Contents
What are the warning signs of bladder cancer?
Bladder cancer can cause bleeding. The blood can sometimes be visible in the urine stream or toilet bowl. This is called gross hematuria. However, if it’s not visible to the naked eye, it can still be detected via urinalysis. The question then becomes whether or not it would always show in a urine sample, once the tumor starts causing any degree of bleeding.
What are the symptoms of a tumor in the bladder?
Bladder cancer can often be found early because it causes blood in the urine or other urinary symptoms that cause a person to see a health care provider. Blood in the urine. In most cases, blood in the urine (called hematuria) is the first sign of bladder cancer. There may be enough blood to change the color of the urine to orange, pink, or, less often, dark red.
What are signs of female bladder cancer?
Why does bladder cancer cause hematuria? Blood in the urine is a hemorrhaging of the tumor. When the blood vessels of a tumor rupture, that blood ends up in the urine. Early on, cancer blood vessels are delicate. Small tears occur easily. As a tumor grows and invades nearby tissues and blood vessels, this causes bleeding.
Can bladder cancer be found early?
Bladder cancer fact according to the National Cancer Institute A urinary tract infection (UTI) can cause visible blood. Though a UTI sounds harmless compared to bladder cancer, it can actually spread to the kidneys and become life threatening if not treated promptly. Beets can make your urine pink or reddish. This is called beeturia.

Can you have bladder cancer with no blood in urine?
Usually, the early stages of bladder cancer (when it’s small and only in the bladder) cause bleeding but little or no pain or other symptoms. Blood in the urine doesn’t always mean you have bladder cancer.
What is usually the first symptom of bladder cancer?
Bladder cancer signs and symptoms may include: Blood in urine (hematuria), which may cause urine to appear bright red or cola colored, though sometimes the urine appears normal and blood is detected on a lab test. Frequent urination. Painful urination.
How often do you pee blood with bladder cancer?
You may see blood one day, but not the next. If you have bladder cancer, the blood eventually comes back. In some cases, you can’t see blood in your urine. Your doctor or lab tech will only detect it with a urine test.
Do benign bladder tumors cause bleeding?
However, some benign masses can bleed or grow very large and cause problems by taking up too much space in your bladder or pressing on other organs in your body. In that case, we usually remove or treat benign masses, using a TURBT procedure.
What are the 5 warning signs of bladder cancer?
Here are five warning signs to watch for:Blood in the urine (hematuria). This is the most common early symptom of bladder cancer and typically the first sign of bladder cancer that is seen. … UTI-like symptoms. … Unexplained pain. … Decreased appetite. … Postmenopausal uterine bleeding.
Which of the following is the most common symptom of cancer of the bladder?
Blood in your urine is the most common symptom of bladder cancer. The medical name for blood in your urine is haematuria and it’s usually painless. You may notice streaks of blood in your urine or the blood may turn your urine brown. The blood isn’t always noticeable and it may come and go.
Can bladder cancer symptoms come and go?
Symptoms often come and go, and are often not severe. The most common symptoms include the following: Hematuria (blood in the urine) — The most common sign of bladder cancer is blood in the urine (hematuria).
Do you feel ill with bladder cancer?
Nausea and vomiting. Burning or pain when you urinate, feeling the need to go often, or blood in urine. Diarrhea. Feeling tired.
How long can you have bladder cancer and not know it?
Even after reporting the problem to their doctors, blood in the urine may be initially misdiagnosed. It may be seen as a symptom of post-menopausal bleeding, simple cystitis or a urinary tract infection. As a result, a bladder cancer diagnosis can be overlooked for a year or more.
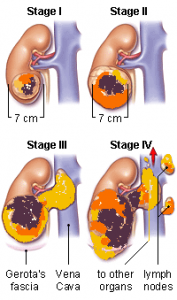
What are the odds that a tumor in the bladder is cancerous?
Risk of bladder cancer Overall, the chance men will develop this cancer during their life is about 1 in 27. For women, the chance is about 1 in 89.
Can ultrasound detect tumors in bladder?
How do ultrasounds help detect and monitor bladder cancer? An ultrasound of the urinary tract can help assess the size of a bladder tumor and whether a bladder cancer has spread. Ultrasound is able to differentiate between fluid-filled cysts and solid tumors, however, it cannot determine if a tumor is cancerous.
What are the symptoms of polyps in the bladder?
Bladder polyps are small, often cauliflower-like growths that protrude from the lining of the urinary bladder where a person stores urine….Symptoms of bladder polyps can include:constant or urgent need to urinate.pain in the abdomen.pain while urinating.more frequent urination.blood in the urine.
Where do you feel pain with bladder cancer?
Bladder cancer can cause lower back pain when it reaches a more advanced form of the disease. The pain is typically only on one side of the back, but it can be centrally located. Lower back pain might occur once the tumors increase in size or cancer cells start to spread to other parts of your body.
Where does bladder cancer begin?
Most bladder cancers start in the innermost lining of the bladder, which is called the urothelium or transitional epithelium. As the cancer grows into or through the other layers in the bladder wall, it has a higher stage, becomes more advanced, and can be harder to treat.
How long can you have bladder cancer and not know it?
Even after reporting the problem to their doctors, blood in the urine may be initially misdiagnosed. It may be seen as a symptom of post-menopausal bleeding, simple cystitis or a urinary tract infection. As a result, a bladder cancer diagnosis can be overlooked for a year or more.
How do I find out if I have bladder cancer?
Tests for bladder cancer look for different substances and/or cancer cells in the urine. Urinalysis: One way to test for bladder cancer is to check for blood in the urine ( hematuria). This can be done during a urinalysis, which is a simple test to check for blood and other substances in a sample of urine.
What are the symptoms of bladder cancer?
Being unable to urinate. Lower back pain on one side. Loss of appetite and weight loss. Feeling tired or weak. Swelling in the feet. Bone pain. Again, many of these symptoms are more likely to be caused by something other than bladder cancer, but it’s important to have them checked.
Why is bladder cancer so early?
Bladder cancer can often be found early because it causes blood in the urine or other urinary symptoms that cause a person to see a health care provider.
Why does urine have blood in it?
More often it’s caused by other things like an infection, benign (not cancer) tumors, stones in the kidney or bladder, or other benign kidney diseases. Still, it’s important to have it checked by a doctor so the cause can be found.
Why do I have trouble peeing?
Having to get up to urinate many times during the night. These symptoms are more likely to be caused by a urinary tract infection (UTI), bladder stones, an overactive bladder, or an enlarged prostate (in men).
How long does urine stay clear after bladder cancer?
Blood may be present one day and absent the next, with the urine remaining clear for weeks or even months. But if a person has bladder cancer, at some point the blood reappears.
Is it normal for blood to turn orange?
There may be enough blood to change the color of the urine to orange, pink, or, less often, dark red. Sometimes, the color of the urine is normal but small amounts of blood are found when a urine test (urinalysis) is done because of other symptoms or as part of a general medical check-up.
Can bladder cancer cause a change in urination?
Bladder cancer can sometimes cause changes in urination, such as: Having to urinate more often than usual. Pain or burning during urination. Feeling as if you need to go right away, even when your bladder isn’t full. Having trouble urinating or having a weak urine stream.
What is hematuria?
Hematuria is the medical term for the presence of blood in the urine. It can have several causes, including bladder cancer. Other causes may include urinary tract infection (UTI), prostate infection, kidney disease, and kidney or prostate cancer. Many of you shared a misdiagnosis of recurrent UTIs. 2
Why does bladder cancer cause hematuria?
Blood in the urine is a hemorrhaging of the tumor. When the blood vessels of a tumor rupture, that blood ends up in the urine. Early on, cancer blood vessels are delicate. Small tears occur easily. As a tumor grows and invades nearby tissues and blood vessels, this causes bleeding.
Large or visible hematuria
Large or visible hematuria is also called gross hematuria. They may appear pink, red, or brown in the toilet. When visible, the color varies depending on:
Microscopic hematuria
Contrary to gross hematuria, microscopic hematuria is invisible to the naked eye. Blood cells are visible only through a microscope. Most adults have microscopic hematuria in routine urinalysis. It is troubling to find more than 3 blood cells per high-power field in several urine samples. These levels require further testing. 1
Blood clots
A blood clot develops if enough blood is present in the urine. A large clot blocks urine flow. This results in severe pain and the inability to urinate. Many of you passed blood clots in your urine before your bladder cancer diagnosis. 2
Learning together
We appreciate all the responses to our Facebook prompt. Your comments sparked curiosity about hematuria and bladder cancer. Thank you for the chance to learn together.
How do you know if you have bladder cancer?
Bladder cancer signs and symptoms may include: Blood in urine (hematuria), which may cause urine to appear bright red or cola colored, though sometimes the urine appears normal and blood is detected on a lab test. Frequent urination. Painful urination. Back pain.
How does bladder cancer develop?
Bladder cancer develops when cells in the bladder begin to grow abnormally, forming a tumor in the bladder. Bladder cancer begins when cells in the bladder develop changes (mutations) in their DNA. A cell’s DNA contains instructions that tell the cell what to do.
What is the most common type of bladder cancer?
Urothelial carcinoma is the most common type of bladder cancer in the United States. Squamous cell carcinoma. Squamous cell carcinoma is associated with chronic irritation of the bladder — for instance, from an infection or from long-term use of a urinary catheter. Squamous cell bladder cancer is rare in the United States.
What is the male urinary system?
Male urinary system. Your urinary system — which includes your kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra — removes waste from your body through urine. Your kidneys, located in the rear portion of your upper abdomen, produce urine by filtering waste and fluid from your blood. Bladder cancer is a common type …
What type of cancer is a bladder cancer?
Types of bladder cancer include: Urothelial carcinoma. Urothelial carcinoma , previously called transitional cell carcinoma, occurs in the cells that line the inside of the bladder. Urothelial cells expand when your bladder is full and contract when your bladder is empty.
Why are men more likely to get bladder cancer than women?
Men are more likely to develop bladder cancer than women are. Exposure to certain chemicals. Your kidneys play a key role in filtering harmful chemicals from your bloodstream and moving them into your bladder. Because of this, it’s thought that being around certain chemicals may increase the risk of bladder cancer.
Where does bladder cancer start?
Bladder cancer is a common type of cancer that begins in the cells of the bladder. The bladder is a hollow muscular organ in your lower abdomen that stores urine. Bladder cancer most often begins in the cells (urothelial cells) that line the inside of your bladder. Urothelial cells are also found in your kidneys and the tubes (ureters) …
What percentage of men have bladder cancer?
2.4 % of men and women will be diagnosed with bladder cancer. Patients on blood thinners have similar rates of malignancy after evaluation for hematuria as those not on anticoagulant medications. Bladder cancer is the most common secondary cancer after radiation to the prostate.
What is the most common cancer after radiation?
Bladder cancer is the most common secondary cancer after radiation to the prostate.
Do blood thinners cause malignancy?
Patients on blood thinners have similar rates of malignancy after evaluation for hematuria as those not on anticoagulant medications.
Can hematuria recur spontaneously?
Natural history of gross hematuria is that it may often resolve spontaneously only to recur. Empiric treatment with antibiotics may give an impression that antibiotics are effective.
How do you know if you have bladder cancer?
Signs and symptoms of bladder cancer are blood in the urine (visible or microscopic), painful and frequent urination, and pelvic or back pain.
What causes blood in urine?
The common causes of blood in the urine are urinary tract infections (UTI), urinary tract stones, benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH), bladder tumors, urethritis, and prostate cancer. Cancers, as we all know, are serious medical conditions. Various organs in the body can be affected by cancer.
Why does blood in urine hurt?
Cancers that Cause Blood in the Urine (Hematuria) The presence of blood in the urine may be accompanied by pain during urination or it could also be painless. A painless hematuria may be caused by various health conditions such as cancers.
How do you know if you have prostate cancer?
Common symptoms include difficulty in urinating, blood in the urine, reduced force in the urine stream, erectile dysfunction, and bone pain. Prostate cancer that’s detected during its early course has a better chance of survival and success of treatment.
Why do you need a urine test?
Normally, a urine test is recommended by a physician to further examine the nature of the underlying condition that caused blood in the urine. Expert Answers.
Where is bladder cancer located?
Bladder Cancer. The bladder is a balloon-shaped organ located in the pelvis, with the main function of storing the urine. Bladder cancer, as the name implies, affects the bladder. Cancer in this organ starts in the cells lining the inside of the bladder. Bladder cancer may develop at any age, but it is most common in older adults.
Where does blood come from?
The blood may come from the kidneys or the collecting system.
What does it mean when you see blood in your urine?
While in many instances the cause is harmless, blood in urine (hematuria) can indicate a serious disorder. Blood that you can see is called gross hematuria. Urinary blood that’s visible only under a microscope (microscopic hematuria) is found when your doctor tests your urine.
Why does my urine turn red?
Some medications, such as the laxative Ex-lax, and certain foods , including beets , rhubarb and berries , can cause your urine to turn red. A change in urine color caused by drugs, food or exercise might go away within a few days. Bloody urine looks different, but you might not be able to tell the difference. It’s best to see your doctor anytime you …
What is the name of the gland that compresses the urethra and blocks urine flow?
Enlarged prostate. The prostate gland — which is just below the bladder and surrounding the top part of the urethra — often enlarges as men approach middle age. It then compresses the urethra, partially blocking urine flow. Signs and symptoms of an enlarged prostate (benign prostatic hyperplasia, or BPH) include difficulty urinating, an urgent or persistent need to urinate, and either visible or microscopic blood in the urine. Infection of the prostate (prostatitis) can cause the same signs and symptoms.
What causes a urine leakage?
These occur when bacteria enter your body through the urethra and multiply in your bladder. Symptoms can include a persistent urge to urinate, pain and burning with urination, and extremely strong-smelling urine.
Why is my urine pink?
Gross hematuria produces pink, red or cola-colored urine due to the presence of red blood cells. It takes little blood to produce red urine, and the bleeding usually isn’t painful. Passing blood clots in your urine, however, can be painful.
Why do men have hematuria?
Age. Many men older than 50 have occasional hematuria due to an enlarged prostate gland. A recent infection. Kidney inflammation after a viral or bacterial infection (post-infectious glomerulonephritis) is one of the leading causes of visible urinary blood in children.
What is the name of the blood that is visible only under a microscope?
Urinary blood that’s visible only under a microscope (microscopic hematuria) is found when your doctor tests your urine. Either way, it’s important to determine the reason for the bleeding. Treatment depends on the cause.