s any blood, or other substances, in your urine. Urine cytology. Your doctor will use a microscope to check your urine for cancer cells.

What to do if a cystoscopy doesn’t look right?
If your doctor finds something that doesn’t look right during your cystoscopy, they’ll take a sample of it ( biopsy) to see whether it’s cancer. During a TURBT, your surgeon will remove the tumor and some of the bladder muscle near it. They’ll be sent to the lab to check for cancer. Imaging Tests.
What are the symptoms of bladder cancer?
Being unable to urinate. Lower back pain on one side. Loss of appetite and weight loss. Feeling tired or weak. Swelling in the feet. Bone pain. Again, many of these symptoms are more likely to be caused by something other than bladder cancer, but it’s important to have them checked.
Why is bladder cancer so early?
Bladder cancer can often be found early because it causes blood in the urine or other urinary symptoms that cause a person to see a health care provider.

Why does urine have blood in it?
More often it’s caused by other things like an infection, benign (not cancer) tumors, stones in the kidney or bladder, or other benign kidney diseases. Still, it’s important to have it checked by a doctor so the cause can be found.
Why do I have trouble peeing?
Having to get up to urinate many times during the night. These symptoms are more likely to be caused by a urinary tract infection (UTI), bladder stones, an overactive bladder, or an enlarged prostate (in men).
How long does urine stay clear after bladder cancer?
Blood may be present one day and absent the next, with the urine remaining clear for weeks or even months. But if a person has bladder cancer, at some point the blood reappears.

Can bladder cancer cause a change in urination?
Bladder cancer can sometimes cause changes in urination, such as: Having to urinate more often than usual. Pain or burning during urination. Feeling as if you need to go right away, even when your bladder isn’t full. Having trouble urinating or having a weak urine stream.
What type of cancer is a bladder cancer?
Types of bladder cancer include: Urothelial carcinoma. Urothelial carcinoma , previously called transitional cell carcinoma, occurs in the cells that line the inside of the bladder. Urothelial cells expand when your bladder is full and contract when your bladder is empty.
What is the most common type of bladder cancer?
Urothelial carcinoma is the most common type of bladder cancer in the United States. Squamous cell carcinoma. Squamous cell carcinoma is associated with chronic irritation of the bladder — for instance, from an infection or from long-term use of a urinary catheter. Squamous cell bladder cancer is rare in the United States.

What is the male urinary system?
Male urinary system. Your urinary system — which includes your kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra — removes waste from your body through urine. Your kidneys, located in the rear portion of your upper abdomen, produce urine by filtering waste and fluid from your blood. Bladder cancer is a common type …
Why are men more likely to get bladder cancer than women?
Men are more likely to develop bladder cancer than women are. Exposure to certain chemicals. Your kidneys play a key role in filtering harmful chemicals from your bloodstream and moving them into your bladder. Because of this, it’s thought that being around certain chemicals may increase the risk of bladder cancer.
How do you know if you have bladder cancer?
Bladder cancer signs and symptoms may include: Blood in urine (hematuria), which may cause urine to appear bright red or cola colored, though sometimes the urine appears normal and blood is detected on a lab test. Frequent urination. Painful urination. Back pain.

How does bladder cancer develop?
Bladder cancer develops when cells in the bladder begin to grow abnormally, forming a tumor in the bladder. Bladder cancer begins when cells in the bladder develop changes (mutations) in their DNA. A cell’s DNA contains instructions that tell the cell what to do.
Where does bladder cancer start?
Bladder cancer is a common type of cancer that begins in the cells of the bladder. The bladder is a hollow muscular organ in your lower abdomen that stores urine. Bladder cancer most often begins in the cells (urothelial cells) that line the inside of your bladder. Urothelial cells are also found in your kidneys and the tubes (ureters) …
What is the first treatment for bladder cancer?
Chemo (with or without radiation) is typically the first treatment when bladder cancer has spread to distant parts of the body (M1). After this treatment the cancer is rechecked. If it looks like it’s gone, a boost of radiation to the bladder may be given or cystectomy might be done.
What is stage 0 bladder cancer?
Stage 0 bladder cancer includes non-invasive papillary carcinoma (Ta) and flat non-invasive carcinoma (Tis or carcinoma in situ). In either case, the cancer is only in the inner lining layer of the bladder. It has not invaded (spread deeper into) the bladder wall.
What to do if you have cancer that hasn’t been removed?
(Less often, close follow-up alone might be an option.) If all of the cancer wasn’t removed, options are intravesical BCG or cystectomy (removal of part or all of the bladder).
How to get rid of stage IV cancer?
The tumor is then rechecked. If it appears to be gone, chemo with or without radiation or cystectomy are options.

What is the treatment for cancer that recurs in distant parts of the body?
Cancers that recur in distant parts of the body can be harder to remove with surgery, so other treatments, such as chemotherapy, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, or radiation therapy , might be needed. For more on dealing with a recurrence, see Understanding Recurrence.
Can you get a radical cystectomy before surgery?
Radical cystectomy may be the only treatment for people who are not well enough to get chemo. But most doctors prefer to give chemo before surgery because it’s been shown to help patients live longer than surgery alone. When chemo is given first, surgery is delayed. This is not a problem if the chemo shrinks the bladder cancer, but it might be harmful if the tumor continues to grow during chemo.
Can you get a partial cystectomy for bladder cancer?
Lymph nodes near the bladder are often removed as well. If cancer is in only one part of the bladder, a partial cystectomy may be done instead. But this is possible in only a small number of patients . Radical cystectomy may be the only treatment for people who are not well enough to get chemo.
How to test for bladder cancer?
Urinalysis: One way to test for bladder cancer is to check for blood in the urine ( hematuria ). This can be done during a urinalysis, which is a simple test to check for blood and other substances in a sample of urine. This test is sometimes done as part of a general health check-up.
What is the best test to check for bladder cancer?
Urine cytology: In this test, a microscope is used to look for cancer cells in urine. Urine cytology does find some cancers, but it’s not reliable enough to make a good screening test. Urine tests for tumor markers: Newer tests look for certain substances in urine that might be a sign of bladder cancer. These include:
Why do we need to do a bladder screening?
This is because no screening test has been shown to lower the risk of dying from bladder cancer in people who are at average risk.

What causes blood in urine?
This test is sometimes done as part of a general health check-up. Blood in the urine is usually caused by benign (non-cancer) problems, like infections, but it also can be the first sign of bladder cancer. Large amounts of blood in urine can be seen if the urine turns pink or red, but a urinalysis can find even small amounts.
Can urine be found with cancer?
Large amounts of blood in urine can be seen if the urine turns pink or red, but a urinalysis can find even small amounts. Urinalysis can help find some bladder cancers early, but it has not been shown to be useful as a routine screening test. Urine cytology: In this test, a microscope is used to look for cancer cells in urine.
Can bladder cancer be detected early?
No screening tests are recommended for people at average risk, but bladder cancer can be found early because it causes blood in the urine or other urinary symptoms. (See Bladder Cancer Signs and Symptoms for details.) Many of these symptoms often have less serious causes, but it’s important to have them checked right away so the cause can be found and treated, if needed. If the symptoms are from bladder cancer, finding it early offers the best chance for successful treatment.

How long do people with bladder cancer live?
Overall, 70 to 90 percent of people with localized bladder cancer will live for at least five years or more . The physician calculates this with the help of survival rates. Survival rates indicate the percentage of people who live with a certain type of cancer for a specific time. The physician often uses an overall five-year survival rate.
Where does bladder cancer start?
Bladder cancer is a tumor (uncontrolled growth of cells) that starts in your urinary bladder. The urinary bladder is a balloon-like organ present in the lower abdomen near the pelvis. Its function is to store urine coming from the kidneys through the ureters (pipe-like passageways for urine) until it is expelled from the body through the tube-like passage called the urethra.
What is the first line of treatment for metastatic bladder cancer?
Then, the physician may perform a radical cystectomy to remove cancer that has invaded beyond the bladder wall. Metastatic bladder cancer: Platinum-based chemotherapy is the first line of treatment for this type of bladder cancer.

What is gallbladder cancer?
Gallbladder cancer (GBC) is one of the aggressive cancers of the biliary tract. The gallbladder generates and concentrates bile that aids in the digestion of fats. GBC is a rare, yet deadly cancer of the gastrointestinal tract.
What is the procedure to remove bladder cancer?
Tumors in the bladder muscle: In case of bladder cancer that has invaded the muscle wall but hasn’t spread to the lymph nodes, the physician recommends radical cystectomy. In this procedure, the physician removes the bladder, nearby lymph nodes and other nearby organs.
What is the treatment for high grade bladder cancer?
High-grade bladder cancer: High-grade cancers that are life-threatening and spread quickly need to be treated with chemotherapy, radiation or surgery.

What is SEER in cancer?
The surveillance, epidemiology, and end results (SEER) stages are taken from the SEER database, maintained by the National Cancer Institute. SEER database groups cancers into localized, regional, and distant stages.
What is bladder cancer?
Bladder cancer is any of several types of cancer arising from the tissues of the urinary bladder. Symptoms include blood in the urine, pain with urination, and low back pain. It is caused when epithelial cells that line the bladder become malignant.
What are the risk factors for bladder cancer?
Risk factors for bladder cancer include smoking, family history, prior radiation therapy, frequent bladder infections, and exposure to certain chemicals. The most common type is transitional cell carcinoma. Other types include squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. Diagnosis is typically by cystoscopy with tissue biopsies. Staging of the cancer is determined by transurethral resection and medical imaging.

How to treat non-muscle invasive bladder cancer?
Non-muscle invasive bladder cancer (those not entering the muscle layer of the bladder) can be “shaved off” using an electrocautery device attached to a cystoscope, which in that case is called a resectoscope. The procedure is called transurethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT) and serves primarily for pathological staging. In case of non-muscle invasive bladder cancer the TURBT is in itself the treatment, but in case of muscle invasive cancer, the procedure is insufficient for final treatment. Additionally, blue light cystoscopy with optical-imaging agent Hexaminolevulinate (HAL) is recommended at initial TURBT to increase lesion detection (especially carcinoma in situ) and improve resection quality thereby reducing recurrence. It is important to assess the quality of the resection, if there is evidence of incomplete resection or there is no muscle in the specimen (without which muscle invasiveness cannot be determined) a second TURBT is strongly recommended. Moreover, nearly half of the people with high grade non-invasive disease have residual tumor after primary TURBT, in such cases a second TURBT is important for avoiding under-staging. At this point classifying people into risk groups is recommended. Treatment and surveillance for different risk groups is indicated in the table below.
What are the genes that cause bladder cancer?
Mutations in FGFR3, TP53, PIK3CA, KDM6A, ARID1A, KMT2D, HRAS, TERT, KRAS, CREBBP, RB1 and TSC1 genes may be associated with some cases of bladder cancer. Deletions of parts or whole of chromosome 9 is common in bladder cancer. Low grade cancer are known to harbor mutations in RAS pathway and the fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) gene, both of which play a role in the MAPK/ERK pathway. p53 and RB gene mutations are implicated in high-grade muscle invasive tumors. Eighty nine percent of muscle invasive cancers have mutations in chromatin remodeling and histone modifying genes. Deletion of both copies of the GSTM1 gene has a modest increase in risk of bladder cancer. GSTM1 gene product glutathione S-transferase M1 (GSTM1) participates in the detoxification process of carcinogens such as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons found in cigarette smoke. Similarly, mutations in NAT2 ( N-acetyltransferase) is associated with increased risk for bladder cancer. N-acetyltransferase helps in detoxification of carcinogens like aromatic amines (also present in cigarette smoke). Various single-nucleotide polymorphisms in PSCA gene present on chromosome 8 have shown to increase the risk for bladder cancer. PSCA gene promoter region has an androgen response region. Loss of reactivity of this region to androgens is hypothesized as a cause of more number of aggressive tumors in women (unlike in men who have higher amount of androgen).
How long does it take for bladder cancer to go away?
Risk of bladder cancer decreases by 30% within 1–4 years and continues to decrease by 60% at 25 years after smoking cessation. However, former smokers will most likely always be at a higher risk of bladder cancer compared to people who have never smoked. Passive smoking also appear to be a risk.

How many cigarettes a day can you smoke to get bladder cancer?
A risk plateau at smoking about 15 cigarettes a day can be observed (meaning that those who smoke 15 cigarettes a day are approximately at the same risk as those smoking 30 cigarettes a day).
What is the survival rate of a urinary bladder infection?
Surgical options may include transurethral resection, partial or complete removal of the bladder, or urinary diversion. The typical five-year survival rates in the United States is 77%, Canada is 75%, and Europe is 68%.