Contents
Common tests & procedures
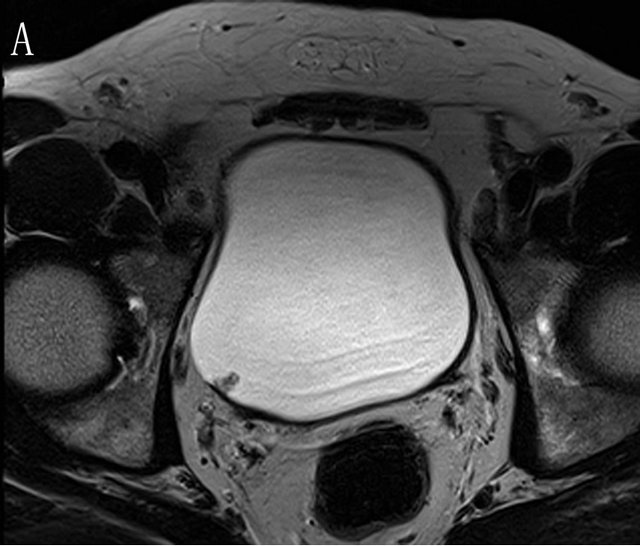
Diagnosing bladder cancer is a process that involves multiple steps. Many patients diagnosed with bladder cancer experience symptoms related to urination— visible blood in the urine is the most common symptom—and visit their primary healthcare provider to have their symptoms checked. Other patients have not noticed symptoms, but their healthcare provider finds a sign …
What are the early warning signs of bladder cancer?
Cystoscopy. Cystoscopy is the key diagnostic procedure for bladder cancer. It allows the doctor to see inside the body with a thin, lighted, flexible tube called a cystoscope. Flexible cystoscopy is performed in a doctor’s office and does not require anesthesia, which is medication that blocks the awareness of pain.
Do you know the early signs of bladder cancer?
If an abnormal area (or areas) is seen during a cystoscopy, it needs to be biopsied to see if it’s cancer. A biopsy is when tiny pieces (called samples) of the abnormal-looking tissue are taken out and tested for cancer cells. If bladder cancer is suspected, a biopsy …
What are the chances of having bladder cancer?
How is Bladder Cancer Diagnosed? Arriving at a diagnosis of bladder cancer may involve one or more of these steps: Urine tests to detect blood, cancer cells and other signs of disease. A 24-hour urine collection can measure volume of urine output, an indicator of kidney function.
What is the prognosis for Stage 1 bladder cancer?
Stages and Outlook (Prognosis) After a cancer diagnosis, staging provides important information about the extent (amount) of cancer in the body and the likely response to treatment. Bladder Cancer Stages. Survival Rates for Bladder Cancer.
See more
We conduct a thorough diagnostic examination and tests that may include: Cystoscopy and Transurethral Resection A cystoscopy is a procedure in which a small tube with a camera is inserted into the urethra (the duct through which urine …

How is bladder cancer first diagnosed?
A sample of your urine is analyzed under a microscope to check for cancer cells in a procedure called urine cytology. Imaging tests. Imaging tests, such as computerized tomography (CT) urogram or retrograde pyelogram, allow your doctor to examine the structures of your urinary tract.
Can bladder cancer be detected with a urine test?
Urinalysis can help find some bladder cancers early, but it has not been shown to be useful as a routine screening test. Urine cytology: In this test, a microscope is used to look for cancer cells in urine. Urine cytology does find some cancers, but it’s not reliable enough to make a good screening test.
Which of the following is usually the first symptom of bladder cancer?
For most people, the first symptom of bladder cancer is blood in the urine, also called hematuria. Sometimes the blood is visible, prompting the patient to visit a doctor.
What are the warning signs of bladder cancer?
Bladder Cancer: Symptoms and SignsBlood or blood clots in the urine.Pain or burning sensation during urination.Frequent urination.Feeling the need to urinate many times throughout the night.Feeling the need to urinate, but not being able to pass urine.Lower back pain on 1 side of the body.
Does bladder cancer feel like a UTI?
Bladder cancer can be mistaken for a Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) because many of the symptoms overlap. Patients may experience increased frequency and urgency of urination, pain with urination, or urinary incontinence.
Can bladder cancer be seen on ultrasound?
How do ultrasounds help detect and monitor bladder cancer? An ultrasound of the urinary tract can help assess the size of a bladder tumor and whether a bladder cancer has spread. Ultrasound is able to differentiate between fluid-filled cysts and solid tumors, however, it cannot determine if a tumor is cancerous.
Can CT scan detect bladder cancer?
A CT scan uses X-rays and a computer to create three-dimensional, cross-sectional pictures of the bladder, as well as the ureters and kidneys. A CT scan may be used to see whether bladder cancer has invaded the bladder wall or has spread to other organs or nearby lymph nodes.
Who is at high risk for bladder cancer?
Age: Most people who get bladder cancer are older in age. The average age at diagnosis is 73, and 90 percent of patients are over age 55. Race: Bladder cancer is twice as common among Caucasians as African Americans. This disease is less common among Hispanics, Asians and Native Americans.
Medical History and Physical Exam
Your doctor will want to get your medical history to learn more about your symptoms. The doctor might also ask about possible risk factors, includi…
Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumor (TURBT)
If an abnormal area (or areas) is seen during a cystoscopy, it will be biopsied to see if it is cancer. A biopsy is the removal of small samples of…
Biopsies to Look For Cancer Spread
If imaging tests suggest the cancer might have spread outside of the bladder, a biopsy might be needed to be sure.In some cases, biopsy samples of…

How to diagnose bladder cancer?
The first step in diagnosing bladder cancer usually involves a visit to a primary healthcare provider about symptoms a patient has had, such as blood in the urine. 2 The healthcare provider will typically ask about the patient’s symptoms and general health habits, as well as asking about risk factors for bladder cancer, such as smoking or a family history of bladder cancer.
What is the best way to find out if you have bladder cancer?
Ultrasound. Imaging tests can also be used together with biopsies to find out if a patient has bladder cancer that has spread to other parts of the body, such as the liver, bones, or lungs.
What is the procedure called when you take samples of bladder tissue?
If signs of cancer are found, then a procedure called transurethral resection of bladder tumor can be used to take samples of tissue from the bladder to be further analyzed in the lab to confirm a diagnosis of bladder cancer.

What is the procedure to examine bladder?
Some of these procedures include physical examination of the patient’s bladder while the patient is under anesthesia, cystoscopy, and transurethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT). Cystoscopy involves inserting a very thin, flexible tube, with a tiny camera on the end of it, into the patient’s bladder to examine the bladder’s inner lining.
What is urine test for bladder cancer?
Patients with symptoms that may be caused by bladder cancer are usually asked to provide a urine sample for testing in the laboratory. 3 The results of the test can indicate if there is blood or other contents in the urine (urinalysis testing), as well as indicating if the symptoms may be caused by a urinary tract infection (urine culture testing). Other types of urine testing can be used to check for the presence of cancer or pre-cancer cells (urine cytology testing), or for the presence of substances that are often associated with cancer cells (urine tumor marker testing).
What is the most common symptom of bladder cancer?
Many patients diagnosed with bladder cancer experience symptoms related to urination— visible blood in the urine is the most common symptom—and visit their primary healthcare provider to have their symptoms checked. Other patients have not noticed symptoms, but …

What is the process of staging bladder cancer?
A process called staging is used to describe a patient’s specific type of bladder cancer after diagnosis. 5 This provides detailed information about the cancer and helps the patient’s cancer care team to determine the best possible treatment options.
What is the best test for bladder cancer?
There are other urine tests using molecular analysis that can be done to help find cancer, usually at the same time as urinary cytology. Cystoscopy. Cystoscopy is the key diagnostic procedure for bladder cancer. It allows the doctor to see inside the body with a thin, lighted, flexible tube called a cystoscope.
What is a biopsy of a bladder tumor?
A biopsy is the removal of a small amount of tissue for examination under a microscope. This surgical procedure is called a transurethral bladder tumor resection or TURBT.

What is a TURBT test?
A TURBT is used to diagnose bladder cancer and find out the type of tumor, how deeply it has grown into the layers of the bladder, and identify any additional microscopic cancerous changes, called carcinoma in situ (CIS) (see Stages and Grades ).
How to check for tumors in urine?
Urine tests. If your doctor has found any amount of blood in the urine, a urine cytology test can be ordered. Urine cytology often uses a random urine sample from normal urination to find out if the urine contains tumor cells. If a patient is undergoing a cystoscopy (see below), an additional test may be performed that involves rinsing the bladder and collecting the liquid through the cystoscope or through another small tube that is inserted into the urethra. The sample can be tested in a variety of ways. The most common way is to look at the cells under a microscope, called urinary cytology. There are other urine tests using molecular analysis that can be done to help find cancer, usually at the same time as urinary cytology.
What is a urologist’s job in a TURBT?
A pathologist is a doctor who specializes in interpreting laboratory tests and evaluating cells, tissues, and organs to diagnose disease.

Why do we need a PET scan?
A PET scan is a way to create pictures of organs and tissues inside the body. A small amount of a radioactive substance is injected into the patient’s body. This substance is taken up by cells that use the most energy. Because cancer tends to use energy actively, it absorbs more of the radioactive substance.
What is a CT scan for cancer?
A computer combines these pictures into a detailed, 3-dimensional image that shows abnormalities or tumors. A CT scan can be used to measure the tumor’s size and to identify enlarged lymph nodes, which may indicate that cancer has spread. Sometimes, a special dye called a contrast medium is given before the scan to provide better detail on the image. This dye can be injected into a patient’s vein (intravenous) or given as a liquid to swallow. Before taking this test, patients should tell the staff giving this test if they are allergic to iodine or other contrast media. The intravenous contrast dye used in a CT scan can cause renal problems, so patients with any kind of kidney problems should tell the staff before the scan is done.
What is the best way to diagnose bladder cancer?
Cystoscopy. If bladder cancer is suspected, most doctors will recommend a cystoscopy. . A urologist uses a cystoscope, which is a long, thin, flexible tube with a light and a lens or a small video camera on the end. For details on how this procedure is done, see Cystoscopy.

What tests are used to check for bladder cancer?
These include the tests called NMP22 ® (or BladderChek ® ), BTA Stat ®, Immunocyt ® , and UroVysion ®, which are discussed in Can Bladder Cancer Be Found Early?
What is the blue light in a cystoscopy?
Fluorescence cystoscopy (also known as blue light cystoscopy) may be done along with routine cystoscopy. For this exam, a light-activated drug is put into the bladder during cystoscopy. It’s taken up by cancer cells. When the doctor then shines a blue light through the cystoscope, any cells containing the drug will glow (fluoresce). This can help the doctor see abnormal areas that might have been missed by the white light normally used.
What is the biopsy for bladder cancer?
A biopsy is when tiny pieces (called samples) of the abnormal-looking tissue are taken out and tested for cancer cells. If bladder cancer is suspected, a biopsy is needed to be sure of the diagnosis.
What is a physical exam for bladder cancer?
A physical exam can provide information about possible signs of bladder cancer and other health problems. The doctor might do a digital rectal exam (DRE), during which a gloved, lubricated finger is put into your rectum. If you are a woman, the doctor might do a pelvic exam as well.
How long does it take for a urine culture to show up?
It can take time for the bacteria to grow, so it may take a few days to get the results of this test.
How does ultrasound help with bladder cancer?
Ultrasound uses sound waves to create pictures of internal organs. It can be useful in determining the size of a bladder cancer and whether it has spread beyond the bladder to nearby organs or tissues. It can also be used to look at the kidneys. This is usually an easy test to have, and it uses no radiation.

What is the tool used to remove a tumor from the bladder?
During a TURBT procedure, the surgeon inserts a tool called a resectoscope through the urethra to reach the inside of your bladder and remove a piece of tumor tissue, or the entire tumor from your bladder. Make an Appointment.
What is a numbing gel?
A numbing gel is inserted into the urethra to prevent any discomfort. During this test, the doctor can collect cells from your bladder’s lining to examine, diagnose and even treat various bladder conditions, and perform a bladder wash.
What is the tube that is used to see the inside of the bladder?
You have symptoms such as urinary frequency or urgency. In this procedure, a tube called a cystoscope (fitted with a tiny light and camera) is passed through the urethra and into your bladder, allowing your doctor to visualize the inside of your bladder and detect any tumors.

What happens if you seek a second opinion at Roswell Park?
If you seek a second opinion at Roswell Park, our bladder cancer team will review your tests, scans and pathology. In about 10% of cases we review, the diagnosis is changed, impacting your treatment options and decisions.
What tests are done to determine if a tumor has spread?
Blood tests to assess kidney and liver function. Cystoscopy to see inside the bladder and identify any tumor. Imaging Scans to determine if a cancer has spread. Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumor (TURBT) to obtain a biopsy, confirm a cancer diagnosis, and determine the stage and grade of a cancer.
What is urine test?
Urine tests to detect blood, cancer cells and other signs of disease. A 24-hour urine collection can measure volume of urine output, an indicator of kidney function. Bladder wash during which a solution is delivered through a catheter (tube) to the bladder to loosen cells on the bladder’s inner lining. The solution is removed, and …
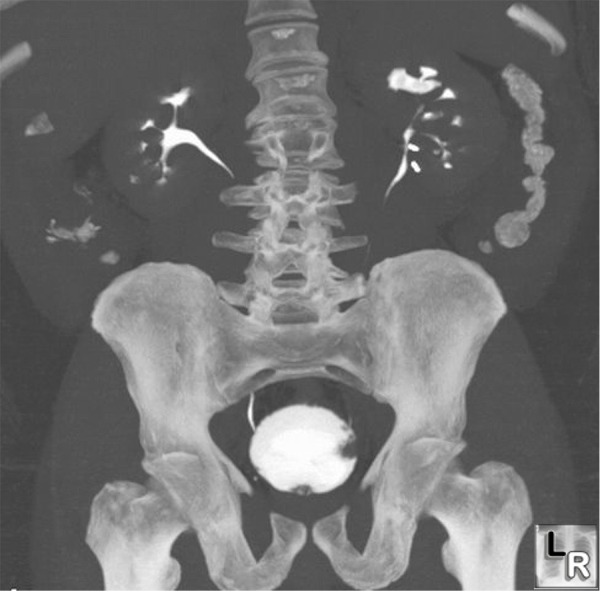
How to diagnose bladder cancer?
Arriving at a diagnosis of bladder cancer may involve one or more of these steps: 1 Urine tests to detect blood, cancer cells and other signs of disease. A 24-hour urine collection can measure volume of urine output, an indicator of kidney function. 2 Bladder wash during which a solution is delivered through a catheter (tube) to the bladder to loosen cells on the bladder’s inner lining. The solution is removed, and a sample is examined under a microscope. 3 Blood tests to assess kidney and liver function 4 Cystoscopy to see inside the bladder and identify any tumor 5 Imaging Scans to determine if a cancer has spread 6 Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumor (TURBT) to obtain a biopsy, confirm a cancer diagnosis, and determine the stage and grade of a cancer
What can help doctors see if the cancer has invaded the muscle in the bladder wall?
MRI , which can help doctors see if the cancer has invaded the muscle in the bladder wall and, if so, how deeply
What is the MSK test for bladder cancer?
For people with advanced bladder cancer that has spread, we use a test called MSK-IMPACT ™. It can look for genetic mutations and other changes in a tumor. This test provides essential information that can guide treatment choices and, in some cases, identify candidates for a clinical trial. It can also spare people from treatments that are not likely to be effective. MSK-IMPACT was developed by MSK pathologists and researchers. It has been used to analyze the tumors of MSK patients with advanced cancer since January 2014. It was authorized by the Food and Drug Administration in November 2017.

What is urine cytology?
A urine sample called urine cytology can be checked for cancer cells.
What is the procedure called when a camera is inserted into the urethra?
A cystoscopy is a procedure in which a small tube with a camera is inserted into the urethra (the duct through which urine leaves the body) and slowly moved into the bladder. This allows the doctor to examine the lining of the bladder and take a sample (biopsy).
What tests are done to diagnose bladder cancer?
Tests to diagnose bladder cancer. If bladder cancer is suspected, these tests may be performed to diagnose the disease: Physical exam. Blood test: Blood samples are used to measure certain substances released into the blood by organs and tissues in the body.

What is the best test to confirm bladder cancer?
Cystoscopy is best used in combination with other tests to confirm early-stage or small tumors. Biopsy: The removal of a small tissue sample for review under a microscope. This procedure is usually performed only if the tests above suggest bladder cancer.
What is the stage of bladder cancer?
The stage of bladder cancer is the most important factor in determining your treatment plan. These stages — or categories — are based on the size and spread of cancer beyond the bladder and into other places in the body (metastasis), such as the lymph nodes, blood, or other organs.
What percentage of bladder cancer is transitional cell carcinoma?
Transitional cell: About 90 percent of bladder cancers are transitional cell carcinomas, which means the cancer began in the cells that line the inside of the bladder. Cancer that is confined to the lining of the bladder is called non-invasive bladder cancer.

What is the difference between stage 2 and stage 3 bladder cancer?
This stage generally means the cancer is muscle-invasive and localized to the bladder. Stage III indicates that the cancer has spread from the bladder wall to the muscle , as well to the fatty layer of tissue surrounding it.
Where is Lank Center for Genitourinary Oncology?
Beginning with your first appointment at the Lank Center for Genitourinary Oncology at Dana-Farber/Brigham and Women’s Cancer Center (DF/BWCC), you will be matched with specialists and researchers who study genitourinary cancers exclusively. We are home to the largest team of genitourinary specialists in the world, and are one of the few clinical centers globally with a team focused on genitourinary cancers. Our team is at the forefront of bladder cancer research, educating and improving the understanding of bladder cancer worldwide.
Where does bladder cancer start?
Invasive bladder cancer begins in the cells that line the inside of the bladder, which proceed to invade the muscle wall (muscle-invasive) of the bladder or spread to nearby organs and lymph nodes (metastasized). Early-stage bladder cancer rarely grows into the muscular wall of the bladder, and rarely spreads.

What is an IVP x-ray?
An Intravenous pyelogram (IVP) is a conventional x-ray test using dye to examine the pelves of the kidneys (where urine collects within the kidneys), ureters, and bladder. This x-ray allows visualization of the upper and lower urinary tract to determine the presence of any abnormality.
How to diagnose bladder cancer?
The diagnosis of bladder cancer is based on examining cells from the bladder, either from a urine specimen or biopsy of the bladder. Only a pathologist can diagnose if a bladder cancer is present and the type of bladder cancer, by looking at the bladder tissue.
What is the purpose of a cystoscopy?
The purpose of routine outpatient cystoscopy is to evaluate the lining of the lower urinary tract.

Which is more sensitive, CT or MRI?
More sensitive than CT scanning. CT and MRI have the added benefit of detecting enlarged lymph nodes near the tumors, which can suggest that a cancer has spread (metastasized) to the lymph nodes.
Is it necessary to get a second opinion on bladder cancer?
The pathology of the bladder is complex and therefore a second opinion is often advisable and can have a major impact in therapy.
What tests are done to check for bladder cancer?
This might include a rectal exam, during which a gloved finger is put into your rectum. If you are a woman, a pelvic exam might also be done.

What is the best test to find out if you have bladder cancer?
Ultrasound: This test uses sound waves to make pictures of the organs inside your body, like your bladder and kidneys. It can help show the size of a bladder cancer and if it has spread. Bone scan: A bone scan can help show if bladder cancer has spread to the bones. This test is not done unless you have bone pain.
How do you know if you have bladder cancer?
Signs of bladder cancer are problems peeing, pain when peeing, needing to go more often than normal, and seeing blood in your urine
What is urine test?
Urine tests: For these tests, you’ll be asked to pee in a cup. Your urine is then tested for cancer cells, blood, or certain proteins (called tumor markers).

What is the blue light on a cystoscopy?
Blue light cystoscopy: Sometimes, special drugs are put into the bladder during the exam. Cancer cells soak up these drugs and then glow when the doctor shines a blue light through the scope. This can help the doctor see cancer cells that might have been missed with the normal light.
Why do you need a cystoscope?
More than one sample may be taken because sometimes cancer starts in more than one part of the bladder. Salt water washings of the inside of your bladder may also be collected to look for cancer cells.
Where does urine go when you pee?
Urine flows through the ureters and into your bladder, where it’s stored. When you urinate (pee), the bladder squeezes the urine out through a tube called the urethra. Bladder cancer usually starts in the lining or inner layer of the bladder wall.