Contents

How can genes cause bladder cancer?
· Bladder cancer isn’t usually hereditary. There are some genetic syndromes and mutations that increase your risk of developing bladder and other cancers, though. Most cases of bladder cancer are not linked to family history or heritable genetic mutations but, rather, are factors you can control.
What are the risks of bladder cancer?
In nearly all cases of bladder cancer, these genetic changes are acquired during a person’s lifetime and are present only in certain cells in the bladder. These changes, which are called somatic mutations, are not inherited. Somatic mutations in many different genes have been found in bladder cancer cells.
Why do we get bladder cancer?
· The gene mutations that lead to bladder cancer differ person-to-person. Acquired mutations in certain genes, such as the TP53 or RB1 tumor suppressor genes and the FGFR and RAS oncogenes, are thought to be important in the development of some bladder cancers.
What is the rarest form of bladder cancer?
· Bladder cancer has a high number of genetic mutations compared to other cancers. Many of these mutations are random. Their effect on tumor growth is unknown. Some mutations affect genes that are important for cell growth, survival, and DNA damage repair. Your doctor may want to find out if you have certain gene mutations. How do your genes relate to …

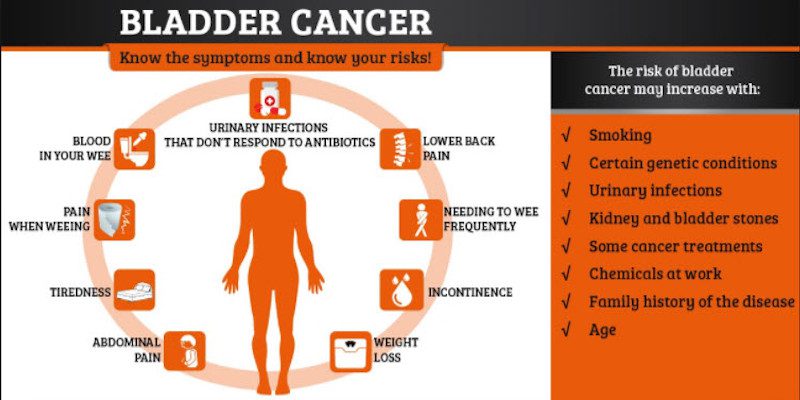
What Causes Bladder Cancer?
Risk factors are anything that impacts the likelihood that you will develop a specific condition. Having a risk factor does not mean you will develop that disease. Not having a risk factor also doesn’t mean you won’t get the disease.
Bladder Cancer Statistics
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), bladder cancer is diagnosed in 56,000 men and 17,500 women every year, and about 12,000 men and 4,700 women die from the disease annually. 5
Summary
Bladder cancer isn’t usually hereditary. There are some genetic syndromes and mutations that increase your risk of developing bladder and other cancers, though.
A Word From Verywell
A bladder cancer diagnosis for yourself or a family member can be worrying, especially if you’ve seen another loved one battle this cancer. But keep in mind their cancer isn’t your cancer, even if you are genetically linked.
What is bladder cancer?
Description. Bladder cancer is a disease in which certain cells in the bladder become abnormal and multiply uncontrollably to form a tumor. The bladder is a muscular organ in the lower abdomen that stores urine until it can be removed (excreted) from the body. Bladder cancer may cause blood in the urine, pain during urination, frequent urination, …
What are the factors that contribute to bladder cancer?
Researchers have identified many lifestyle and environmental factors that expose individuals to cancer-causing compounds ( carcinogens), which increase the rate at which somatic mutations occur, contributing to a person’s risk of developing bladder cancer. The greatest risk factor is long-term tobacco smoking.
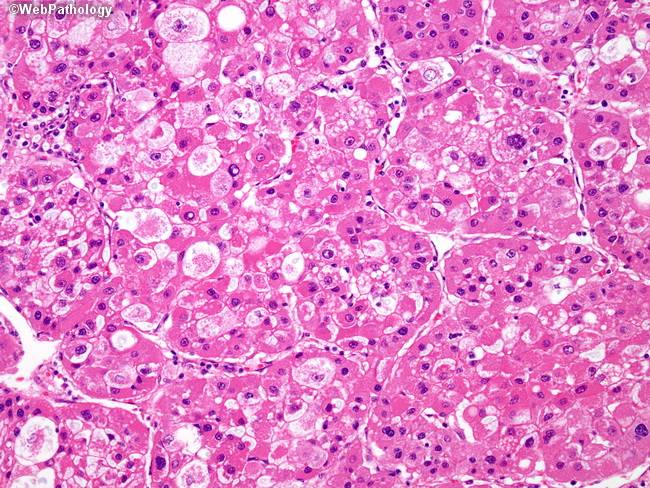
What are somatic mutations in bladder cancer?
Somatic mutations in the FGFR3, PIK3CA, KDM6A, and TP53 genes are common in bladder cancers.
What is the most common type of bladder cancer?
The most common type is transitional cell carcinoma (also known as urothelial carcinoma); others include squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. If the tumor spreads ( metastasizes) beyond the lining of the bladder into nearby tissues or organs, it is known as invasive bladder cancer.
How many men have bladder cancer?
Bladder cancer occurs four times more often in men than in women, with about 60,000 men and 18,000 women diagnosed with the condition each year.
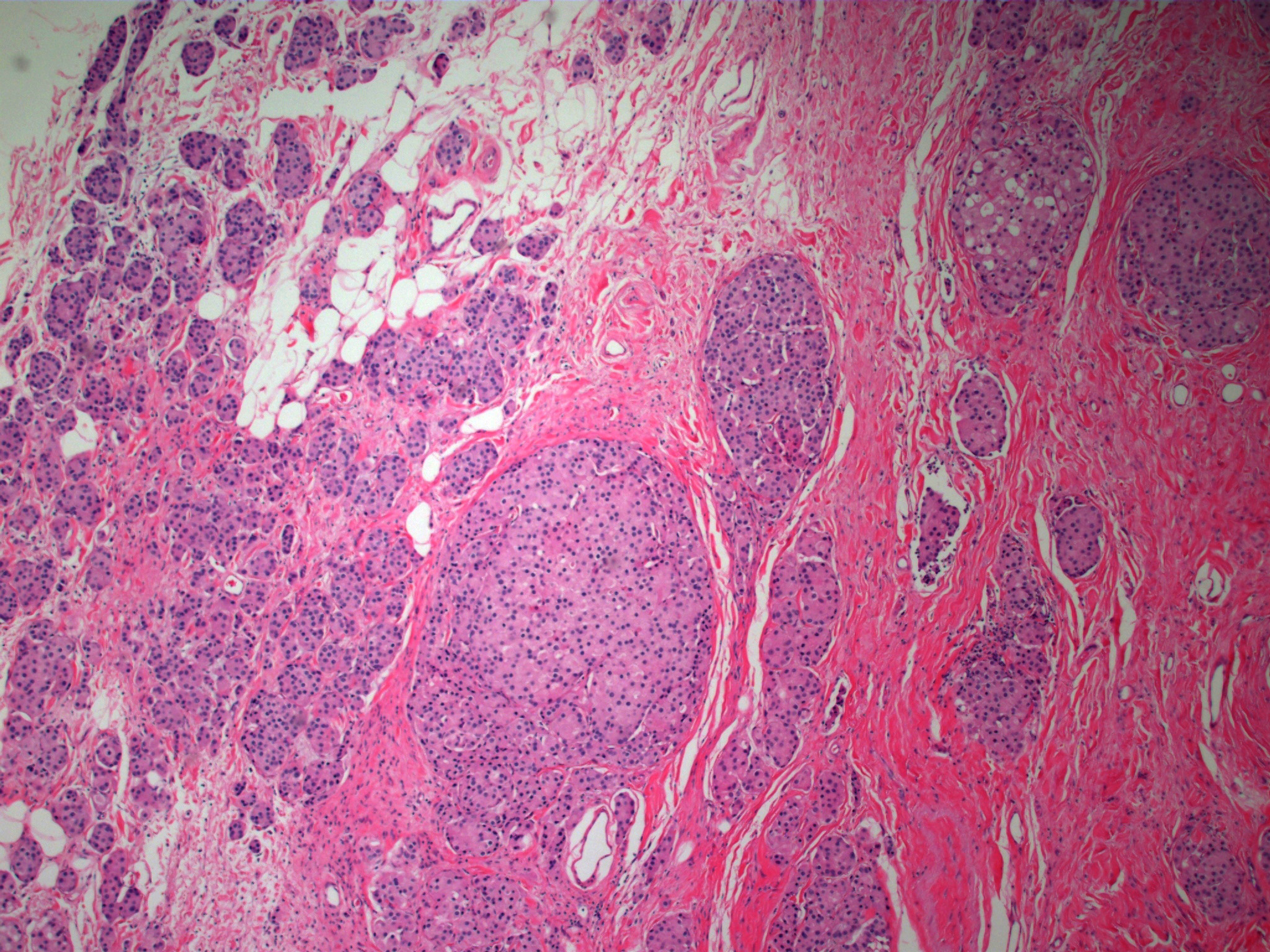
What are somatic mutations?
Somatic mutations in the FGFR3, PIK3CA, KDM6A, and TP53 genes are common in bladder cancers. Each of these genes plays a critical role in regulating gene activity and cell growth, ensuring cells do not grow and divide too rapidly or uncontrollably. It is likely that mutations in these genes disrupt normal gene regulation, …
Why do cancer cells grow?
Cancers occur when genetic mutations build up in critical genes, specifically those that control cell growth and division (proliferation) or the repair of damaged DNA. These changes allow cells to grow and divide uncontrollably to form a tumor.
What happens if you have mutations in bladder cancer?
If mutations modify the behaviour of oncogenes or tumor suppressor genes, cells can begin to divide uncontrollably and grow to form a tumor which can then spread into nearby tissue. The gene mutations that lead to bladder cancer differ person-to-person.

What are the risk factors for bladder cancer?
Bladder Cancer Risk Factors 1 Smoking: According to the American Cancer Society, smokers are at least three times as likely to get bladder cancer than non-smokers, and smoking contributing to around half of all cases. 2 Being over the age of 55: Your risk of developing bladder cancer increases as you become older. About 90% of those with bladder cancer are over the age of 55. 3 Being male: Men are about four times more likely to get bladder cancer than women. 4 Being white: Whites have twice as much risk of receiving a bladder cancer diagnosis as African Americans and Hispanics. 5 Working around chemicals: Certain chemicals 6 applied in the rubber, textile, paint, print and dye industries can increase your risk of developing bladder cancer.
How to lower bladder cancer risk?
Here are some tips to reduce your risk. Quit smoking: One of the best things you can do to prevent bladder cancer is to quit smoking.
How many times more likely is a smoker to get bladder cancer than a non smoker?
Smoking: According to the American Cancer Society, smokers are at least three times as likely to get bladder cancer than non-smokers, and smoking contributing to around half of all cases.

How to detect mutations in genes?
Researchers can detect the presence of gene mutations by testing specific molecular biomarkers, or biological indicators, which can be found and measured in the blood, tissues or other bodily fluids like urine. Emerging methods are also increasingly incorporating genetic sequencing to classify tumours into molecular subtypes, in order to determine patient risk profiles and personalise treatment.
Why do cells grow abnormally?
A cell can begin to grow abnormally and become cancerous when an acquired gene mutation leads to a permanent change in its DNA. Environmental factors such as tobacco smoke can lead to acquired mutations. An acquired mutation may also occur as your body creates new cells.
Is bladder cancer rare?
Although bladder cancer has been associated with an inherited gene mutation in some families, this is relatively rare. It is considered to be more common that the gene mutations leading to bladder cancer are acquired during a person’s lifetime (for example, because of occupational or environmental exposure).

How to determine if bladder cancer is genetically inherited?
To identify the genetic alterations of a bladder cancer, a physician needs to evaluate 1) tumor tissue and 2) DNA that is present in the blood. In some cases, the genetic analysis also includes cell-free DNA that is circulating in the blood.
What mutations are found in bladder cancer?
Genetic testing identifies “germline” mutations in all stages and locations of bladder cancer. They include BRCA1, BRCA2, MSH2, CHEK2, and ERCC3. These alterations would have potentially critical implications to patients with bladder cancer, but also their siblings and children.
Why do we have mutations in DNA?
It is a change that occurs in our DNA sequence. Mutations are either due to mistakes that occur when the cells divide and make copies of the DNA. Or as a result of contact with things in your environment. This can include exposure to smoking or certain chemicals.

When was the MIBC gene atlas created?
The National Cancer Institute first published a comprehensive description of 131 patients with Stage II or greater muscle invasive bladder cancer (MIBC) in 2014. This genetic analysis created a molecular atlas or blueprint of bladder cancer called the “ bladder cancer genome atlas ,” and is free and publicly available for researchers, physicians and patients.
Can you get bladder cancer from mutations?
With certain mutations, you may be more likely to get bladder cancer. Bladder cancer has a high number of genetic mutations compared to other cancers. Many of these mutations are random. Their effect on tumor growth is unknown.
Can bladder cancer be different from other bladder cancers?
There is a great deal of variability between mutations in different parts of a bladder cancer tumor. If the cancer has grown out of the bladder there may be differences in mutations between different sites of the urothelial cancer. There may even be important differences from the same tumor if sampled at different times.

Can medications slow bladder cancer growth?
Some of these mutations help your bladder cancer tumor to grow and survive. There may be drugs or combinations of medications that specifically target these mutation pathways that can slow a tumor’s growth.
What causes bladder cancer?
In addition to environmental factors like smoking and chemical exposure, bladder cancer can be caused by inherited gene mutations including Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome, Cowden Syndrome and Lynch Syndrome.
What are the factors that increase the risk of bladder cancer?
These include smoking and exposure to specific chemicals over long periods of time.
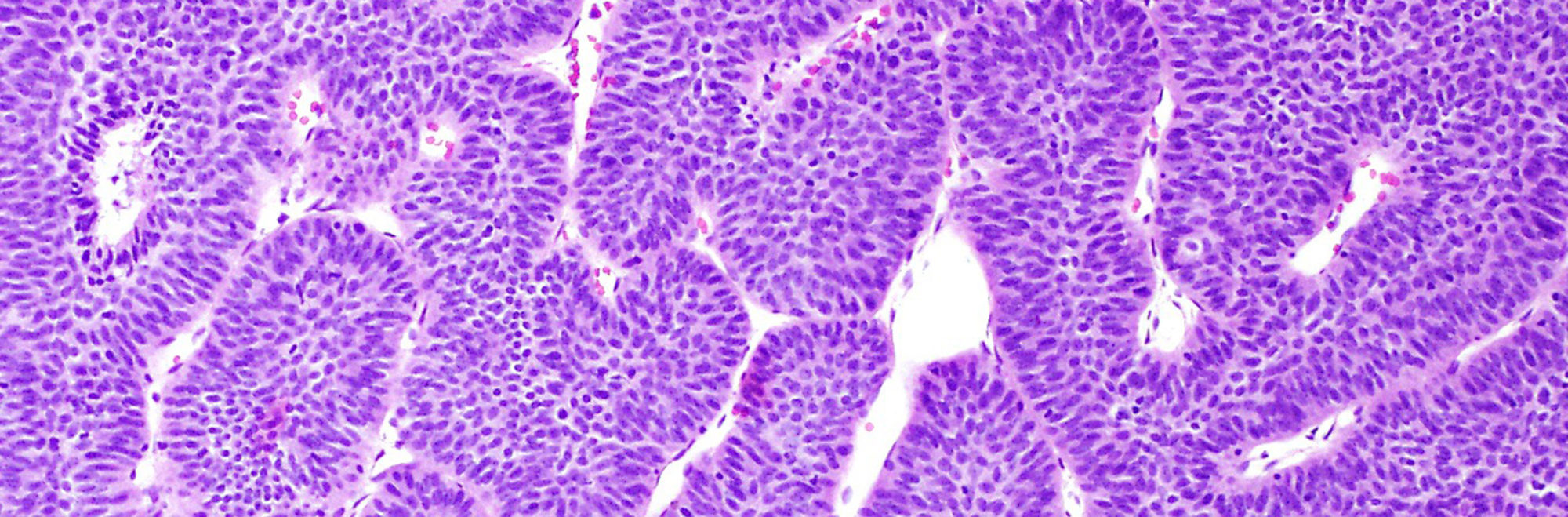
How does cancer happen?
Cancer is caused by genetic mutations that change the way that cells function. Some of these mutations can be inherited, but many are also acquired over the course of a person’s lifetime. Genetic alterations can cause cells to divide rapidly and form a tumor.
Why do we need genetic testing?
Genetic testing helps identify specific genes that have mutated or been altered in a way that causes normal cells to become cancerous. These results are used by healthcare providers to predict responses to various types of treatment and monitor the progress of the disease. Genetic testing can refer to both germline testing (mutations in cells without cancer ) and also somatic testing of a patient’s tumor (mutations in cells with cancer).
Why do doctors use genetic testing?
Doctors use genetic testing to analyze the genetic abnormalities present in different patients’ cancers, helping them to predict which treatment options might be most effective.

How to increase the likelihood of bladder cancer response?
To increase the likelihood of response, bladder cancer treatments need to be combined with interventions designed to help your immune system target and kill cancer cells.
Can bladder cancer be inherited?
While it’s possible, inherited gene mutations aren’t as commonly associated with bladder cancer as they are with other types of cancer, such as breast and ovarian. Sometimes, bladder cancer may occur in families because of toxic chemical or environmental exposures.
What is bladder cancer?
Listen. Bladder cancer is a form of cancer that occurs due to abnormal and uncontrolled cell growth in the bladder. Signs and symptoms of the condition may include abdominal pain, blood in the urine, fatigue, painful urination, frequent urination, incontinence, and/or weightloss.
/iStock-691662000-2a225983e48d4b3289bf0bac718c0e75.jpg)
How to find a genetics specialist?
To find a medical professional who specializes in genetics, you can ask your doctor for a referral or you can search for one yourself. Online directories are provided by the American College of Medical Genetics and the National Society of Genetic Counselors. If you need additional help, contact a GARD Information Specialist. You can also learn more about genetic consultations from MedlinePlus Genetics.
Can you get bladder cancer if you have no family history?
Most cases of bladder cancer occur sporadically in people with no family history of the condition. Risk factors for the condition include smoking, exposure to certain chemicals, and having chronic bladder infections.
What are the genes that cause bladder cancer?
Acquired changes in certain genes, such as the TP53 or RB1 tumor suppressor genes and the FGFR and RAS oncogenes , are thought to be important in the development of some bladder cancers. Changes in these and similar genes may also make some bladder cancers more likely to grow and spread into the bladder wall than others.

How do bladder cancer mutations occur?
Some of these acquired gene mutations result from exposure to cancer-causing chemicals or radiation. For example, chemicals in tobacco smoke can be absorbed into the blood, filtered by the kidneys, and end up in urine, where they can affect bladder cells. Other chemicals may reach the bladder the same way. But sometimes, gene changes may just be random events that sometimes happen inside a cell, without having an outside cause.
What causes cancer cells to turn on oncogenes?
Cancers can be caused by DNA changes (gene mutations) that turn on oncogenes or turn off tumor suppressor genes. Several different gene changes are usually needed for a cell to become cancer.
Can bladder cancer cause cancer?
Researchers do not know exactly what causes most bladder cancers. But they have found some risk factors (see Bladder Cancer Risk Factors ) and are starting to understand how they cause cells in the bladder to become cancer. Certain changes in the DNA inside normal bladder cells can make them grow abnormally and form cancers.

Can bladder cancer be caused by inherited mutations?
Inherited gene mutations. Some people inherit gene changes from their parents that increase their risk of bladder cancer. But bladder cancer does not often run in families, and inherited gene mutations are not thought to be a major cause of this disease.
What tests are used to detect bladder cancer?
Other types of testing to help find and treat bladder cancer may include genetic and biomarker testing. Genetic testing looks for certain gene alterations that are inherited from our parents. Biomarker testing looks for molecular changes in urine or blood-based tests that show signs of cancer.
What will happen to the bladder in 2021?
Posted on: 09 Jul 2021. The bladder is the organ where the body stores urine before it leaves the body. When cells of the bladder grow in an abnormal way, they can turn into bladder cancer. A person with bladder cancer will have one or more tumors in his/her bladder.
What is the Urology Care Foundation?
The Urology Care Foundation Humanitarian Program recognizes and supports individuals and projects that provide direct urologic patient care for impoverished individuals and communities in underserved areas, either within or outside the United States.
Why is Urology Care Foundation important?
The Urology Care Foundation is a driving force in the discovery of new treatments, because we invest in the next generation of researchers.
Can a urologist see if you have bladder cancer?
In talking with your urologist, if they then suspect any signs of bladder cancer, a biopsy may be suggested. For a biopsy, your doctor will remove a piece of bladder tissue so a pathologist can look for cancer cells with a microscope. This biopsy tissue may also go through more testing.