Contents

How dangerous is bladder cancer?
Blood in the urine In most cases, blood in the urine (called hematuria) is the first sign of bladder cancer. There may be enough blood to change the color …
What are the chances of dying from bladder cancer?
Many people in the bladder cancer community have described coming face to face with their bladder tumor in the exam room during a cystoscopy. One survivor described the moment by saying, “The first glimpse I had of a tumor of mine, I was struck by how pretty it was. I always imagined a tumor to be ugly. This one looked like a sea anemone…”
What are the symptoms and signs of bladder cancer?
· Ultrasound images show evidence of trabeculation of the urinary bladder. This is seen asfolds of hypertrophied bladder mucosa and bladder smooth muscle. There is also evidence of bilateral moderate hydronephrosis . The cause of Lower urinary tract obstruction appears tothe enlarged prostate with intravesical enlargement of the median lobe .
How do you detect bladder cancer?
Carcinoma in situ (CIS) is a cancerous patch of bladder lining, often referred to as a “flat tumor.” The patch may look almost normal or may look red and inflamed. CIS is a type of nonmuscle-invasive bladder cancer that is of higher grade and increases the …

What is usually the first symptom of bladder cancer?
In most cases, blood in the urine (called hematuria) is the first sign of bladder cancer. There may be enough blood to change the color of the urine to orange, pink, or, less often, dark red.
What does cancer look like in a bladder?
Bladder cancer signs and symptoms may include: Blood in urine (hematuria), which may cause urine to appear bright red or cola colored, though sometimes the urine appears normal and blood is detected on a lab test. Frequent urination. Painful urination.
Does bladder cancer spread fast?
They tend to grow and spread slowly. High-grade bladder cancers look less like normal bladder cells. These cancers are more likely to grow and spread.
Do you feel ill with bladder cancer?
Feeling weak or fatigued: You may feel lethargic and extremely tired a lot of the time. Bone pain: If your cancer has spread to the bone, it can cause bone pain or a bone fracture.
What are the 5 warning signs of bladder cancer?
Here are five warning signs to watch for:Blood in the urine (hematuria). This is the most common early symptom of bladder cancer and typically the first sign of bladder cancer that is seen. … UTI-like symptoms. … Unexplained pain. … Decreased appetite. … Postmenopausal uterine bleeding.
How do I find out if I have bladder cancer?
Tests for bladder cancer look for different substances and/or cancer cells in the urine. Urinalysis: One way to test for bladder cancer is to check for blood in the urine ( hematuria). This can be done during a urinalysis, which is a simple test to check for blood and other substances in a sample of urine.
Can you have bladder cancer for years and not know it?
It may be seen as a symptom of post-menopausal bleeding, simple cystitis or a urinary tract infection. As a result, a bladder cancer diagnosis can be overlooked for a year or more.
Where is the first place bladder cancer spreads?
When bladder cancer spreads, it first invades the bladder wall, which is made up of four distinct layers. It can take some time for cancer to penetrate all of these layers, but once it has, it can then spread into the surrounding fatty tissues and lymph nodes.
Is there pain with bladder cancer?
Bladder cancer can cause changes in urination. You might experience pain or a burning sensation when you urinate, and you may see blood in your urine. You may also feel: an urge to urinate more frequently than you used to.
Which of the following is the most common symptom of cancer of the bladder?
Blood in your urine is the most common symptom of bladder cancer. The medical name for blood in your urine is haematuria and it’s usually painless. You may notice streaks of blood in your urine or the blood may turn your urine brown. The blood isn’t always noticeable and it may come and go.
How does a urologist check for bladder cancer?
Cystoscopy. If bladder cancer is suspected, most doctors will recommend a cystoscopy. . A urologist uses a cystoscope, which is a long, thin, flexible tube with a light and a lens or a small video camera on the end.
Do you lose weight with bladder cancer?
Weight loss is a common symptom of many types of cancer, including bladder cancer.
What is the life expectancy of someone with bladder cancer?
5-year relative survival rates for bladder cancerSEER Stage5-year Relative Survival RateIn situ alone Localized96% 70%Regional38%Distant6%All SEER stages combined77%Mar 1, 2022
What is the survival rate of bladder cancer?
The general 5-year survival rate for people with bladder cancer is 77%. However, survival rates depend on many factors, including the type and stage of bladder cancer that is diagnosed. The 5-year survival rate of people with bladder cancer that has not spread beyond the inner layer of the bladder wall is 96%.
Where does bladder cancer spread first?
When bladder cancer spreads, it first invades the bladder wall, which is made up of four distinct layers. It can take some time for cancer to penetrate all of these layers, but once it has, it can then spread into the surrounding fatty tissues and lymph nodes.
Can you have bladder cancer for years and not know it?
It may be seen as a symptom of post-menopausal bleeding, simple cystitis or a urinary tract infection. As a result, a bladder cancer diagnosis can be overlooked for a year or more.

What are the symptoms of bladder cancer?
Being unable to urinate. Lower back pain on one side. Loss of appetite and weight loss. Feeling tired or weak. Swelling in the feet. Bone pain. Again, many of these symptoms are more likely to be caused by something other than bladder cancer, but it’s important to have them checked.
How long does urine stay clear after bladder cancer?
Blood may be present one day and absent the next, with the urine remaining clear for weeks or even months. But if a person has bladder cancer, at some point the blood reappears.
Why is bladder cancer so early?
Bladder cancer can often be found early because it causes blood in the urine or other urinary symptoms that cause a person to see a health care provider.

Why does urine have blood in it?
More often it’s caused by other things like an infection, benign (not cancer) tumors, stones in the kidney or bladder, or other benign kidney diseases. Still, it’s important to have it checked by a doctor so the cause can be found.
Can bladder cancer cause a change in urination?
Bladder cancer can sometimes cause changes in urination, such as: Having to urinate more often than usual. Pain or burning during urination. Feeling as if you need to go right away, even when your bladder isn’t full. Having trouble urinating or having a weak urine stream.
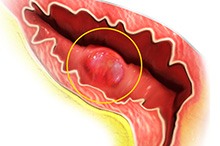
Actos And Bladder Cancer What Does Bladder Cancer Look Like
Ultrasound Video showing a large vesical growth in the urinary bladder.
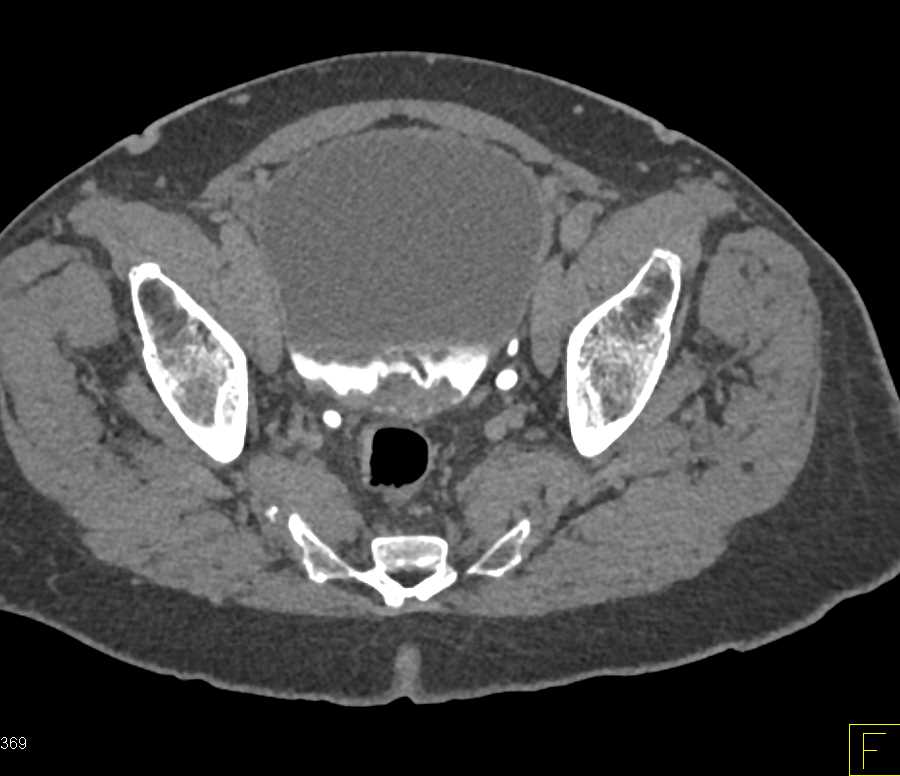
Endoscopic Teflon Or Deflux Gel Treatment For Vesico
This patient shows an echogenic mound in the left vesico-ureteric junction. The Color Doppler image shows a ureteric jet emerging from this region suggesting that the left distal ureteric orificeis patent. This patient had a history of vesico-ureteric reflux.
Bilharziasis Of The Urinary Bladder
This patient presented with lower urinary symptoms, dysuria and hematuria. Sonography of the pelvis showed thickening of the wall of the urinary bladder with extensive calcification. Theseultrasound images suggest a diagnosis of schistosomiasis or bilharziasis of the wall of the urinary bladder.
If You Have Liver Disease
Certain diseases can make you more likely to get liver cancer, including:
Detecting Bladder Cancer With Ct Scans
A CT scan uses x-rays to obtain cross-sectional images of the body. Compared to a general x-ray test, which directs a broad x-ray beam from a single angle, the CT scan uses a number of thin beams to produce a series of images from different angles.
Screening For Bladder Cancer
Early-stage bladder cancer often shows no symptoms, or symptoms that are similar to those of benign conditions such as bladder stones, an enlarged prostate, or urinary tract infection. For this reason it is important to be examined regularly by a physician.
Can An Ultrasound Tell If An Ovarian Cyst Is Cancerous
Vaginal ultrasound can help to show whether any cysts on your ovaries contain cancer or not. If a cyst has any solid areas it is more likely to be cancer. Sometimes, in women who are past their menopause, the ovaries do not show up on an ultrasound. This means that the ovaries are small and not likely to be cancerous.

What are the different grades of bladder cancer?
What are the different “grades” for a bladder cancer tumor? Grade is expressed as a number between 1 (low) and 3 (high, i.e. G3); the higher the number the less the tumor resembles a normal cell. In lieu of numbers to grade a bladder cancer tumor, your doctor may refer to the tumor simply as low or high grade.
Where do bladder cancers occur?
While the majority of bladder cancers (approximately 90-95%) arise in the bladder, the urothelial cells that line the bladder are found in other locations in the urinary system. Sometimes these urothelial cancers can occur in the lining of the kidney or in the ureter that connects the kidney to the bladder.
How many types of bladder cancer are there?
Three types of bladder cancer may form, and each type of tumor can be present in one or more areas of the bladder, and more than one type can be present at the same time: Papillary tumors stick out from the bladder lining on a stalk. They tend to grow into the bladder cavity, away from the bladder wall, instead of deeper into the layers …

Where is urothelial cancer located?
This is known as upper tract urothelial cancer (UTUC) correspond to a subset of urothelial cancers that arise in the urothelial cells in the lining of the kidney (called the renal pelvis) or the ureter ( the long, thin tube that connects that kidney to the bladder). Learn more about UTUC here.
What doctor examines cancer tissue?
Urologists typically send a sample of the cancer tissue to a pathologist, a doctor who specializes in examining tissue to determine the stage and grade of the cancer. The pathologist writes a report with a diagnosis, and then sends it to your urologist.
What is a sessile tumor?
Sessile tumors lie flat against the bladder lining. Sessile tumors are much more likely than papillary tumors to grow deeper into the layers of the bladder wall.

How do you know if you have bladder cancer?
Signs of bladder cancer are problems peeing, pain when peeing, needing to go more often than normal, and seeing blood in your urine
What is the best test to find out if you have bladder cancer?
Ultrasound: This test uses sound waves to make pictures of the organs inside your body, like your bladder and kidneys. It can help show the size of a bladder cancer and if it has spread. Bone scan: A bone scan can help show if bladder cancer has spread to the bones. This test is not done unless you have bone pain.
What is urine test?
Urine tests: For these tests, you’ll be asked to pee in a cup. Your urine is then tested for cancer cells, blood, or certain proteins (called tumor markers).

What is the blue light on a cystoscopy?
Blue light cystoscopy: Sometimes, special drugs are put into the bladder during the exam. Cancer cells soak up these drugs and then glow when the doctor shines a blue light through the scope. This can help the doctor see cancer cells that might have been missed with the normal light.
What tests are done to check for bladder cancer?
This might include a rectal exam, during which a gloved finger is put into your rectum. If you are a woman, a pelvic exam might also be done.
Where does urine go when you pee?
Urine flows through the ureters and into your bladder, where it’s stored. When you urinate (pee), the bladder squeezes the urine out through a tube called the urethra. Bladder cancer usually starts in the lining or inner layer of the bladder wall.
What is it called when cancer cells spread to other parts of the body?
For instance, cancer cells in the bladder can travel to the bone and grow there. When cancer cells spread, it’s called metastasis . Cancer is always named for the place where it starts.
What does it mean when you feel the need to urinate but can’t pass urine?
Feeling the need to urinate, but not being able to pass urine. Lower back pain on 1 side of the body. Most often, bladder cancer is diagnosed after a person tells their doctor about blood in the urine, also called hematuria. “Gross hematuria” means that enough blood is present in the urine that the patient can see it.
Can you see blood in urine?
It is also possible that there are small amounts of blood in the urine that cannot be seen. This is called “microscopic hematuria,” and it can only be found with a urine test. General urine tests are not used to make a specific diagnosis of bladder cancer because hematuria can be a sign of several other conditions that are not cancer, …
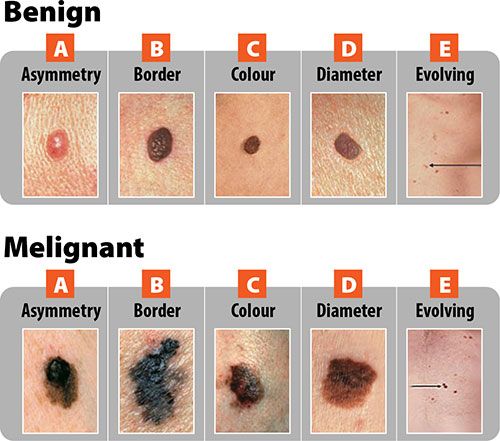
Can bladder cancer spread to other parts of the body?
Sometimes when the first symptoms of bladder cancer appear, the cancer has already spread to another part of the body. In this situation, the symptoms depend on where the cancer has spread. For example, cancer that has spread to the lungs may cause a cough or shortness of breath, spread to the liver may cause abdominal pain or jaundice …
Can bladder cancer cause pain?
People with bladder cancer may experience the following symptoms or signs. Sometimes, people with bladder cancer do not have any of these changes. Or, the cause of a symptom may be a different medical condition that is not cancer. Blood or blood clots in the urine. Pain or burning sensation during urination.
What are the symptoms of bladder cancer?
Listen to surgeon Bernard Bochner discuss some of the most common symptoms of bladder cancer. Blood in the urine (hematuria) is often the most common sign of bladder cancer. There are other symptoms to watch for as well.

Can blood be seen in urine?
Hematuria often occurs without pain or other urinary symptoms. Blood may not be present in the urine all the time — it may come and go. If blood is not visibly noticeable, it may be detected by a urine test.
Can bladder cancer wake you up at night?
Bladder cancer may wake you up at night with an overwhelming need to urinate.
Can bladder cancer make you uncomfortable?
Bladder cancer may make it uncomfortable to eat or make you feel like you don’t want to eat at all.

What color is the bladder cancer?
In the blue light cystoscopy a fluorescent dye has been used that turns bladder cancer cells pink when they are exposed to blue light.
How long does it take for a cystoscopy to show blood?
For 1 or 2 days after a cystoscopy, patients may notice blood in the urine and/or a burning sensation when passing urine. Drinking plenty of fluids usually helps to minimize these symptoms. Returning to work, physical, and sexual activities is usually quick, for example later the same day after a flexible cystoscopy and 1 to 2 days after a rigid cystoscopy. If discomfort is severe or symptoms do not improve as expected, it is important to promptly seek medical help.
What is rigid cystoscopy?
Rigid cystoscopy uses a hard, straight cystoscope. For this type of cystoscopy, patients are usually under general anesthesia; in some patients, spinal anesthesia that numbs the lower half of the body may be used instead. Rigid cystoscopy is performed when tissue samples (biopsies) and/or removal of small bladder tumors are required. Long, small-diameter instruments can be passed down the cystoscope to take biopsies from the bladder lining, and a tool called a resectoscope that has a cutting wire loop at the end may be used to remove abnormal tissue or small tumors. This procedure is referred to as ‘transurethral resection of a bladder tumor’ or ‘TURBT’.

What is a flexible cystoscope?
Flexible cystoscopy uses a flexible cystoscope tube that is able to bend easily as it passes through the urethra. This procedure can be carried out under local anesthetic while the patient is awake and is commonly used for simple visual examination of the inside of the bladder, although the collection of bladder washings (for cytology testing) or small tissue samples may be undertaken.
What is a thin tube with a light and camera attached to the end?
A cystoscope is a thin tube with a light and camera attached to the end. During a cystoscopy, the cystoscope is passed through the urethra (the tube through which urine leaves the bladder) into the bladder. The two main types of cystoscopy are termed flexible and rigid:
What is the most common light source used for cystoscopy?
A white light source or blue light source may be used for flexible and rigid cystoscopy procedures. White light cystoscopy is traditionally the most commonly used technique for the detection of bladder cancer. Blue light cystoscopy (sometimes referred to as ‘photodynamic diagnosis’) has been developed more recently, and while not as common, its use in clinical settings is increasing. For this procedure, a fluorescent dye is injected into the bladder through a catheter in the urethra. The dye is absorbed by cancer cells, which then appear red or pink when examined under the blue light of the cystoscope.
What are the side effects of a rigid cystoscopy?
Common side effects of general anesthesia include nausea, vomiting, sore throat, muscle aches, itching, shivering, and sleepiness; side effects most frequently associated with spinal anesthesia include itchiness, a drop in blood pressure, and temporary difficulty passing urine (particularly in men).