Contents
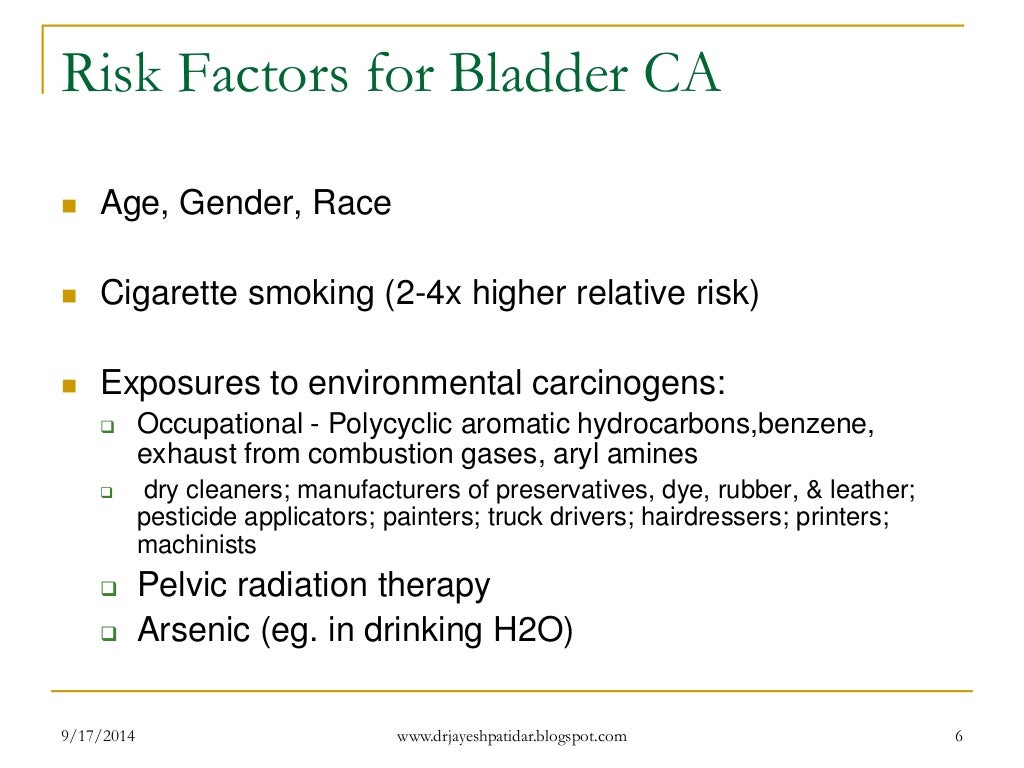
What are the chances of dying from bladder cancer?
Bladder cancer cells can recur in the bladder or they can recur in other parts of the body. Some people who are treated for bladder cancer never have a recurrence. Although recurrence is not uncommon among people who are treated for bladder cancer, in many cases the recurrence can be treated effectively.
What is the newest treatment for bladder cancer?
· Nearly three-fourths of patients diagnosed with high-risk bladder cancer will recur, progress, or die within ten years of their diagnosis. Even though most patients do not die of bladder cancer, the vast majority endures the morbidity of …
What is the survival rate for Stage 3 bladder cancer?
The average amount of time to bladder cancer recurrence was 12 months, with 80% of recurrences happening in the first three years. These 548 recurring bladder cancer patients account for about 33% (or a third) of the study patients who were treated, which is less than the national average of 50% of patients having bladder recurrence.
What is the recovery time for bladder cancer surgery?
For other people, bladder cancer might never go away completely or might come back in another part of the body. Some people may get regular treatment with chemotherapy , immunotherapy, or other treatments to try to keep the cancer in check. Learning to live with cancer that doesn’t go away can be difficult and very stressful.

Does bladder cancer usually come back?
Bladder cancer cells can recur in the bladder or they can recur in other parts of the body. Some people who are treated for bladder cancer never have a recurrence. Although recurrence is not uncommon among people who are treated for bladder cancer, in many cases the recurrence can be treated effectively.
What are the chances of bladder cancer returning?
Recurrence rates for bladder cancer depend on the stage of the original tumor, with 5-year recurrence rates of approximately 65% in patients with non-invasive or in situ tumors and 73% in patients with slightly more advanced disease at first diagnosis.
How do you know if bladder cancer comes back?
Tell your doctor about any new symptoms, such as pain during urination, blood in the urine, frequent urination, an immediate need to urinate, and any other symptoms. These symptoms may be signs that the cancer has come back or signs of another medical condition.
When does bladder cancer usually recur?
Conclusions. Nearly three-fourths of patients diagnosed with high-risk bladder cancer will recur, progress, or die within ten years of their diagnosis.
Can bladder cancer be cured completely?
The outlook for people with stage 0a (non-invasive papillary) bladder cancer is very good. These cancers can be cured with treatment. During long-term follow-up care, more superficial cancers are often found in the bladder or in other parts of the urinary system.
Can bladder cancer come back after bladder is removed?
For other people, bladder cancer might never go away completely or might come back in another part of the body. Some people may get regular treatment with chemotherapy , immunotherapy, or other treatments to try to keep the cancer in check.
How often should you have a cystoscopy after bladder cancer?
In general, doctors recommend a test to examine the inside of your urethra and bladder (cystoscopy) every three to six months for the first few years after bladder cancer treatment. After a few years of surveillance without detecting cancer recurrence, you may need a cystoscopy exam only once a year.
Does bladder cancer lead to other cancers?
Being treated for bladder cancer doesn’t mean you can’t get another cancer. Survivors of bladder cancer can get any type of second cancer, but they have an increased risk these cancers compared to the general population: A second bladder cancer (This is different from the first cancer coming back.)
Can you live 10 years with bladder cancer?
Bladder cancer survival rates by stage According to the American Cancer Society , the relative survival rates for all stages of bladder cancer are: 5 years: 77 percent. 10 years: 70 percent. 15 years: 65 percent.
How can you prevent recurring bladder cancer?
The largest body of evidence suggests that a diet rich in fruits and vegetables, which contain cancer-protective compounds, is the best way to avoid cancer and its recurrence. Fluids, coffee, and alcohol appear to have no significant influence on recurrence rate.
How long can you live after bladder cancer?
Survival for all stages of bladder cancer almost 55 out of every 100 (almost 55%) survive their cancer for 5 years or more after they are diagnosed. around 45 out of every 100 (around 45%) survive their cancer for 10 years or more after diagnosis.
What foods should you avoid if you have bladder cancer?
However, avoid high intake of foods like red and processed meat, chewing areca nuts, consuming arsenic containing water, taking fried eggs and lifestyle factors such as smoking tobacco as it may increase the risk of bladder cancer, impact the prognosis and treatment outcomes, worsen symptoms, or increase the chances of …
Ask Your Doctor For A Survivorship Care Plan
Talk with your doctor about developing a survivorship care plan for you. This plan might include: 1. A suggested schedule for follow-up exams and t…
Typical Follow-Up Schedules After Bladder Cancer
If you have completed treatment, your doctors will still want to watch you closely. People who have had bladder cancer have a high risk of developi…
Keeping Health Insurance and Copies of Your Medical Records
Even after treatment, it’s very important to keep health insurance. Tests and doctor visits cost a lot, and even though no one wants to think of th…
Can I Lower My Risk of The Cancer Progressing Or Coming back?
If you have (or have had) bladder cancer, you probably want to know if there are things you can do that might lower your risk of the cancer growing…
Could I Get A Second Cancer After Bladder Cancer Treatment?
People who’ve had bladder cancer can still get other cancers. In fact, bladder cancer survivors are at higher risk for getting some other types of…
Moving on After Bladder Cancer
If you had a radical cystectomy and now have a urostomy, you might worry even about everyday activities at first. You might have to alter some of y…

How long does it take for bladder cancer to recur?
The average amount of time to bladder cancer recurrence was 12 months, with 80% of recurrences happening in the first three years. These 548 recurring bladder cancer patients account for about 33% (or a third) of the study patients who were treated, which is less than the national average of 50% of patients having bladder recurrence.
What is the procedure to remove bladder cancer?
While there are several different treatments for bladder cancer available, many patients with high-risk or muscle-invasive cancer will undergo a procedure known as a radical cystectomy, or total removal of the bladder. A radical cystectomy (often with the removal of some of the surrounding pelvic lymph nodes and other organs) …
Where is bladder cancer most common?
The most common site of recurrence of bladder cancer after a radical cystectomy, both in early and late recurrence, was in the abdomen or pelvic region, in about 60-70% of patients. The next most common sites of recurrence were the chest and the bones, with the chest more common in early recurrence, and the bones in late recurrence. Other sites included the brain and the urothelial regions (that is the urethra, ureters, and kidney area); these areas tend to be the least common areas of bladder cancer recurrence. Just under 40% of patients (both early and late recurrence bladder cancer) had a recurrence in multiple regions.

Can bladder cancer return after radical cystectomy?
Patients who undergo a radical cystectomy may wonder if their cancer can return if they no longer have a bladder. This article will look at the possibilities of recurrence, and some of the risk factors for recurrence in bladder cancer patients who have undergone a radical cystectomy.
Can cystectomy cause bladder cancer?
Multiple studies have shown that having a radical cystectomy at a younger age can be a risk factor for recurrence. Patients who have bladder cancer that is not confined to the bladder, or that has involvement in the surrounding muscle tissue may also be at risk for late recurrence, but there is a need for more studies to show a better correlation.
What does it mean to live after bladder cancer?
Life after bladder cancer means returning to some familiar things and also making some new choices.
What to do if you have bladder cancer?
If you have (or have had) bladder cancer, you probably want to know if there are things you can do that might lower your risk of the cancer growing or coming back, such as exercising, eating a certain type of diet, or taking nutritional supplements. Unfortunately, it’s not yet clear if there are things you can do that will help.
How often should I have a urine test for cancer?
Most experts recommend repeat exams every 3 to 6 months for people who have no signs of cancer after treatment. These are done to see if the cancer is growing back or if there’s a new cancer in the bladder or urinary system. Your follow-up plan might include urine tests, physical exams, imaging tests (like x-rays, MRI, or CT scans), and blood tests. These doctor visits and tests will be done less often as time goes by and no new cancers are found.
How often should you have a cystoscopy?
If your bladder hasn’t been removed, regular cystoscopy exams will also be done every 3 months for at least the first 2 years. If you have a urinary diversion, you will be checked for signs of infection and changes in the health of your kidneys. Urine tests, blood tests, and x-rays might be used to do this.

What happens if you have a radical cystectomy and a urostomy?
If you had a radical cystectomy and now have a urostomy, you might worry even about everyday activities at first. You might have to alter some of your daily (and nightly) routines because of changes in how you urinate. Other issues such as having sex might also cause concerns (see below).
Can bladder cancer affect your sex life?
Bladder cancer treatment can often affect your sex life. (See Bladder Cancer Surgery for more on this.) Learning to be comfortable with your body during and after bladder cancer treatment is a personal journey, one that’s different for everyone. Information and support can help you cope with these changes over time.
Does bladder cancer go away?
For other people, bladder cancer might never go away completely or might come back in another part of the body. Some people may get regular treatment with chemotherapy , immunotherapy, or other treatments to try to keep the cancer in check. Learning to live with cancer that doesn’t go away can be difficult and very stressful.
What is the progress made in bladder cancer?
The progress that has been made in the treatment of bladder cancer has resulted from improved treatments evaluated in clinical trials. Future progress in the treatment of bladder cancer will result from continued participation in appropriate studies. Currently, there are several areas of active exploration aimed at improving the treatment of bladder cancer.
How many people with superficial bladder cancer will eventually progress to advanced bladder cancer?
Approximately 20-40% of all patients with superficial bladder cancer will ultimately progress to more advanced stages or muscle invasive bladder cancer. When this occurs, patients are treated based on new staging of the current more invasive bladder cancer. For treatment of patients with superficial bladder cancer who have progressed, select one of the following:
What is the treatment for superficial bladder cancer?
For treatment of patients with superficial bladder cancer who have progressed, select one of the following: Patients who experience a recurrence after initial treatment for stage II-IV blad der cancer may be treated with cystectomy (if not performed previously), chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or enrollment in a clinical trial.

What is phase 1 in cancer?
Phase I Trials: New anti-cancer therapies continue to be developed and evaluated in phase I clinical trials. The purpose of phase I trials is to evaluate new drugs and/or therapeutic approaches in order to determine the best way of administering the treatment and whether the treatment has any anti-cancer activity in patients with bladder cancer.
Why is cancer treatment important?
The purpose of receiving cancer treatment may be to improve symptoms through local control of the cancer, increase a patient’s chance of cure, or prolong a patient’s survival. The potential benefits of receiving cancer treatment must be carefully balanced with the potential risks of receiving cancer treatment.
Can bladder cancer be drug resistant?
Multiple Drug Resistance Inhibitors: Bladder cancer can be drug resistant at the outset of treatment or develop drug resistance after treatment. Several drugs are being tested to determine if they will overcome or prevent the development of multiple drug resistance in bladder cancer and other cancers.

Does targeted therapy slow cancer cell growth?
Some targeted therapies block growth signals from reaching cancer cells; others reduce the blood supply to cancer cells; and still others stimulate the immune system to recognize and attack the cancer cell. Depending on the specific “target”, targeted therapies may slow cancer cell growth or increase cancer cell death.
What is the first treatment for bladder cancer?
Chemo (with or without radiation) is typically the first treatment when bladder cancer has spread to distant parts of the body (M1). After this treatment the cancer is rechecked. If it looks like it’s gone, a boost of radiation to the bladder may be given or cystectomy might be done.
What is stage 0 bladder cancer?
Stage 0 bladder cancer includes non-invasive papillary carcinoma (Ta) and flat non-invasive carcinoma (Tis or carcinoma in situ). In either case, the cancer is only in the inner lining layer of the bladder. It has not invaded (spread deeper into) the bladder wall.

What to do if you have cancer that hasn’t been removed?
(Less often, close follow-up alone might be an option.) If all of the cancer wasn’t removed, options are intravesical BCG or cystectomy (removal of part or all of the bladder).
How to get rid of stage IV cancer?
The tumor is then rechecked. If it appears to be gone, chemo with or without radiation or cystectomy are options.
How long after TA surgery can you get chemo?
For low-grade (slow-growing) non-invasive papillary (Ta) tumors, weekly intravesical chemotherapy may be started a few weeks after surgery. If the cancer comes back, the treatments can be repeated. Sometimes intravesical chemo is repeated over the next year to try to keep the cancer from coming back.
What is the treatment for cancer that recurs in distant parts of the body?
Cancers that recur in distant parts of the body can be harder to remove with surgery, so other treatments, such as chemotherapy, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, or radiation therapy , might be needed. For more on dealing with a recurrence, see Understanding Recurrence.
Can you get a radical cystectomy before surgery?
Radical cystectomy may be the only treatment for people who are not well enough to get chemo. But most doctors prefer to give chemo before surgery because it’s been shown to help patients live longer than surgery alone. When chemo is given first, surgery is delayed. This is not a problem if the chemo shrinks the bladder cancer, but it might be harmful if the tumor continues to grow during chemo.
How long does bladder cancer last?
Bladder cancer survival rates by stage. According to the American Cancer Society, the relative survival rates for all stages of bladder cancer are: 5 years: 77 percent. 10 years: 70 percent. 15 years: 65 percent. When you look at the five-year survival rates broken down by stage, you get a clearer picture of why stage matters.

How long do you live with bladder cancer?
This figure conveys the percentage of people with bladder cancer who are likely to live at least five years after diagnosis compared to those who don’t have bladder cancer. Survival rates don’t specify if survivors are in remission …
How to prevent bladder cancer from recurring?
It’s not clear if there’s anything you can do to prevent bladder cancer from recurring. Recurrence can be treated, especially when localized, so it’s important to: see your doctor regularly. adhere to a follow-up schedule of lab tests or imaging tests as advised. report signs and symptoms of bladder cancer right away.
What percentage of cancer is stage 2?
Stage 2: 63 percent . Stage 3: 46 percent. Stage 4: 15 percent. Survival rates by stage are based on stage at diagnosis. Another important factor for outlook is the tumor grade. The grade represents how quickly the cancer is likely to grow and spread.

What are the factors that affect your outlook on cancer?
As for your own outlook, there are quite a few variables to consider. In addition to cancer stage and tumor grade, your age and general health may play a role. The therapies you and your doctor choose and how quickly you start treatment will also affect your outlook. Additionally, not everyone responds to a particular treatment the same way.
How long do people live after cancer?
But they can’t tell you much about your individual outlook. One key thing to keep in mind is the type of statistic you’re looking at. A five-year survival rate, for example, reflects the percentage of people who live at least five years after diagnosis.
Is bladder cancer a high risk disease?
Bladder cancer has a tendency to recur, so when treatment ends, you’re still considered at high risk. Some people with superficial bladder cancer experience frequent recurrences throughout their lives. In general, the prognosis is worse. when recurrence involves distant tissues, organs, or lymph nodes.

How long do people with bladder cancer live?
Overall, 70 to 90 percent of people with localized bladder cancer will live for at least five years or more . The physician calculates this with the help of survival rates. Survival rates indicate the percentage of people who live with a certain type of cancer for a specific time. The physician often uses an overall five-year survival rate.
Where does bladder cancer start?
Bladder cancer is a tumor (uncontrolled growth of cells) that starts in your urinary bladder. The urinary bladder is a balloon-like organ present in the lower abdomen near the pelvis. Its function is to store urine coming from the kidneys through the ureters (pipe-like passageways for urine) until it is expelled from the body through the tube-like passage called the urethra.
What is the first line of treatment for metastatic bladder cancer?
Then, the physician may perform a radical cystectomy to remove cancer that has invaded beyond the bladder wall. Metastatic bladder cancer: Platinum-based chemotherapy is the first line of treatment for this type of bladder cancer.

What is gallbladder cancer?
Gallbladder cancer (GBC) is one of the aggressive cancers of the biliary tract. The gallbladder generates and concentrates bile that aids in the digestion of fats. GBC is a rare, yet deadly cancer of the gastrointestinal tract.
What is the procedure to remove bladder cancer?
Tumors in the bladder muscle: In case of bladder cancer that has invaded the muscle wall but hasn’t spread to the lymph nodes, the physician recommends radical cystectomy. In this procedure, the physician removes the bladder, nearby lymph nodes and other nearby organs.
What is the treatment for high grade bladder cancer?
High-grade bladder cancer: High-grade cancers that are life-threatening and spread quickly need to be treated with chemotherapy, radiation or surgery.

What is SEER in cancer?
The surveillance, epidemiology, and end results (SEER) stages are taken from the SEER database, maintained by the National Cancer Institute. SEER database groups cancers into localized, regional, and distant stages.
How often should I give BCG to a patient?
I treat patients initially with 50 mg of BCG (Tice) once a weekfor 6 weeks and prescribe another 6 week cycle if the 3-monthcystoscopy shows evidence of recurrence. Responders are offeredmaintenance therapy since the randomized Southwest Oncology Group (SWOG) trial of maintenance vs no maintenance therapy clearlygives the edge to maintenance treatment. [3]
Why is photodynamic therapy not widespread?
Grossman discusses, photodynamic therapy offers anotheralternative but has not come into widespread use probably dueto its cost and increased technologic complexity.
Is bladder cancer a fertile ground for gene therapy?
Finally, superficial bladder cancer provides a fertile groundfor gene therapy strategies, which, in the future, may be ableto target high-risk patients.
Is bladder cancer a nuisance?
Superficial bladder cancer can be a frustrating disease for both the patient and physician. It has been referred to as a “nuisance disease” because of its propensity for recurrence, necessitating frequent cystoscopies and trips to the operating room for resection of recurrent disease. In addition, however, there looms for …