Contents

Does cystoscopy detect tumors in bladder?
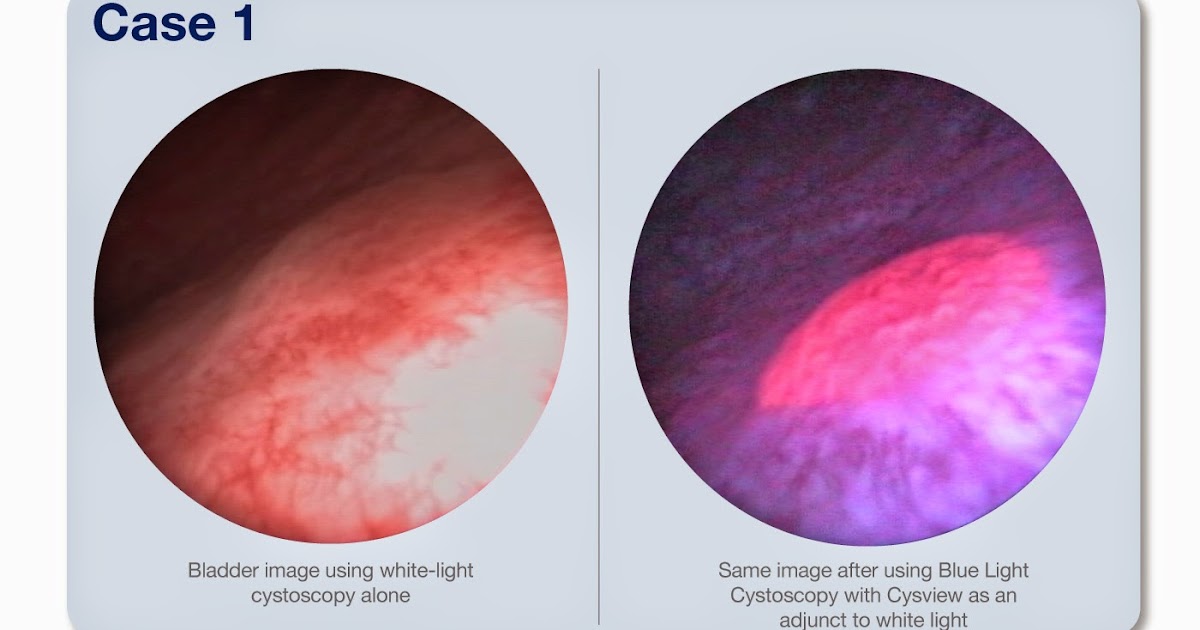
· The figure below shows images of bladder cancers taken by standard white light cystoscopy (at left) and blue light cystoscopy (at right). In the blue light cystoscopy a fluorescent dye has been used that turns bladder cancer cells pink when they are exposed to blue light. Source: Wikimedia Commons Can a cystoscopy miss bladder cancer?
Is a cystoscopy considered surgery?
Many people in the bladder cancer community have described coming face to face with their bladder tumor in the exam room during a cystoscopy. One survivor described the moment by saying, “The first glimpse I had of a tumor of mine, I was struck by how pretty it was. I always imagined a tumor to be ugly. This one looked like a sea anemone…”
What are the symptoms of a bladder tumor?
Cystoscopy is a procedure a doctor uses to look at the inside of the bladder and urethra (the tube that connects the bladder to the outside of the body). This is done with a cystoscope, a thin tube with a light and a lens or small video camera on the end. The tube is put in through your urethra.
How do you remove a bladder tumor?
Blue light cystoscopy or Photodynamic diagnosis (PDD) This is another type of cystoscopy using a blue light instead of a white light to pick up bladder cancer. You usually have it under general anaesthetic. To have the test your doctor puts a thin tube (catheter) into your bladder.
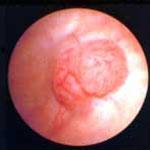
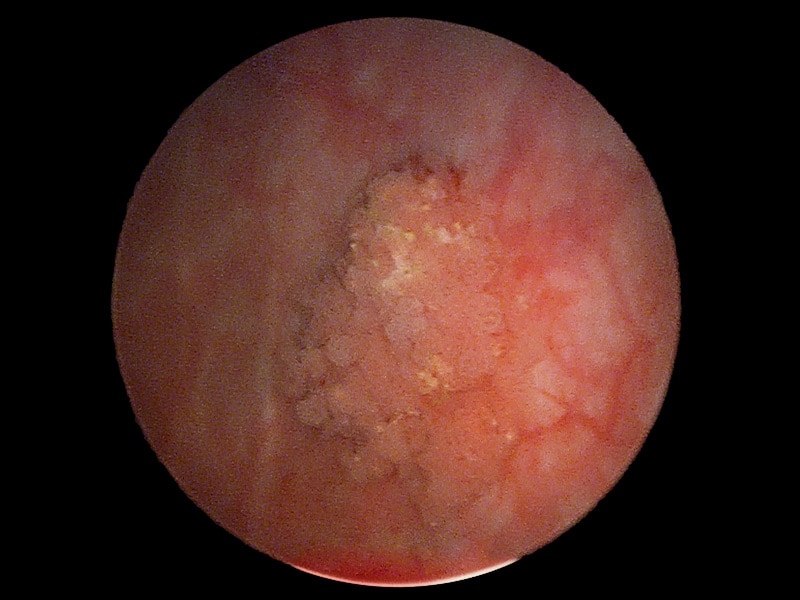
Can you see bladder cancer on a cystoscopy?
Urine tumor marker tests Some doctors find these urine tests useful in looking for bladder cancers, but they may not help in all cases. Most doctors feel that cystoscopy is still the best way to find bladder cancer.
What does cancer look like in a bladder?
Bladder cancer signs and symptoms may include: Blood in urine (hematuria), which may cause urine to appear bright red or cola colored, though sometimes the urine appears normal and blood is detected on a lab test. Frequent urination. Painful urination.
Are red patches in bladder always cancer?
Blood in the urine doesn’t always mean you have bladder cancer. More often it’s caused by other things like an infection, benign (not cancer) tumors, stones in the kidney or bladder, or other benign kidney diseases. Still, it’s important to have it checked by a doctor so the cause can be found.
How can a doctor tell if you have bladder cancer?
A sample of your urine is analyzed under a microscope to check for cancer cells in a procedure called urine cytology. Imaging tests. Imaging tests, such as computerized tomography (CT) urogram or retrograde pyelogram, allow your doctor to examine the structures of your urinary tract.
Which of the following is usually the first symptom of bladder cancer?
For most people, the first symptom of bladder cancer is blood in the urine, also called hematuria. Sometimes the blood is visible, prompting the patient to visit a doctor.
What are the 5 warning signs of bladder cancer?
Here are five warning signs to watch for:Blood in the urine (hematuria). This is the most common early symptom of bladder cancer and typically the first sign of bladder cancer that is seen. … UTI-like symptoms. … Unexplained pain. … Decreased appetite. … Postmenopausal uterine bleeding.
What color are bladder cancers?
Which ribbon colors represent bladder cancer? The most widely accepted ribbon by various bladder cancer organizations is the color orange. Some people use a yellow ribbon. The tricolor ribbon is most broadly utilized for bladder cancer in the United States.
What are red spots inside the bladder?
Interstitial cystitis is chronic inflammation of the bladder. People who have interstitial cystitis have a bladder wall that is irritated and inflamed (sore and red). This inflammation can scar the bladder or make it stiff.
Is a mass in the bladder always cancer?
Bladder tumors are abnormal growths that occur in the bladder. If the tumor is benign, it’s noncancerous and won’t spread to other parts of your body. This is in contrast to a tumor that’s malignant, which means it’s cancerous. There are several types of benign tumors that can develop within the bladder.
Do you feel ill with bladder cancer?
Nausea and vomiting. Burning or pain when you urinate, feeling the need to go often, or blood in urine. Diarrhea. Feeling tired.
What will a cystoscopy show?
Cystoscopy is a procedure that lets the healthcare provider view the urinary tract, particularly the bladder, the urethra, and the openings to the ureters. Cystoscopy can help find problems with the urinary tract. This may include early signs of cancer, infection, narrowing, blockage, or bleeding.
Do you feel bloated with bladder cancer?
Abdominal Pain The types of pains can vary and include: Generalized pain — felt in more than half of the stomach area. Cramp-like pain — less serious and most likely due to bloating and gas.

What is a bladder cancer test?
This test can be used to look for the causes of signs or symptoms in the bladder (such as trouble urinating or blood in the urine), or to look at an abnormal area seen on an imaging test (such as a CT scan). If you have had bladder cancer, it might also be used to look for new tumors.
What is a cystoscopy?
What is cystoscopy? Cystoscopy is a procedure a doctor uses to look at the inside of the bladder and urethra ( the tube that connects the bladder to the outside of the body). This is done with a cystoscope, a thin tube with a light and a lens or small video camera on the end. The tube is put in through your urethra.
What is the procedure that a doctor uses to look at the inside of the bladder and urethra?
Cystoscopy is a procedure a doctor uses to look at the inside of the bladder and urethra (the tube that connects the bladder to the outside of the body). This is done with a cystoscope, a thin tube with a light and a lens or small video camera on the end. The tube is put in through your urethra.

What is the best way to take a biopsy of the bladder?
This is done by passing long, thin instruments down the cystoscope, such as small forceps (tweezers) to collect the samples. The biopsy samples are then looked at in the lab.
How long does it take to get a cytoscopy?
If any abnormal areas are seen, they can be biopsied at this time. Cystoscopy might only take about 10 to 20 minutes, but it might take longer, depending on what’s being done.
How long does it take for a biopsy to show results?
If biopsies were done as part of the procedure, the results will typically be available within a few days, although some tests on the biopsy samples might take longer.

Can you sleep during a cystoscopy?
You might also be given a sedative through an IV line to help you relax during the test. For a rigid cystoscopy, you might be asleep (under general anesthesia) for the test. The doctor will then insert the cystoscope into your urethra and up into your bladder.
Why do you need a cystoscopy for bladder cancer?
Other reasons you might have a cystoscopy is to check: whether your cancer has come back. for spread from another type of cancer.
What is the test that looks at the inside of the bladder called?
Cystoscopy. A cystoscopy is a test to look at the inside of your bladder and tube that carries urine from your bladder out of your body (urethra). It uses a thin tube called a cystoscope. There are different types of cystoscopies:

What is a blue light cystoscopy?
Blue light cystoscopy or Photodynamic diagnosis (PDD) This is another type of cystoscopy using a blue light instead of a white light to pick up bladder cancer. You usually have it under general anaesthetic. To have the test your doctor puts a thin tube (catheter) into your bladder.
How to take a look at the inside of your bladder?
They then fill your bladder with sterile water. And take a look at the inside of your bladder and urethra using the cystoscope. If they need to they will take samples of tissue (biopsies) from any areas that look abnormal. Your doctor may also take biopsies from areas of bladder lining that look normal.
Why do you need a rigid cystoscopy?
You might have a rigid cystoscopy if you have biopsies taken or need treatment for a problem with your bladder.
Where does urine go when you empty it?
The bladder stores urine and when we empty it the urine passes from the bladder down a tube called the urethra and out of the body. The urethra in men passes through the prostate gland and down the penis. In women the urethra is much shorter and passes from the bladder down to an opening just in front of the vagina.
Why does the doctor put water in the scope?
You may find this uncomfortable and feel like you need to pass urine. The doctor puts water in through the scope to make it easier to see the bladder wall
What is the best way to diagnose bladder cancer?
The cystoscope can be used to remove small tissue samples (a biopsy ) to be examined under a microscope. A biopsy is the best way to diagnose cancer. Swipe to advance. 1 / 22.

What tests can show if a cancerous tumor has spread beyond the bladder?
If cancer is found, imaging tests can show whether it has spread beyond the bladder. An intravenous pyelogram uses dye to outline the kidneys, bladder, and ureters, the tubes that carry urine to the bladder. CT and MRI scans give more detailed images of these, and can show the lymph nodes nearby.
How long do people with bladder cancer live?
About half of bladder cancers are caught when the disease is confined to the inner lining of the bladder. About 96% of these people will live at least 5 years, compared to people without bladder cancer.
What jobs can cause bladder cancer?
Research suggests that certain jobs may increase your risk for bladder cancer. Metal workers, mechanics, and hairdressers are among those who may be exposed to cancer-causing chemicals. If you work with dyes, or in the making of rubber, textiles, leather, or paints, be sure to follow safety procedures to reduce contact with dangerous chemicals. Smoking further increases risk from chemical exposure.

Why does urine look red?
Most commonly, blood in the urine is not caused by cancer, but by other causes. These include exercise, trauma, infections, blood or kidney disorders, or drugs, such as blood thinners.
What is the procedure to remove the bladder?
Transurethral surgery is most often done for early-stage cancers. If cancer has invaded more of the bladder, the surgeon will likely perform a total cystectomy, removing the entire bladder and nearby lymph nodes. For men, the prostate and seminal vesicles may also be removed..
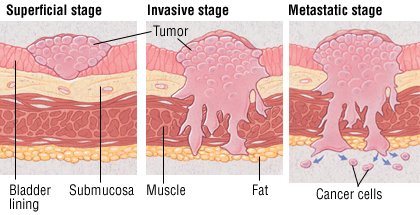
Where does bladder cancer start?
Cancer is the growth of abnormal cells in the body. Bladder cancer typically begins in the inner lining of the bladder, the organ that stores urine after it passes from the kidneys. Most bladder cancers are caught early, when treatments are highly successful and the disease has not spread beyond the bladder.
What is the name of the doctor who performs a cytoscopy on bladder cancer?
Cystoscope have lens (like telescope or microscope) placed at its inserting end that reproduces the inside image focused upon by enlarging it. Urologist is the specialist Doctor that conducts Cystoscopy test for Bladder Cancer. Usually stones, blockages, enlarged glands, bleeding, and related bladder abnormalities causes Cystoscopy.
How long does it take to get a urine sample after a cystoscopy?
Usually the Cystoscopy test procedure takes 15 to 30 minutes. With anesthesia the pain is reduced to negligible or very minute that the patient might face during the Cystoscopy test procedure.
What is a cystoscope?
Cystoscopy derives from the thin fiber-optic tube instrument cystoscope that is inserted in your body through bladder to diagnose the internal happenings of your body. A German Army Surgeon Dr. Phillip Bozzinni invented and developed the instrument in 1807.

Why do urologists collect urine samples?
This helps the Urologist to examine and investigate the bladder clearly. The Urologist may collect tissue samples for laboratory testing. The inner happenings and functioning of the bladder can be visual on the TV or computer Monitor. Some patients maybe asked for giving urine samples as well before or after Cystoscopy test for bladder cancer.
What causes a cytoscopy?
Usually stones, blockages, enlarged glands, bleeding, and related bladder abnormalities causes Cystoscopy. The Cystoscopy test is conducted to find the cause of urinary system problems, bladder cancer, urinary infections, inject a dye for x-rays and kidney problems, collect tissue samples and eliminate foreign objects from the body.
What happens during the fourth stage of bladder cancer?
During fourth stage the cancer cells advance to other parts of the body like liver, lungs, etc. Cystoscopy test for Bladder Cancer provides clear information about condition of problem. There are different procedures for various cases.
What is urine cytology?
In this case, the urine sample is examined under the micro-scope to detect cancer cells in a procedure called urine cytology. Usually it is conducted in the early stage.
What is a cystoscopy?
A cystoscopy is a test to check the health of your urethra and bladder. You might also hear it called a cystourethroscopy or, more simply, a bladder scope. It’s an outpatient test, which means you can get it at your doctor’s office, a hospital, or clinic and go home the same day. The doctor inserts a tube into your urethra.
How does a cystoscope work?
The cystoscope has a lens on the end that works like a telescope. It makes it easier for the doctor to see inside your body. They might put a video camera over the lens to project images onto a screen. The doctor fills your bladder. They put water or saline in through the cystoscope.
What happens when your bladder is full?
When your bladder is full of water, it stretches. This lets the doctor see your entire bladder wall. They’ll ask you how it feels when it’s full. The doctor takes tissue samples. If an area looks abnormal, the doctor will use the cystoscope to cut a small piece that they can send to the lab for analysis.
How does a doctor use a scope?
Your doctor inserts the scope. They’ll clean your urethra and numb the area. The scope goes through the urethra and into your bladder. They’ll use the smallest scope possible. They might need to use a bigger one to take samples or bring surgical tools into your bladder. The doctor examines your urethra and bladder.
Where is the urethra tube?
The doctor inserts a tube into your urethra. If you’re a man, the opening is at the end of your penis. If you’re a woman, it’s just above your vagina. The test lets your doctor check the complete length of your urethra and the bladder for polyps, narrow areas called strictures, abnormal growths, and other problems.
Can cystoscopy be a complication?
Complications of cystoscopy are rare but can happen. The risks of having a cystoscopy include:
How long does a cystoscopy take?
A diagnostic cystoscopy usually only takes about five minutes, but may take a little longer. If you’re having a biopsy or treatment, the procedure may take longer. During a cystoscopy, your doctor: Slides a lubricated cystoscope through the urethra to the bladder. Injects sterile salt water through the cystoscope into the bladder.
What is a cystoscopy used for?
Urologists use cystoscopies to diagnose and treat urinary tract problems. A cystoscopy can diagnose:

How to stop a urine leakage?
Inject medication to stop urine leakage. Remove a ureteral stent (a tiny tube that holds open a ureter) placed during an earlier procedure. Remove bladder stones, abnormal tissue, polyps or tumors. Take small pieces of bladder or urethral tissue to biopsy (examine in a lab).
What is the name of the tube that a doctor uses to view the inside of the bladder?
Your healthcare provider may use a cystoscopy to view the inside of the bladder and urethra. The bladder stores urine until it flows out of the body through a tube called the urethra. A urologist, or urinary tract specialist, performs a cystoscopy. For the procedure, your doctor uses a cystoscope, a pencil-sized lighted tube with a camera …
What are bladder control issues?
Bladder control issues, such as urinary retention (being unable to empty the bladder all the way) or incontinence (not being able to control urine flow). Bladder stones. Blood in urine (hematuria). Frequent urinary tract infections (UTIs).

What does a full bladder do?
A stretched, full bladder makes it easier to see the bladder lining. You may feel like you need to pee. Looks at the inside of the bladder and urethra. Inserts small instruments through the cystoscope. Your provider uses these tools to remove tissue samples or tumors, if needed.
How to prepare for a cystoscopy?
Generally, you will: Give a urine sample the day of the procedure to check for a UTI. If you have an infection, you’ll need treatment before you can get a cystoscopy. Urinate immediately before the procedure.
Actos And Bladder Cancer What Does Bladder Cancer Look Like
Ultrasound Video showing a large vesical growth in the urinary bladder.

Endoscopic Teflon Or Deflux Gel Treatment For Vesico
This patient shows an echogenic mound in the left vesico-ureteric junction. The Color Doppler image shows a ureteric jet emerging from this region suggesting that the left distal ureteric orificeis patent. This patient had a history of vesico-ureteric reflux.
Bilharziasis Of The Urinary Bladder
This patient presented with lower urinary symptoms, dysuria and hematuria. Sonography of the pelvis showed thickening of the wall of the urinary bladder with extensive calcification. Theseultrasound images suggest a diagnosis of schistosomiasis or bilharziasis of the wall of the urinary bladder.
If You Have Liver Disease
Certain diseases can make you more likely to get liver cancer, including:

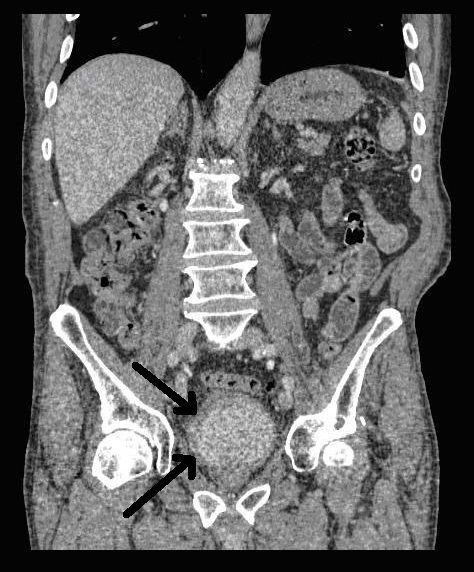
Detecting Bladder Cancer With Ct Scans
A CT scan uses x-rays to obtain cross-sectional images of the body. Compared to a general x-ray test, which directs a broad x-ray beam from a single angle, the CT scan uses a number of thin beams to produce a series of images from different angles.
Screening For Bladder Cancer
Early-stage bladder cancer often shows no symptoms, or symptoms that are similar to those of benign conditions such as bladder stones, an enlarged prostate, or urinary tract infection. For this reason it is important to be examined regularly by a physician.
Can An Ultrasound Tell If An Ovarian Cyst Is Cancerous
Vaginal ultrasound can help to show whether any cysts on your ovaries contain cancer or not. If a cyst has any solid areas it is more likely to be cancer. Sometimes, in women who are past their menopause, the ovaries do not show up on an ultrasound. This means that the ovaries are small and not likely to be cancerous.