Contents

What are the early warning signs of bladder cancer?
A mass (tumor) that is found on the bladder – the muscular sac in the pelvic region that stores urine – can sometimes be indicative of bladder cancer. In other cases, a bladder mass could be a benign (noncancerous) polyp, which is a small, cauliflower-like growth that can potentially turn into bladder cancer in the future.
What are the chances of survival for bladder cancer?
· Bladder cancer or bladder tumors are relatively common in the United States, and most bladder tumors are cancerous. Bladder cancer signs and symptoms may include the following: hematuria (blood in the urine, painless) in about 80-90 % of patients; frequent urination; painful urination; pelvic pain; back pain; a mass or lump found on physical exam
What percentage of bladder tumors are cancerous?
· You probably cant detect a bladder mass on your own, so its beneficial to be familiar with the potential symptoms of bladder cancer and seek medical care if they occur. Some of the most common signs of this condition include: Blood in …
What are the most common symptoms of bladder cancer?
· A bladder mass is any large lump, tumor, or cyst that is found on the bladder or in the immediate area. The mass may be noticed after symptoms arise or during a pelvic exam regarding another condition. Not all instances of a bladder mass indicate cancer, but since it is a risk, a biopsy may be performed. In some cases a mass may be detected during certain urine …


Can bladder cancer be benign?
In other cases, a bladder mass could be a benign (noncancerous) polyp, which is a small, cauliflower-like growth that can potentially turn into bladder cancer in the future.
How to tell if you have bladder cancer?
You probably can’t detect a bladder mass on your own, so it’s beneficial to be familiar with the potential symptoms of bladder cancer and seek medical care if they occur. Some of the most common signs of this condition include: 1 Blood in the urine 2 Burning sensations or pain while urinating 3 Difficulty emptying the bladder 4 An unusually weak urine stream 5 A frequent urge to urinate, even when the bladder is empty 6 Low back pain on one side
Can bladder cancer cause urinary tract infections?
It’s important to note that bladder cancer shares many symptoms with urinary tract infections and other benign conditions. If you notice changes in your urination or have any symptoms that concern you, be sure to promptly speak with a physician.

What is Moffitt Cancer Center?
Moffitt Cancer Center caters to patient in all stages of treatment and recovery. The multispecialty team in our Urologic Oncology Program provides screening for high-risk patients, diagnostics, advanced treatment and supportive care in a single location.
Is bladder cancer a tumor?
Bladder cancer or bladder tumors are relatively common in the United States, and most bladder tumors are cancerous. Bladder cancer signs and symptoms may include the following: The types of bladder cancers include urothelial carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. Tests are used to determine if the tumor is cancerous.
What causes bladder tumors?
Tumors or swelling of a part of the body, usually without inflammation, are caused by the abnormal tissue growth. Tumors can be either benign (not malignant or cancerous) or cancerous (malignant, out-of-control cell growth). Bladder cancer or bladder tumors are relatively common in the United States, and most bladder tumors are cancerous. Bladder cancer signs and symptoms may include the following: 1 hematuria ( blood in the urine, painless) in about 80-90 % of patients 2 frequent urination 3 painful urination 4 pelvic pain 5 back pain 6 a mass or lump found on physical exam

What doctor can diagnose bladder cancer?
If you suspect you may have a bladder tumor, your primary care doctor can refer you to a urologist to examine you and run the various tests used to diagnose bladder cancer. The earlier the diagnosis, the more likely for you to have a successful treatment outcome.
What is the stage of bladder cancer?
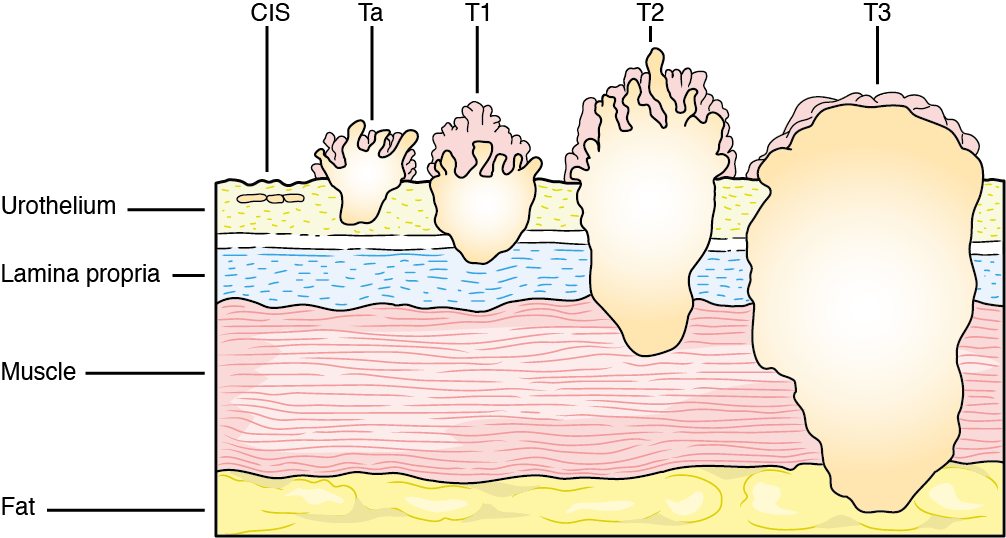
Bladder cancers (tumors) are staged from stage I through stage IV : Stage I: cancer occurs in the bladders inner lining but not to muscular bladder wall. Stage II: cancer invades the muscular bladder wall but goes no further. Stage III: cancer is through the bladder wall and into surrounding tissue. Stage IV: cancer has metastasized …
What tests are used to determine if a tumor is cancerous?
Tests are used to determine if the tumor is cancerous. The tests may include cystoscopy, biopsy, urine cytology, and/or imaging by CT or other tests to use a contrast dye to provide a detailed view of the bladder (and ureters).

How does bladder cancer develop?
Bladder cancer develops when cells in the bladder begin to grow abnormally, forming a tumor in the bladder. Bladder cancer begins when cells in the bladder develop changes (mutations) in their DNA. A cell’s DNA contains instructions that tell the cell what to do.
Where does bladder cancer start?
Bladder cancer is a common type of cancer that begins in the cells of the bladder. The bladder is a hollow muscular organ in your lower abdomen that stores urine. Bladder cancer most often begins in the cells (urothelial cells) that line the inside of your bladder. Urothelial cells are also found in your kidneys and the tubes (ureters) …
Where is the bladder located?
Your kidneys, located in the rear portion of your upper abdomen, produce urine by filtering waste and fluid from your blood. Bladder cancer is a common type of cancer that begins in the cells of the bladder. The bladder is a hollow muscular organ in your lower abdomen that stores urine. Bladder cancer most often begins in …

Where is urothelial cancer found?
Urothelial cells are also found in your kidneys and the tubes (ureters) that connect the kidneys to the bladder. Urothelial cancer can happen in the kidneys and ureters, too, but it’s much more common in the bladder. Most bladder cancers are diagnosed at an early stage, when the cancer is highly treatable.
Can bladder cancer come back?
But even early-stage bladder cancers can come back after successful treatment. For this reason, people with bladder cancer typically need follow-up tests for years after treatment to look for bladder cancer that recurs.
How do you know if you have bladder cancer?
Bladder cancer signs and symptoms may include: Blood in urine (hematuria), which may cause urine to appear bright red or cola colored, though sometimes the urine appears normal and blood is detected on a lab test. Frequent urination. Painful urination. Back pain.

What is the most common type of bladder cancer?
Urothelial carcinoma is the most common type of bladder cancer in the United States. Squamous cell carcinoma. Squamous cell carcinoma is associated with chronic irritation of the bladder — for instance, from an infection or from long-term use of a urinary catheter. Squamous cell bladder cancer is rare in the United States.
What are the symptoms of bladder cancer?
Being unable to urinate. Lower back pain on one side. Loss of appetite and weight loss. Feeling tired or weak. Swelling in the feet. Bone pain. Again, many of these symptoms are more likely to be caused by something other than bladder cancer, but it’s important to have them checked.
Can bladder cancer cause bleeding?
Usually, the early stages of bladder cancer (when it’s small and only in the bladder) cause bleeding but little or no pain or other symptoms. Blood in the urine doesn’t always mean you have bladder cancer.
How do you know if you have bladder cancer?
Bladder cancers that have grown large or have spread to other parts of the body can sometimes cause other symptoms, such as: Being unable to urinate. Lower back pain on one side. Loss of appetite and weight loss. Feeling tired or weak.
Can bladder cancer spread to other parts of the body?
Bladder cancers that have grown large or have spread to other parts of the body can sometimes cause other symptoms, such as: Again, many of these symptoms are more likely to be caused by something other than bladder cancer, but it’s important to have them checked.
Can bladder cancer cause lower back pain?
Bladder cancers that have grown large or have spread to other parts of the body can sometimes cause other symptoms, such as: Being unable to urinate. Lower back pain on one side. Loss of appetite and weight loss. Feeling tired or weak.
What does it mean when you have blood in your urine?
Blood in the urine. In most cases, blood in the urine (called hematuria) is the first sign of bladder cancer. There may be enough blood to change the color of the urine to orange, pink, or, less often, dark red.
Is urine a normal color?
Sometimes, the color of the urine is normal but small amounts of blood are found when a urine test (urinalysis) is done because of other symptoms or as part of a general medical check-up. Blood may be present one day and absent the next, with the urine remaining clear for weeks or even months.
What is bladder tumor?
What are bladder tumors? Bladder tumors are abnormal growths that occur in the bladder. If the tumor is benign, it’s noncancerous and won’t spread to other parts of your body. This is in contrast to a tumor that’s malignant, which means it’s cancerous.

How to tell if bladder tumor is a tumor?
Bladder tumors are typically diagnosed by a biopsy or a urine analysis. However, certain symptoms can indicate that a tumor or bladder issue is the possible cause, including: blood in the urine. pain while urinating. inability to urinate. having the urge to urinate more frequently. blockage of the urine stream.
What is the most common benign tumor in women?
Leiomyomas . Leiomyomas are the most common benign tumor found in women. That said, they’re rarely located in the bladder: According to a study. on bladder leiomyomas, they account for less than 1 percent of all bladder tumors. Leiomyomas form in the smooth muscle cells.
What is a tumor that grows fat cells?
Lipomas are tumor growths of fat cells. They’re often caused by an overgrowth of such cells. Lipomas are fairly common and usually don’t cause any pain unless they press against other organs or nerves.

How to treat a tumor?
Treatment for your tumor will depend on what type of tumor you have. First, your doctor may diagnose the tumor via biopsy or endoscopy. An endoscopy will provide a visual look, while a biopsy will provide a tissue sample of the tumor. After diagnosing the tumor, your doctor will develop a treatment plan that best suits your condition.
How to diagnose a tumor?
First, your doctor may diagnose the tumor via biopsy or endoscopy. An endoscopy will provide a visual look, while a biopsy will provide a tissue sample of the tumor. After diagnosing the tumor, your doctor will develop a treatment plan that best suits your condition.
What to do after a tumor is diagnosed?
After diagnosing the tumor, your doctor will develop a treatment plan that best suits your condition. If the tumor is positioned so the risk of surgery damaging blood vessels, nerves, and the surrounding area is relatively low, they’ll most likely recommend removing the tumor.

What is mass in cancer?
According to the National Cancer Institute, a mass is a lump in the body that can be caused by the abnormal growth of cells, a cyst, …
Can a mass cause pain?
Many patients are surprised to find out they have one at all. On the other hand, if a mass is pressing on a nerve or organ, it can cause pain. Masses in the brain might cause dizziness or blurred vision.
Can you remove a benign tumor?
For benign or noncancerous tumors that are not causing any symptoms, no treatment may be necessary. Medication can sometimes be used to reduce the size of the mass. Birth control pills, for instance, can be used to decrease the symptoms of uterine fibroids. For those that cause troubling symptoms, surgery can remove the tumor.

What is the treatment for cancer?
If a mass turns out to be cancer, treatment could involve surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy or immunotherapy.
Evaluating A Bladder Mass
-
To assess a bladder mass, urologists perform a physical examination, and blood and urine tests to evaluate for the presence of blood in the urine. You may also have a bladder wash to obtain cells from your bladder for a pathologist to analyze. But ultimately, the urologist needs to look inside your bladder via a procedure called cystoscopy. Cystoscopy involves passing a cystoscop…
Recognizing Problematic Symptoms
-
You always should report unusual urinary symptoms to your primary healthcare provider, including: 1. Difficulty with urination: feeling the need to empty your bladder but having little or no urine coming out, or the need to strain or bear down while urinating 2. Urgent need to urinate to prevent leakage 3. Frequent and/or painful urination 4. Blood in the urine: your urine may appear …
Do Benign Tumors Need to Be removed?
-
“It depends,” says Dr. Guru. “Benign bladder masses usually grow very slowly and will not spread to other tissues or organs in the body. In some cases, we will just monitor patients on a regular basis. However, some benign masses can bleed or grow very large and cause problems by taking up too much space in your bladder or pressing on other organs …