Contents
Symptoms
Chemotherapy followed by radical cystectomy (removal of the bladder and nearby lymph nodes) is then the standard treatment. Partial cystectomy is rarely an option for stage III cancers. Chemotherapy (chemo) before surgery (with or without radiation) can shrink the tumor, which may make surgery easier.
Causes
· Ultrasound: This test uses sound waves to make pictures of the organs inside your body, like your bladder and kidneys. It can help show the size of a bladder cancer and if it has spread. Bone scan: A bone scan can help show if bladder cancer has spread to the bones. This test is not done unless you have bone pain.
Prevention
A relative survival rate compares people with the same type and stage of bladder cancer to people in the overall population. For example, if the 5-year relative survival rate for a specific stage of bladder cancer is 90%, it means that people who have that cancer are, on average, about 90% as likely as people who don’t have that cancer to live for at least 5 years after being …
Complications
· For bladder cancer, if the cancer has spread to the regional lymph nodes, the 5-year survival rate is 36.3 percent. If it has spread to a more …
What happens on a patient with terminal bladder cancer?
· While bladder cancer is relatively common, the average five-year survival rate is quite high at 76.9%. This rate has improved over the past several years, and a person’s chance of survival is influenced by many factors. What Is the Bladder? The bladder is flexible, being made of smooth muscle.
How long will you live if you have bladder cancer?
Bladder cancer can often be found early because it causes blood in the urine or other urinary symptoms that cause a person to see a health care provider. Blood in the urine. In most cases, blood in the urine (called hematuria) is the first sign of bladder cancer. There may be enough blood to change the color of the urine to orange, pink, or …
What are the chances of dying from bladder cancer?
But nothing prepared me for being told that a well-loved family member had in fact been diagnosed with terminal bladder cancer. Dealing with the emotions. This was something that should have come relatively easily to me. After all, I have spent the last 3 years dealing with my own bladder cancer diagnosis, plus advocating for and supporting …
What are the early warning signs of bladder cancer?
· Stage 0is (flat carcinoma in situ): Cancer grows flat against the bladder’s tissue lining, but it hasn’t spread to the bladder wall’s muscle or connective tissue and hasn’t spread outside the bladder. The TNM characteristics are Tis, N0, M0. Stage 1. Stage 1 bladder cancer doesn’t have substages.

Is cancer in the bladder fatal?
It also affects females. In 2019, the American Cancer Society (ACS) predict that around 80,470 people will receive a diagnosis of bladder cancer and 17,670 will die from it in the United States. Bladder cancer can be benign or malignant. Malignant bladder cancer may be life threatening, as it can spread quickly.
Does bladder cancer spread fast?
They tend to grow and spread slowly. High-grade bladder cancers look less like normal bladder cells. These cancers are more likely to grow and spread.
How long can you live after being diagnosed with bladder cancer?
Survival rates can give you an idea of what percentage of people with the same type and stage of cancer are still alive a certain amount of time (usually 5 years) after they were diagnosed….5-year relative survival rates for bladder cancer.SEER Stage5-year Relative Survival RateAll SEER stages combined77%3 more rows•Mar 1, 2022
Is bladder cancer highly curable?
Bladder cancer is highly treatable when it is diagnosed in the early stages. The main types of treatments for bladder cancer include: Surgery : Bladder cancer treatment almost always has a surgical component that may be combined with other non-invasive approaches, including those listed below.
Where is the first place bladder cancer spreads?
When bladder cancer spreads, it first invades the bladder wall, which is made up of four distinct layers. It can take some time for cancer to penetrate all of these layers, but once it has, it can then spread into the surrounding fatty tissues and lymph nodes.
What are the signs that bladder cancer has spread?
The signs and symptoms of bladder cancer that has spread to other parts of the body include:tiredness or weakness.pain when urinating.difficulty urinating or inability to urinate.pain in the lower back on one side of the body.weight loss.swollen feet.bone pain.
Can you live 10 years with bladder cancer?
Bladder cancer survival rates by stage According to the American Cancer Society , the relative survival rates for all stages of bladder cancer are: 5 years: 77 percent. 10 years: 70 percent. 15 years: 65 percent.
Is bladder cancer aggressive?
It has not grown in toward the hollow part of the bladder, and it has not spread to the thick layer of muscle or connective tissue of the bladder (Tis, N0, M0). This is always a high-grade cancer (see “Grades,” below) and is considered an aggressive disease because it can lead to muscle-invasive disease.
What is the main cause of bladder cancer?
Smoking. Smoking is the single biggest risk factor for bladder cancer. This is because tobacco contains cancer-causing (carcinogenic) chemicals. If you smoke for many years, these chemicals pass into your bloodstream and are filtered by the kidneys into your urine.
What are the 5 warning signs of bladder cancer?
Here are five warning signs to watch for:Blood in the urine (hematuria). This is the most common early symptom of bladder cancer and typically the first sign of bladder cancer that is seen. … UTI-like symptoms. … Unexplained pain. … Decreased appetite. … Postmenopausal uterine bleeding.
Is bladder cancer a silent killer?
Bladder cancer is the most expensive cancer to treat, and it has a reputation for being a silent killer. As with most cancers, awareness and early detection are critical in saving lives. According to Bladder Cancer Canada, about 120,000 people will be diagnosed with bladder cancer this year alone.
How long can you live after bladder removal?
Patients in group 1 achieved a progression-free 5-year survival rate of 77% and an overall survival rate of 63% after 5 years. In group 2 patients achieved a progression-free survival rate of 51% after 5 years and an overall survival rate of 50%.
Treating Stage 0 Bladder Cancer
Stage 0 bladder cancer includes non-invasive papillary carcinoma (Ta) and flat non-invasive carcinoma (Tis). In either case, the cancer has not inv…
Treating Stage I Bladder Cancer
Stage I bladder cancers have grown into the connective tissue layer of the bladder wall but have not reached the muscle layer.Transurethral resecti…
Treating Stage II Bladder Cancer
These cancers have invaded the muscle layer of the bladder wall. Transurethral resection (TURBT) is typically the first treatment for these cancers…
Treating Stage III Bladder Cancer
These cancers have reached the outside of the bladder and might have grown into nearby tissues or organs.Transurethral resection (TURBT) is typical…
Treating Stage IV Bladder Cancer
These cancers have reached the abdominal or pelvic wall (T4b tumors) or have spread to nearby lymph nodes or distant parts of the body. Stage IV ca…
Treating Bladder Cancer That Progresses Or Recurs
If cancer continues to grow during treatment (progresses) or comes back (recurs), your treatment options will depend on where and how much the canc…
How Does The Doctor Know I Have Bladder Cancer?
Bladder cancer might cause symptoms such as: 1. Having trouble peeing 2. Feeling pain when peeing 3. Needing to go more often than normal 4. Seeing…
Tests to Look For Bladder Cancer
Your doctor may do other tests to find out more about the cancer. Some of them are:X-ray: Dye is put into a vein for a special x-ray of the kidneys…
How Serious Is My Cancer?
If you have bladder cancer, the doctor will want to find out how far it has spread. This is called staging. Your doctor will want to find out the s…
What Kind of Treatment Will I Need?
There’s more than one way to treat bladder cancer. You might want to get a second opinion about the best treatment plan for you. Doctors may have d…
What Will Happen After Treatment?
You will be glad when treatment is over. But it’s hard not to worry about cancer coming back. Even when cancer never comes back, people still worry…

Where does bladder cancer start?
Bladder cancer is a common type of cancer that begins in the cells of the bladder. The bladder is a hollow muscular organ in your lower abdomen that stores urine. Bladder cancer most often begins in the cells (urothelial cells) that line the inside of your bladder. Urothelial cells are also found in your kidneys and the tubes (ureters) …
Can bladder cancer come back?
But even early-stage bladder cancers can come back after successful treatment. For this reason, people with bladder cancer typically need follow-up tests for years after treatment to look for bladder cancer that recurs.
Where is the bladder located?
Your kidneys, located in the rear portion of your upper abdomen, produce urine by filtering waste and fluid from your blood. Bladder cancer is a common type of cancer that begins in the cells of the bladder. The bladder is a hollow muscular organ in your lower abdomen that stores urine. Bladder cancer most often begins in …
Where is urothelial cancer found?
Urothelial cells are also found in your kidneys and the tubes (ureters) that connect the kidneys to the bladder. Urothelial cancer can happen in the kidneys and ureters, too, but it’s much more common in the bladder. Most bladder cancers are diagnosed at an early stage, when the cancer is highly treatable.
How do you know if you have bladder cancer?
Bladder cancer signs and symptoms may include: Blood in urine (hematuria), which may cause urine to appear bright red or cola colored, though sometimes the urine appears normal and blood is detected on a lab test. Frequent urination. Painful urination. Back pain.
How does bladder cancer develop?
Bladder cancer develops when cells in the bladder begin to grow abnormally, forming a tumor in the bladder. Bladder cancer begins when cells in the bladder develop changes (mutations) in their DNA. A cell’s DNA contains instructions that tell the cell what to do.
What is the most common type of bladder cancer?
Urothelial carcinoma is the most common type of bladder cancer in the United States. Squamous cell carcinoma. Squamous cell carcinoma is associated with chronic irritation of the bladder — for instance, from an infection or from long-term use of a urinary catheter. Squamous cell bladder cancer is rare in the United States.
What is the treatment for bladder cancer?
Immunotherapy is treatment that boosts your immune system to attack the cancer cells. Different types of immunotherapy can be used to treat bladder cancer. These drugs can be put right into the bladder (as a liquid) or given into a vein.
Can chemo be used for bladder cancer?
For early-stage bladder cancers, chemo may be used: Before surgery to shrink a tumor. After surgery to kill any cancer cells that remain. With radiation to help it work better. Chemo is usually the main treatment for advanced bladder cancers, such as those that have spread to other parts of the body.
Where does cancer start?
Cancer can start any place in the body. Cancer that starts in the bladder is called bladder cancer. It starts when cells in the bladder grow out of control and crowd out normal cells. This makes it hard for the body to work the way it should. Cancer cells can spread to other parts of the body.
What is it called when cancer spreads to the bone?
For instance, cancer cells in the bladder can travel to the bone and grow there. When cancer cells spread, it’s called metastasis . Cancer is always named for the place where it starts. So when bladder cancer spreads to the bone (or any other place), it’s still called bladder cancer.
What is the tube that connects the kidneys to the bladder?
Tubes called ureters connect your kidneys to the bladder. Urine flows through the ureters and into your bladder, where it’s stored. When you urinate (pee), the bladder squeezes the urine out through a tube called the urethra. Bladder cancer usually starts in the lining or inner layer of the bladder wall.

What tests are done to check for bladder cancer?
This might include a rectal exam, during which a gloved finger is put into your rectum. If you are a woman, a pelvic exam might also be done.
What is the test for cancer?
Urine tests: For these tests, you’ll be asked to pee in a cup. Your urine is then tested for cancer cells, blood, or certain proteins (called tumor markers). Cystoscopy: For this exam, a doctor called a urologist looks at the inside of your bladder using a tool called a cystoscope.
How long does bladder cancer last?
The SEER database tracks 5-year relative survival rates for bladder cancer in the United States, based on how far the cancer has spread. The SEER database, however, does not group cancers by AJCC TNM stages (stage 1, stage 2, stage 3, etc.). Instead, it groups cancers into localized, regional, and distant stages: 1 Localized: There is no sign that the cancer has spread outside of the bladder. 2 Regional: The cancer has spread from the bladder to nearby structures or lymph nodes. 3 Distant: The cancer has spread to distant parts of the body such as the lungs, liver or bones.
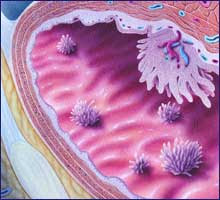
What is the SEER database?
The SEER database tracks 5-year relative survival rates for bladder cancer in the United States, based on how far the cancer has spread.
How long does bladder cancer last?
The later you’re diagnosed and the farther the cancer has traveled, the less chance that your cancer will be cured. The 5-year survival rate is the rate of surviving for 5 years after a cancer diagnosis. For bladder cancer, if the cancer has spread to the regional lymph nodes, the 5-year survival rate is 36.3 percent. Trusted Source.
How do you know if you have bladder cancer?
Symptoms of bladder cancer can include: blood or blood clots in your urine. pain or burning during urination. frequent urination. needing to urinate at night. needing to urinate but not being able to. lower back pain on one side of the body.

What is stage 4 bladder cancer?
Stage 4 bladder cancer is also called metastatic bladder cancer. This means the cancer has spread outside of the bladder into other parts of the body. People with metastatic cancer may experience symptoms relating to where the cancer has spread.
What is the survival rate for bladder cancer?
The 5-year survival rate is the rate of surviving for 5 years after a cancer diagnosis. For bladder cancer, if the cancer has spread to the regional lymph nodes, the 5-year survival rate is 36.3 percent. Trusted Source.
What are the symptoms of metastatic cancer?
For example, if a person’s bladder cancer has spread to their lungs, they may experience chest pain or increased coughing.

What type of cancer is in the bladder?
The two most common types of cancer affecting the bladder are: Transitional cell carcinoma (TCC): Transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder starts in the bladder. In a study of 33,761 patients in Norway, transitional cell carcinoma accounted for 95% of bladder cancer cases. 2.
Can bladder cancer recur?
Most bladder cancers are highly treatable. Many cases of bladder cancer are also caught early, which increases a person’s chances of survival. Even so, some early-stage bladder cancers can recur, and ongoing monitoring is required even if complete remission is achieved.
What are the different types of bladder cancer?
The two most common types of cancer affecting the bladder are: 1 Transitional cell carcinoma (TCC): Transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder starts in the bladder. In a study of 33,761 patients in Norway, transitional cell carcinoma accounted for 95% of bladder cancer cases. 2 2 Non-transitional cell carcinoma: This is a rarer form of bladder cancer, and it includes adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, sarcoma, and small cell carcinoma. 3 In a study examining 125 patients with non-transitional cell bladder cancer, those who were treated with a radical cystectomy and adjuvant treatment had a significantly improved prognosis, which was true for all histological types. 4

How does bladder cancer affect survival?
The factors influencing survival include: 1 Age: Increasing age has been linked to a lower survival rate in people with bladder cancer. 7 2 Sex: A literature review of 27 studies and 23,754 patients found that women had a greater risk for disease recurrence following localized treatment of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. 8 3 Smoking: Smoking increases the risk of recurrence and mortality in people with bladder cancer. 9 4 Recurrence: Recurrence of bladder cancer forebodes a poor prognosis, with a median survival of six months after recurrence. Although people with local recurrence have a slightly better prognosis, those with disease recurrence at local and distant sites perform very poorly.
How long does bladder cancer last?
While bladder cancer is relatively common, the average five-year survival rate is quite high at 76.9%. This rate has improved over the past several years, and a person’s chance of survival is influenced by many factors.
What is the bladder made of?
The bladder is flexible, being made of smooth muscle. It works to collect and then eliminate urine from your body. The bladder’s flexible walls are made perfectly to expand and contract as necessary to hold urine until it is expelled from the body. FatCamera / Getty Images.

What is the survival rate for bladder cancer?
For bladder cancer, the five-year relative survival rate when the cancer is at the localized stage is 69.2%. 1. Five-Year Survival Rates by Stage for Bladder Cancer. Stage.
Can bladder cancer spread to other parts of the body?
Bladder cancers that have grown large or have spread to other parts of the body can sometimes cause other symptoms, such as: Again, many of these symptoms are more likely to be caused by something other than bladder cancer, but it’s important to have them checked.
What are the symptoms of bladder cancer?
Being unable to urinate. Lower back pain on one side. Loss of appetite and weight loss. Feeling tired or weak. Swelling in the feet. Bone pain. Again, many of these symptoms are more likely to be caused by something other than bladder cancer, but it’s important to have them checked.
Can bladder cancer cause bleeding?
Usually, the early stages of bladder cancer (when it’s small and only in the bladder) cause bleeding but little or no pain or other symptoms. Blood in the urine doesn’t always mean you have bladder cancer.
How do you know if you have bladder cancer?
Bladder cancers that have grown large or have spread to other parts of the body can sometimes cause other symptoms, such as: Being unable to urinate. Lower back pain on one side. Loss of appetite and weight loss. Feeling tired or weak.
Can bladder cancer cause lower back pain?
Bladder cancers that have grown large or have spread to other parts of the body can sometimes cause other symptoms, such as: Being unable to urinate. Lower back pain on one side. Loss of appetite and weight loss. Feeling tired or weak.

What does it mean when you have blood in your urine?
Blood in the urine. In most cases, blood in the urine (called hematuria) is the first sign of bladder cancer. There may be enough blood to change the color of the urine to orange, pink, or, less often, dark red.
Is urine a normal color?
Sometimes, the color of the urine is normal but small amounts of blood are found when a urine test (urinalysis) is done because of other symptoms or as part of a general medical check-up. Blood may be present one day and absent the next, with the urine remaining clear for weeks or even months.
Does Macmillan help with pensions?
The help that’s available or that you may be entitled to depend on where you live in the world. In the UK, Macmillan has specially trained individuals who can help with financial matters including pensions, mortgages, insurance, and benefits. Read about opportunities for financial assistance in the US.

Is it important to have good nutrition?
It is common for appetite to decrease, but it’s so very important to provide good nutritious foods and drinks. It may be worth considering asking for help from a dietitian. Also, there are many “wholesome” food/drink supplements available, which may be easier for the patient to digest, and you can rest a little easier knowing that all the relevant vitamins, minerals, etc. are already included. A pharmacist, doctor, or dietitian should be able to help with recommendations.
Is bladder cancer invasive?
Invasive cancers are deeper in the layers of the bladder wall. If a doctor says the cancer is superficial or non-muscle invasive, that means it isn’t in the bladder’s main muscle layer—though it may still be invasive or noninvasive and have the potential to spread to the muscle.
Does bladder cancer have substages?
Stage I bladder cancer doesn’t have substages. In stage I, the cancer is growing into the connective tissue in the bladder wall, called the lamina propria, but hasn’t reached the muscle and hasn’t spread outside the bladder.

What does it mean when a doctor says a bladder is invasive?
Invasive cancers are deeper in the layers of the bladder wall. If a doctor says the cancer is superficial or non-muscle invasive, that means it isn’t in the bladder’s main muscle layer —though it may still be invasive or noninvasive and have the potential to spread to the muscle.
What is the difference between invasive and noninvasive bladder cancer?
Doctors often use the terms “noninvasive” or “invasive” to describe whether cancer has spread into the bladder wall. Noninvasive means the cancer is in the inner cell layers. Invasive cancers are deeper in the layers of the bladder wall.
How many letters are there in bladder cancer?
The most common way doctors describe bladder cancer stages is using the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) TNM system. This system uses three letters, each of which is assigned a different number. Each letter stands for a specific characteristic of the cancer.

What does T1 mean in cancer?
This means that the disease is still localized, or contained within the urothelium layer of the bladder wall. Cancer cells haven’t invaded the deeper layers of bladder wall tissue. T1 means the tumor has grown from the layer of cells lining the bladder into the connective tissue below.
What does T2A mean?
T2a indicates the tumor is in the inner half of the muscle layer. T2b indicates the tumor is in the outer half of the muscle layer. T3 means the tumor has grown through the muscle layer and into the surrounding fatty tissue. T3 has two subcategories:
What is terminal cancer?
Terminal cancer refers to cancer that can’t be cured or treated. It’s sometimes also called end-stage cancer. Any type of cancer can become terminal cancer. Terminal cancer is different from advanced cancer. Like terminal cancer, advanced cancer isn’t curable. But it does respond to treatment, which may slow down its progression.

Is terminal cancer incurable?
Terminal cancer is incurable. This means no treatment will eliminate the cancer. But there are many treatments that can help make someone as comfortable as possible. This often involves minimizing the side effects of both the cancer and any medications being used.
Is advanced cancer curable?
Like terminal cancer, advanced cancer isn’t curable. But it does respond to treatment, which may slow down its progression. Terminal cancer doesn’t respond to treatment. As a result, treating terminal cancer focuses on making someone as comfortable as possible. Read on to learn more about terminal cancer, including its impact on life expectancy …