Contents
What are the early warning signs of bladder cancer?
· What are the Signs and Symptoms of Bladder Cancer? The most common symptom of bladder cancer is painless blood in the urine. This may appear as pink, red or dark brown. Patients often confuse this with amber (or concentrated) urine which is not the same thing. However, if you are unsure, it is best to have your urine checked by your doctor.
What are the chances of dying from bladder cancer?
· For most patients, Kukreja says, the first warning sign of bladder cancer is blood in the urine. Though this can be caused by other conditions — including urinary tract infections and enlarged prostate — it’s important to be checked thoroughly …
Do you know the early signs of bladder cancer?
Bladder cancer can often be found early because it causes blood in the urine or other urinary symptoms that cause a person to see a health care provider. Blood in the urine. In most cases, blood in the urine (called hematuria) is the first sign of bladder cancer. There may be enough blood to change the color of the urine to orange, pink, or, less often, dark red.
What can I do to manage my bladder cancer?
· Cancer that starts in the bladder is called bladder cancer. It starts when cells in the bladder grow out of control and crowd out normal cells. This makes it hard for the body to work the way it should. Cancer cells can spread to other parts of the body. For instance, cancer cells in the bladder can travel to the bone and grow there.
See more
· Bladder cancer is typically diagnosed when the urologist looks inside the bladder by doing a cystoscopy and sees an abnormality. For many patients it’s a small, easily removed, low-grade tumor that could be compared to a wart or colon polyp.

Does bladder cancer spread quickly?
They tend to grow and spread slowly. High-grade bladder cancers look less like normal bladder cells. These cancers are more likely to grow and spread.
What should I know about bladder cancer?
How is bladder cancer typically diagnosed? Bladder cancer is typically diagnosed when the urologist looks inside the bladder by doing a cystoscopy and sees an abnormality. For many patients it’s a small, easily removed, low-grade tumor that could be compared to a wart or colon polyp.
Can you live a normal life with bladder cancer?
The general 5-year survival rate for people with bladder cancer is 77%. However, survival rates depend on many factors, including the type and stage of bladder cancer that is diagnosed. The 5-year survival rate of people with bladder cancer that has not spread beyond the inner layer of the bladder wall is 96%.
What are the signs that bladder cancer is getting worse?
A need to urinate more frequently than usual. Urinary urgency, even when the bladder is not full. A weak urine stream. A need to urinate many times during the night.
What is the life expectancy of someone with bladder cancer?
5-year relative survival rates for bladder cancerSEER Stage5-year Relative Survival RateIn situ alone Localized96% 70%Regional38%Distant6%All SEER stages combined77%Mar 1, 2022
Where does bladder cancer spread first?
When bladder cancer spreads, it first invades the bladder wall, which is made up of four distinct layers. It can take some time for cancer to penetrate all of these layers, but once it has, it can then spread into the surrounding fatty tissues and lymph nodes.
What foods should you avoid if you have bladder cancer?
However, avoid high intake of foods like red and processed meat, chewing areca nuts, consuming arsenic containing water, taking fried eggs and lifestyle factors such as smoking tobacco as it may increase the risk of bladder cancer, impact the prognosis and treatment outcomes, worsen symptoms, or increase the chances of …
Does bladder cancer ever go away?
This is very common if you’ve had cancer. For other people, bladder cancer might never go away completely or might come back in another part of the body. Some people may get regular treatment with chemotherapy , immunotherapy, or other treatments to try to keep the cancer in check.
Can bladder cancer be cured completely?
The outlook for people with stage 0a (non-invasive papillary) bladder cancer is very good. These cancers can be cured with treatment. During long-term follow-up care, more superficial cancers are often found in the bladder or in other parts of the urinary system.
How do you feel when you have bladder cancer?
Pain or burning during urination. Feeling as if you need to go right away, even when your bladder isn’t full. Having trouble urinating or having a weak urine stream. Having to get up to urinate many times during the night.
What is the main cause of bladder cancer?
Smoking. Smoking is the single biggest risk factor for bladder cancer. This is because tobacco contains cancer-causing (carcinogenic) chemicals. If you smoke for many years, these chemicals pass into your bloodstream and are filtered by the kidneys into your urine.
What are the symptoms of stage 1 bladder cancer?
SymptomsBlood in urine (hematuria), which may cause urine to appear bright red or cola colored, though sometimes the urine appears normal and blood is detected on a lab test.Frequent urination.Painful urination.Back pain.
How Does The Doctor Know I Have Bladder Cancer?
Bladder cancer might cause symptoms such as: 1. Having trouble peeing 2. Feeling pain when peeing 3. Needing to go more often than normal 4. Seeing…
Tests to Look For Bladder Cancer
Your doctor may do other tests to find out more about the cancer. Some of them are:X-ray: Dye is put into a vein for a special x-ray of the kidneys…
How Serious Is My Cancer?
If you have bladder cancer, the doctor will want to find out how far it has spread. This is called staging. Your doctor will want to find out the s…
What Kind of Treatment Will I Need?
There’s more than one way to treat bladder cancer. You might want to get a second opinion about the best treatment plan for you. Doctors may have d…
What Will Happen After Treatment?
You will be glad when treatment is over. But it’s hard not to worry about cancer coming back. Even when cancer never comes back, people still worry…

Who is at Risk for Bladder Cancer?
Anybody can get bladder cancer, but it is most common in older adults (over 60-65 years old). There are also risk factors that raise the chance of getting bladder cancer such as:
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Bladder Cancer?
The most common symptom of bladder cancer is painless blood in the urine. This may appear as pink, red or dark brown. Patients often confuse this with amber (or concentrated) urine which is not the same thing. However, if you are unsure, it is best to have your urine checked by your doctor.
How is Bladder Cancer Found?
If your urine shows blood (or you have seen blood – even if only a single time!), you should be tested for bladder cancer. Many patients will have on and off blood in the urine, so just because the blood goes away, does not mean that you are cancer-free. Your urologist will find bladder cancer with two tests:

Can you Screen for Bladder Cancer?
Currently, screening for bladder cancer is not recommended because our tests are not accurate enough to diagnose the disease. However, for some patients who are very high risk, your doctor may want to perform a urine test (urinalysis) to screen for blood in the urine.
What Can I Do to Reduce my Risk of Bladder Cancer?
If you smoke (cigarette, cigar or pipe), it is never too late to quit! Smoking increases your risk of getting bladder cancer by at least 2-3 times that of people who do not smoke. When you quit smoking, your risk goes down (although it may never go back to zero).
What are the symptoms of bladder cancer?
Being unable to urinate. Lower back pain on one side. Loss of appetite and weight loss. Feeling tired or weak. Swelling in the feet. Bone pain. Again, many of these symptoms are more likely to be caused by something other than bladder cancer, but it’s important to have them checked.

How do you know if you have bladder cancer?
Bladder cancers that have grown large or have spread to other parts of the body can sometimes cause other symptoms, such as: Being unable to urinate. Lower back pain on one side. Loss of appetite and weight loss. Feeling tired or weak.
Why is bladder cancer so early?
Bladder cancer can often be found early because it causes blood in the urine or other urinary symptoms that cause a person to see a health care provider.
Does bladder cancer cause blood in urine?
Usually, the early stages of bladder cancer (when it’s small and only in the bladder) cause bleeding but little or no pain or other symptoms. Blood in the urine doesn’t always mean you have bladder cancer.

Can bladder cancer cause a change in urination?
Bladder cancer can sometimes cause changes in urination, such as: Having to urinate more often than usual. Pain or burning during urination. Feeling as if you need to go right away, even when your bladder isn’t full. Having trouble urinating or having a weak urine stream.
Can bladder cancer spread to other parts of the body?
Bladder cancers that have grown large or have spread to other parts of the body can sometimes cause other symptoms, such as: Again, many of these symptoms are more likely to be caused by something other than bladder cancer, but it’s important to have them checked.
Can bladder cancer cause lower back pain?
Bladder cancers that have grown large or have spread to other parts of the body can sometimes cause other symptoms, such as: Being unable to urinate. Lower back pain on one side. Loss of appetite and weight loss. Feeling tired or weak.
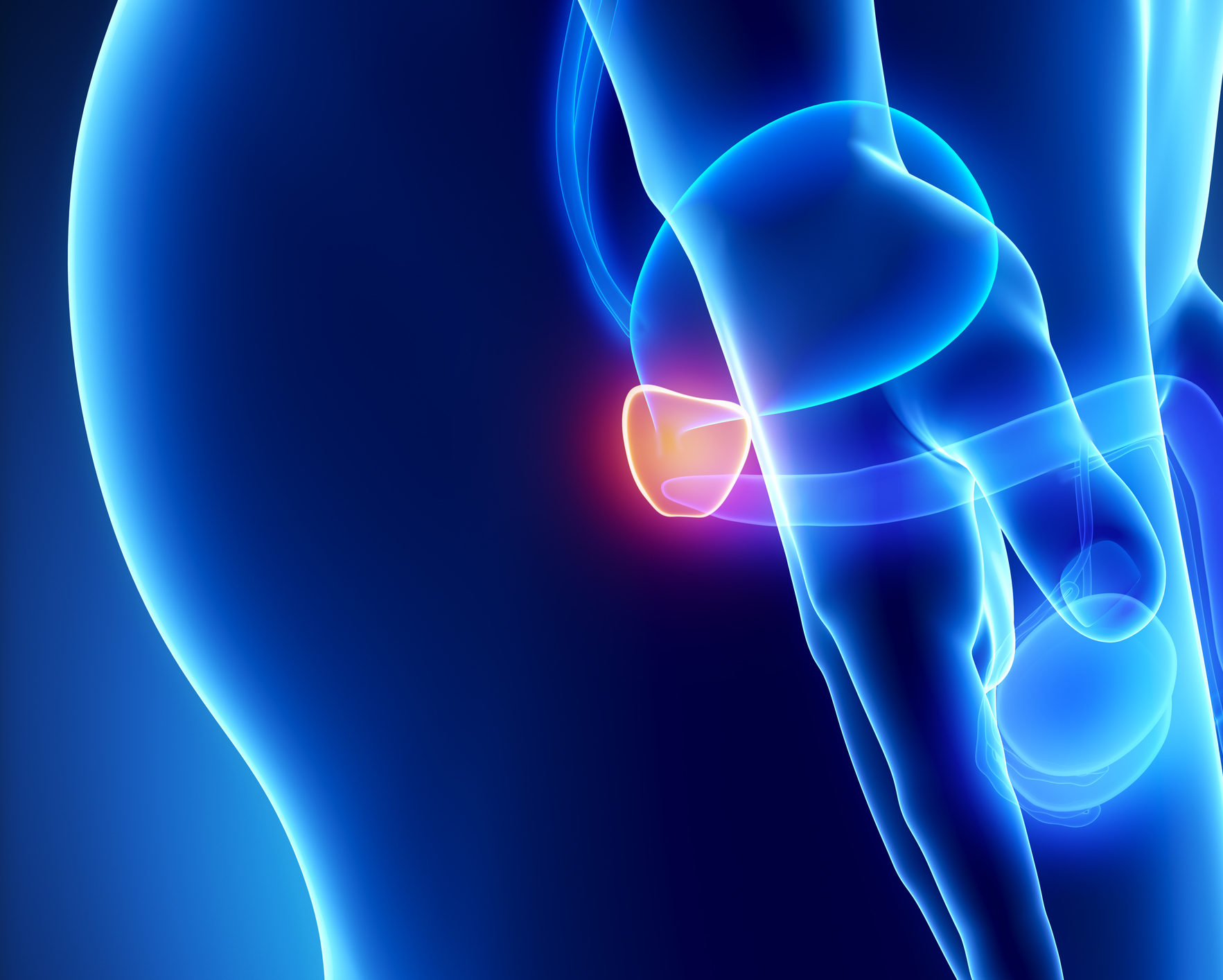
What is it called when cancer grows in the bladder?
If the cancer grows into the outer layers of the bladder, it’s called invasive. Invasive cancers are more likely to spread and can be harder to treat.
How to remove bladder cancer?
This can be done during a cystoscopy. A a cystoscope with a looped wire on the end is used to remove the tumor. When the cancer is more invasive, the cancer is removed along with part of the bladder or the entire bladder.
Where does cancer start?
Cancer can start any place in the body. Cancer that starts in the bladder is called bladder cancer. It starts when cells in the bladder grow out of control and crowd out normal cells. This makes it hard for the body to work the way it should. Cancer cells can spread to other parts of the body.

What is it called when cancer cells spread to other parts of the body?
For instance, cancer cells in the bladder can travel to the bone and grow there. When cancer cells spread, it’s called metastasis . Cancer is always named for the place where it starts.
What is it called when cancer spreads to the bone?
For instance, cancer cells in the bladder can travel to the bone and grow there. When cancer cells spread, it’s called metastasis . Cancer is always named for the place where it starts. So when bladder cancer spreads to the bone (or any other place), it’s still called bladder cancer.
What is the tube that connects the kidneys to the bladder?
Tubes called ureters connect your kidneys to the bladder. Urine flows through the ureters and into your bladder, where it’s stored. When you urinate (pee), the bladder squeezes the urine out through a tube called the urethra. Bladder cancer usually starts in the lining or inner layer of the bladder wall.

What tests are done to check for bladder cancer?
This might include a rectal exam, during which a gloved finger is put into your rectum. If you are a woman, a pelvic exam might also be done.
What are the risks of bladder cancer?
Tobacco use is one of the biggest risk factors for bladder cancer. That includes smoking, as well as every other kind of tobacco use, including snuff, dip and chew. Chemical exposure also can increase a person’s risk of bladder cancer. People who work around a lot of chemicals are more likely to develop bladder cancer.
Can you get bladder cancer at 55?
The vast majority of people diagnosed with this disease are white men over age 55, but bladder cancer can — and does — affect men and women of all ages and races. For many, blood in the urine will be the first tell-tale bladder cancer symptom.

What are the factors that increase the risk of bladder cancer?
What factors make someone more likely to develop bladder cancer? Tobacco use is one of the biggest risk factors for bladder cancer. That includes smoking, as well as every other kind of tobacco use, including snuff, dip and chew. Chemical exposure also can increase a person’s risk of bladder cancer.
Is bladder cancer harder to treat at MD Anderson?
But many patients don’t come to MD Anderson until their disease is late-stage and the bladder cancer has spread. And that, says, Arlene Siefker-Radtke, M.D., associate professor in Genitourinary Medical Oncology, can make it harder to treat.
Can chemicals cause bladder cancer?
Chemical exposure also can increase a person’s risk of bladder cancer. People who work around a lot of chemicals are more likely to develop bladder cancer. Chronic urinary tract infections and kidney stones also can put you at increased risk for bladder cancer.

What type of cancer is a bladder cancer?
Less than 1% of bladder cancers are small-cell carcinomas. They start in nerve-like cells called neuroendocrine cells. These cancers often grow quickly and usually need to be treated with chemotherapy like that used for small cell carcinoma of the lung.
What is the most common type of bladder cancer?
Urothelial carcinoma, also known as transitional cell carcinoma (TCC), is by far the most common type of bladder cancer. In fact, if you have bladder cancer it’s almost certain to be a urothelial carcinoma. These cancers start in the urothelial cells that line the inside of the bladder.
What is the function of the bladder?
It has flexible, muscular walls that can stretch to hold urine and squeeze to send it out of the body. The bladder’s main job is to store urine. Urine is liquid waste made by the 2 kidneys and then carried to the bladder through 2 tubes called ureters.

What is the job of the bladder?
The bladder’s main job is to store urine. Urine is liquid waste made by the 2 kidneys and then carried to the bladder through 2 tubes called ureters. When you urinate, the muscles in the bladder contract, and urine is forced out of the bladder through a tube called the urethra.
What is the name of the tube that takes urine out of the bladder?
When you urinate, the muscles in the bladder contract, and urine is forced out of the bladder through a tube called the urethra .
What percentage of bladder cancers are adenocarcinoma?
Adenocarcinoma. Only about 1% of bladder cancers are adenocarcinomas. These cancer cells have a lot in common with gland-forming cells of colon cancers . Nearly all adenocarcinomas of the bladder are invasive.

What is the name of the cell that starts bladder cancer?
Small cell carcinoma. Less than 1% of bladder cancers are small-cell carcinomas. They start in nerve-like cells called neuroendocrine cells. These cancers often grow quickly and usually need to be treated with chemotherapy like that used for small cell carcinoma of the lung.
Men are at greater risk for bladder cancer
Men are four times more likely to receive a bladder cancer diagnosis in their lifetimes than women, and it’s the fourth most common cancer in men. Doctors aren’t completely sure why this is, but a study shows it might have something to do with a group of hormones known as androgens that seem to influence tumor growth in the bladder
What signs and symptoms should I be looking out for?
Symptoms of bladder cancer can mimic those other conditions such as kidney stones or bladder infection—it’s vital to be aware of signs that something more serious may be going on.

Multiple rounds of treatment are often necessary
A major concern for many people with early-stage bladder cancer is that new cancers often form in other parts of the bladder over time. And in cases of bladder cancer that are locally advanced or metastatic, the cancer almost always returns—up to 86 percent of locally advanced and metastatic cancers progress within two years.
Immunotherapy offers some patients new hope
Immunotherapy is a type of treatment that works with your immune system to find and attack cancer.
What is the most common sign of bladder cancer?
Blood in the urine (hematuria) is often the most common sign of bladder cancer. There are other symptoms to watch for as well. They may be caused by something other than bladder cancer, but it’s important to have them checked out by a doctor.

Can blood be seen in urine?
Hematuria often occurs without pain or other urinary symptoms. Blood may not be present in the urine all the time — it may come and go. If blood is not visibly noticeable, it may be detected by a urine test.
Can hematuria be detected by urine?
Blood may not be present in the urine all the time — it may come and go. If blood is not visibly noticeable, it may be detected by a urine test.